吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_classfication():
'''
加载用于分类问题的数据集
'''
# 使用 scikit-learn 自带的 iris 数据集
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X_train=iris.data
y_train=iris.target
# 分层采样拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4
return train_test_split(X_train, y_train,test_size=0.25,random_state=0,stratify=y_train) #支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型
def test_SVC_linear(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
print('Coefficients:%s, intercept %s'%(cls.coef_,cls.intercept_))
print('Score: %.2f' % cls.score(X_test, y_test)) # 生成用于分类的数据集
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_classfication()
# 调用 test_SVC_linear
test_SVC_linear(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
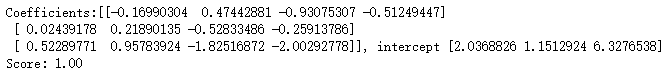
def test_SVC_poly(*data):
'''
测试多项式核的 SVC 的预测性能随 degree、gamma、coef0 的影响.
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
### 测试 degree ####
degrees=range(1,20)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[]
for degree in degrees:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='poly',degree=degree)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,1) # 一行三列
ax.plot(degrees,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(degrees,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_degree ")
ax.set_xlabel("p")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5) ### 测试 gamma ,此时 degree 固定为 3####
gammas=range(1,20)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[]
for gamma in gammas:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='poly',gamma=gamma,degree=3)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)
ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_gamma ")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$\gamma$")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5)
### 测试 r ,此时 gamma固定为10 , degree 固定为 3######
rs=range(0,20)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[]
for r in rs:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='poly',gamma=10,degree=3,coef0=r)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)
ax.plot(rs,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(rs,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_poly_r ")
ax.set_xlabel(r"r")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5)
plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_poly
test_SVC_poly(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_SVC_rbf(*data):
'''
测试 高斯核的 SVC 的预测性能随 gamma 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
gammas=range(1,20)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[]
for gamma in gammas:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='rbf',gamma=gamma)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_rbf")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$\gamma$")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5)
plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_rbf
test_SVC_rbf(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

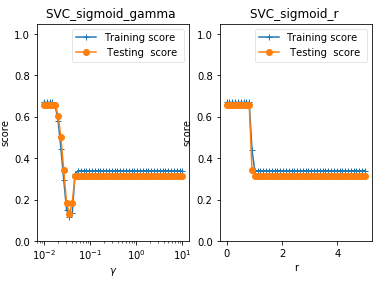
def test_SVC_sigmoid(*data):
'''
测试 sigmoid 核的 SVC 的预测性能随 gamma、coef0 的影响.
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure() ### 测试 gamma ,固定 coef0 为 0 ####
gammas=np.logspace(-2,1)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[] for gamma in gammas:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid',gamma=gamma,coef0=0)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,1)
ax.plot(gammas,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(gammas,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_sigmoid_gamma ")
ax.set_xscale("log")
ax.set_xlabel(r"$\gamma$")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5)
### 测试 r,固定 gamma 为 0.01 ######
rs=np.linspace(0,5)
train_scores=[]
test_scores=[] for r in rs:
cls=svm.SVC(kernel='sigmoid',coef0=r,gamma=0.01)
cls.fit(X_train,y_train)
train_scores.append(cls.score(X_train,y_train))
test_scores.append(cls.score(X_test, y_test))
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,2,2)
ax.plot(rs,train_scores,label="Training score ",marker='+' )
ax.plot(rs,test_scores,label= " Testing score ",marker='o' )
ax.set_title( "SVC_sigmoid_r ")
ax.set_xlabel(r"r")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.legend(loc="best",framealpha=0.5)
plt.show() # 调用 test_SVC_sigmoid
test_SVC_sigmoid(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机SVM非线性分类SVC模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机线性分类LinearSVC模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm fr ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机非线性回归SVR模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm fr ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——支持向量机线性回归SVR模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets, linear_model,svm fr ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——多项式贝叶斯分类器MultinomialNB模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,naive_bayes from skl ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络与原始感知机模型
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理包裹式特征选取模型
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC from sklearn.datasets import load_iris from sklearn.feature_select ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——等度量映射Isomap降维模型
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datas ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——多维缩放降维MDS模型
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datas ...
随机推荐
- vue中jquery详情
jQuery基本语法 $(selector).action() 基本选择器:$("#id") 标签选择器:$("tagName") class选择器:$(&qu ...
- eclipse 项目的创建 编写 'Hello World'
写项目之前确保 eclipse 安装完成 以及JDK 环境配置 成功 开始: 打开eclipse 右键file ->new->java project 如图: 然后输入项目名 点击Fin ...
- 利用 Hexo + Github 搭建自己的博客
扯在前面 在很久很久以前,一直就想搭建属于自己的一个博客,但由于各种原因,最终都不了了之,恰好最近突然有了兴趣,于是就自己参照网上的教程,搭建了属于自己的博客. 至于为什么要搭建自己的博客了?哈哈,大 ...
- Zabbix使用手册
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40025218/article/details/81778754
- Docker之设置加速器
在Docker从仓库下载镜像是非常慢的,所以今天搞一个Docker设置加速器教程. 1. 创建一个Docker的配置文件. sudo vim /etc/docker/daemon.json 2. 编写 ...
- AntDesign(React)学习-13 Warning XX should not be prefixed with namespace XXX
有篇UMI入门简易教程可以看看:https://www.yuque.com/umijs/umi/hello 程序在点击操作时报了一个Warning: [sagaEffects.put] User/up ...
- 装饰器_python
一.装饰器中提及的知识点 装饰器主要作用:在原函数基础上添加新功能 1.作用域:LEGB 2.高阶函数 3.闭包(在一个内部函数中,对在外部作用域(但不是在全局作用域)的变量进行引用,那么内部函数就认 ...
- AD转化器分类及特点和选用
1. AD转换器的分类 下面简要介绍常用的几种类型的基本原理及特点:积分型.逐次逼近型.并行比较型/串并行型.∑-Δ调制型.电容阵列逐次比较型及压频变换型. 1)积分型(如TLC7135)积分型AD工 ...
- XPath注入
XPath基础 XPath 即为 XML 路径语言,是一门在XML文档中查找信息的语言.XPath 基于 XML 的树状结构,有不同类型的节点,包括元素节点,属性节点和文本节点,提供在数据结构树中找寻 ...
- 解决windows10 OBS Studioobsstudio显示器捕获黑屏
前提设置显卡,下载OBS studio 64bit别下载32bit了 如果电脑desktop右键无法显示NAVIDIA 控制面板则需要win+R 输入 msconfig选取服务,勾选所有NAIVI ...
