Machine learning第6周编程作业
1.linearRegCostFunction:
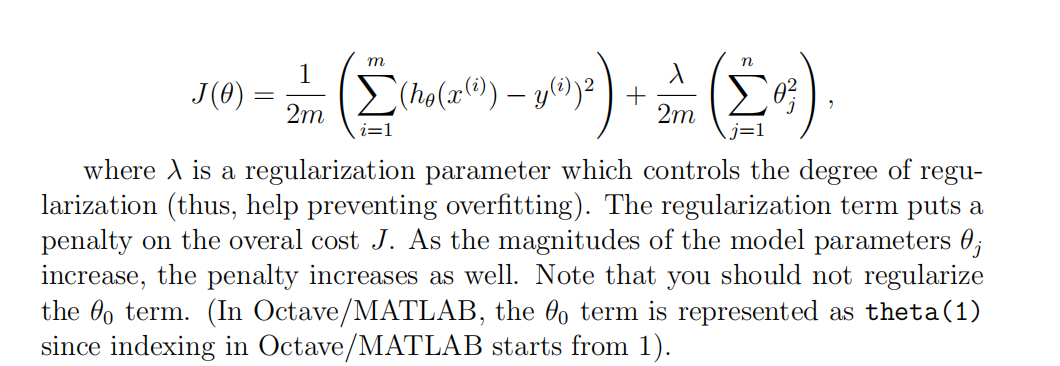
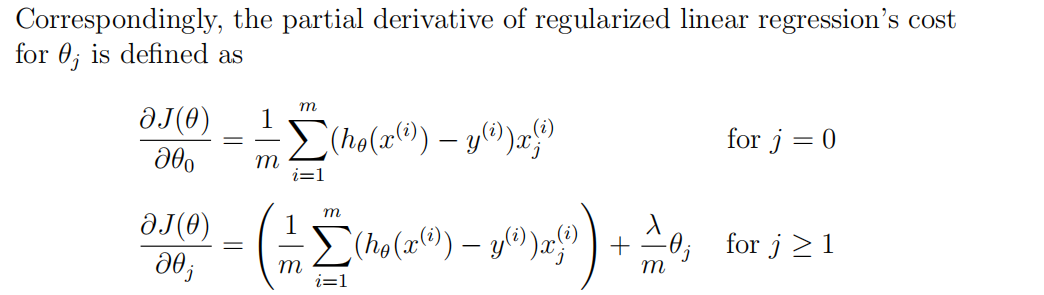
function [J, grad] = linearRegCostFunction(X, y, theta, lambda)
%LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for regularized linear
%regression with multiple variables
% [J, grad] = LINEARREGCOSTFUNCTION(X, y, theta, lambda) computes the
% cost of using theta as the parameter for linear regression to fit the
% data points in X and y. Returns the cost in J and the gradient in grad % Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples % You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta)); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost and gradient of regularized linear
% regression for a particular choice of theta.
%
% You should set J to the cost and grad to the gradient.
% h=(X*theta);
for i=1:m,
J=J+1/(2*m)*(h(i)-y(i))^2;
endfor
n= length(theta);
for i=2:n,
J=J+lambda/(2*m)*theta(i)^2;
endfor grad(1)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,1);
for i=2:n,
grad(i)=1/m*(h-y)'*X(:,i)+lambda/m*theta(i);
endfor % ========================================================================= grad = grad(:); end
2.learningCuvers

function [error_train, error_val] = ...
learningCurve(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda)
%LEARNINGCURVE Generates the train and cross validation set errors needed
%to plot a learning curve
% [error_train, error_val] = ...
% LEARNINGCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval, lambda) returns the train and
% cross validation set errors for a learning curve. In particular,
% it returns two vectors of the same length - error_train and
% error_val. Then, error_train(i) contains the training error for
% i examples (and similarly for error_val(i)).
%
% In this function, you will compute the train and test errors for
% dataset sizes from 1 up to m. In practice, when working with larger
% datasets, you might want to do this in larger intervals.
% % Number of training examples
m = size(X, 1); % You need to return these values correctly
error_train = zeros(m, 1);
error_val = zeros(m, 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the cross validation errors in error_val.
% i.e., error_train(i) and
% error_val(i) should give you the errors
% obtained after training on i examples.
%
% Note: You should evaluate the training error on the first i training
% examples (i.e., X(1:i, :) and y(1:i)).
%
% For the cross-validation error, you should instead evaluate on
% the _entire_ cross validation set (Xval and yval).
%
% Note: If you are using your cost function (linearRegCostFunction)
% to compute the training and cross validation error, you should
% call the function with the lambda argument set to 0.
% Do note that you will still need to use lambda when running
% the training to obtain the theta parameters.
%
% Hint: You can loop over the examples with the following:
%
% for i = 1:m
% % Compute train/cross validation errors using training examples
% % X(1:i, :) and y(1:i), storing the result in
% % error_train(i) and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
% % ---------------------- Sample Solution ---------------------- for i=1:m,
theta=trainLinearReg(X(1:i,:),y(1:i),lambda);
error_train(i)=linearRegCostFunction(X(1:i,:),y(1:i),theta,0);
error_val(i)=linearRegCostFunction(Xval,yval,theta,0);
endfor % ------------------------------------------------------------- % ========================================================================= end
3.polyFeatures

function [X_poly] = polyFeatures(X, p)
%POLYFEATURES Maps X (1D vector) into the p-th power
% [X_poly] = POLYFEATURES(X, p) takes a data matrix X (size m x 1) and
% maps each example into its polynomial features where
% X_poly(i, :) = [X(i) X(i).^2 X(i).^3 ... X(i).^p];
% % You need to return the following variables correctly.
X_poly = zeros(numel(X), p); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Given a vector X, return a matrix X_poly where the p-th
% column of X contains the values of X to the p-th power.
%
% for i=1:p,
X_poly(:,i)=(X.^i);
endfor % ========================================================================= end
4.ValidationCurve

function [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
validationCurve(X, y, Xval, yval)
%VALIDATIONCURVE Generate the train and validation errors needed to
%plot a validation curve that we can use to select lambda
% [lambda_vec, error_train, error_val] = ...
% VALIDATIONCURVE(X, y, Xval, yval) returns the train
% and validation errors (in error_train, error_val)
% for different values of lambda. You are given the training set (X,
% y) and validation set (Xval, yval).
% % Selected values of lambda (you should not change this)
lambda_vec = [0 0.001 0.003 0.01 0.03 0.1 0.3 1 3 10]'; % You need to return these variables correctly.
error_train = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1);
error_val = zeros(length(lambda_vec), 1); % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Fill in this function to return training errors in
% error_train and the validation errors in error_val. The
% vector lambda_vec contains the different lambda parameters
% to use for each calculation of the errors, i.e,
% error_train(i), and error_val(i) should give
% you the errors obtained after training with
% lambda = lambda_vec(i)
%
% Note: You can loop over lambda_vec with the following:
%
% for i = 1:length(lambda_vec)
% lambda = lambda_vec(i);
% % Compute train / val errors when training linear
% % regression with regularization parameter lambda
% % You should store the result in error_train(i)
% % and error_val(i)
% ....
%
% end
%
% for i=1:length(lambda_vec),
Lam=lambda_vec(i);
theta=trainLinearReg(X,y,Lam);
error_train(i)=linearRegCostFunction(X,y,theta,0);
error_val(i)=linearRegCostFunction(Xval,yval,theta,0);
endfor % ========================================================================= end
Machine learning第6周编程作业的更多相关文章
- Machine learning 第7周编程作业 SVM
1.Gaussian Kernel function sim = gaussianKernel(x1, x2, sigma) %RBFKERNEL returns a radial basis fun ...
- Machine learning 第8周编程作业 K-means and PCA
1.findClosestCentroids function idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids) %FINDCLOSESTCENTROIDS compu ...
- Machine learning 第5周编程作业
1.Sigmoid Gradient function g = sigmoidGradient(z) %SIGMOIDGRADIENT returns the gradient of the sigm ...
- Machine learning第四周code 编程作业
1.lrCostFunction: 和第三周的那个一样的: function [J, grad] = lrCostFunction(theta, X, y, lambda) %LRCOSTFUNCTI ...
- 吴恩达深度学习第4课第3周编程作业 + PIL + Python3 + Anaconda环境 + Ubuntu + 导入PIL报错的解决
问题描述: 做吴恩达深度学习第4课第3周编程作业时导入PIL包报错. 我的环境: 已经安装了Tensorflow GPU 版本 Python3 Anaconda 解决办法: 安装pillow模块,而不 ...
- 吴恩达深度学习第2课第2周编程作业 的坑(Optimization Methods)
我python2.7, 做吴恩达深度学习第2课第2周编程作业 Optimization Methods 时有2个坑: 第一坑 需将辅助文件 opt_utils.py 的 nitialize_param ...
- c++ 西安交通大学 mooc 第十三周基础练习&第十三周编程作业
做题记录 风影影,景色明明,淡淡云雾中,小鸟轻灵. c++的文件操作已经好玩起来了,不过掌握好控制结构显得更为重要了. 我这也不做啥题目分析了,直接就题干-代码. 总结--留着自己看 1. 流是指从一 ...
- Machine Learning - 第7周(Support Vector Machines)
SVMs are considered by many to be the most powerful 'black box' learning algorithm, and by posing构建 ...
- Machine Learning - 第6周(Advice for Applying Machine Learning、Machine Learning System Design)
In Week 6, you will be learning about systematically improving your learning algorithm. The videos f ...
随机推荐
- Java方法_数组
/* 方法:完成特定功能的代码块. 注意:在很多语言里面有函数的定义,而在Java中函数被称为方法. 方法格式: 修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名1,参数类型 参数名2...) { ...
- python 探测网站目录的GUI程序-乾颐堂
1.pyqt4写的界面 find_ui.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 ...
- http://angular.github.io/router/
Angular New Router Guide Configuring the Router- This guide shows the many ways to map URLs to compo ...
- python进行数据清理之pandas中的drop用法
好久好久没有更新博客了,之前自学的估计也都忘记差不多了.由于毕业选择从事的行业与自己的兴趣爱好完全两条路,心情也难过了很久,既然入职了就要好好干,仍要保持自己的兴趣,利用业余时间重拾之前的乐趣. 从基 ...
- viewDidAppear在何时调用?
[viewDidAppear在何时调用] If the view belonging to a view controller is added to a view hierarchy directl ...
- tomcat服务器输入localhost可以访问,ip无法访问解决办法
最近在开发项目中,遇到的一个问题是: 在 tomcat中发布一个web项目,但是发布成功后,只能用http://localhost:8080/fm访问项目,不能用 http://127.0.0.1:8 ...
- redis windows下安装
1.下载redis windows文件包 下载地址 2.解压文件包 复制压缩包地址 3.进入cmd 命令行 cd进入redis文件包目录 4.执行 redis-server.exe 使用netsta ...
- 装饰者模式及C++实现
装饰者模式 时常会遇到这样一种情况,我已经设计好了一个接口,并且也有几个实现类,但是这时我发现我设计的时候疏忽了,忘记了一些功能,或者后来需求变动要求加入一些功能,最简单的做法就是修改接口,添加函数, ...
- FDMemTable三层提交数据总是不成功的原因
提交数据的代码如下: procedure TForm1.btnSaveClick(Sender: TObject);var LDeltas: TFDJSONDeltas;begin if FDMemT ...
- windows 10 RelativePanel
The new RelativePanel implements a style of layout that is defined by the relationships between its ...
