算法练习LeetCode初级算法之链表
删除链表中的节点

|
/** |
|
* Definition for singly-linked list. |
|
* public class ListNode { |
|
* int val; |
|
* ListNode next; |
|
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; } |
|
* } |
|
*/ |
|
class Solution { |
|
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) { |
|
node.val=node.next.val; |
|
node.next=node.next.next; |
|
} |
|
} |
删除链表的倒数第N个节点
两次遍历算法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy.next=head;
int length=0;
ListNode p=head;
while (p!=null) {
length++;
p=p.next;
}
ListNode first=dummy;
length-=n;
while (length>0) {
length--;
first=first.next;
}
first.next=first.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
一次遍历算法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode first = dummy;
ListNode second = dummy;
// Advances first pointer so that the gap between first and second is n nodes apart
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
first = first.next;
}
// Move first to the end, maintaining the gap
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
}
反转链表
我的解法:利用Linklist比较好理解,有点投机取巧,面试不一定可以得吧!!!哈哈哈,但是测试通过了
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
x.val=list.removeLast();
}
return head;
}
}
迭代法,一开始不好理解,仔细琢磨后还是很好理解的
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=null;
while (head!=null) {
ListNode temp=head.next;//先把后面的数据储存到temp
head.next=newHead;//把head添加到newHead
newHead=head;//把head添加到newHead,newHead重新作为新的头指针
head=temp;//让头指针指向下一个数据,已保存在temp里
}
return newHead;
}
}
递归法,仔细研究后还是可以理解的
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return newHead(head);
}
public ListNode newHead(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=newHead(head.next);
head.next.next=head;//反转链表,把把下一个数连接到newHead上
head.next=null;//指向空,防止再次递归导致覆盖后面的内容。
return newHead;
}
}
以上两种方法,通过从网站学习理解,必须站在巨人的肩膀上,哈哈哈!
注明学习网址:https://blog.csdn.net/fx677588/article/details/72357389,虽然不是转载,但有借鉴。
合并两个有序链表
我的解法:很好实现,思路简单,但耗时长一点
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=l1;x!=null;x=x.next)
{
list.add(x.val);
}
for(ListNode x=l2;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
Collections.sort(list);
ListNode head=null;
for (int i = list.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ListNode n=new ListNode(list.get(i));
n.next=head;
head=n;
}
return head;
}
}
大神一解法,递归解法,代码简洁
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode rspHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode rsp=rspHead;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
rspHead.next=l1;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l1=l1.next;
}else{
rspHead.next=l2;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(l1==null){
rspHead.next=l2;
}else{
rspHead.next=l1;
}
return rsp.next;
}
}
大神二解法,利用双指针,现将带头链表头指针用rsp保存,最后返回rsp.next
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode rspHead=new ListNode(0);
ListNode rsp=rspHead;
while(l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
rspHead.next=l1;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l1=l1.next;
}else{
rspHead.next=l2;
rspHead=rspHead.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
}
if(l1==null){
rspHead.next=l2;
}else{
rspHead.next=l1;
}
return rsp.next;
}
}
回文链表
我的解法:感觉已经脱离了链表,不行,不好,时间太长!
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return true;
}
LinkedList<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
for(ListNode x=head;x!=null;x=x.next) {
list.add(x.val);
}
for (int i = 0; i < list.size()/2; i++) {
if (list.get(i).compareTo(list.get(list.size()-i-1))!=0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
大神解法:挺好!先找链表中点,然后再反转后半部分,最后再分别遍历比较,直到后半部分遍历完!
class Solution {
ListNode node1=new ListNode(0);
ListNode node2=new ListNode(0);
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow=head;
ListNode fast=head;
while (fast.next!=null&&fast.next.next!=null) {
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
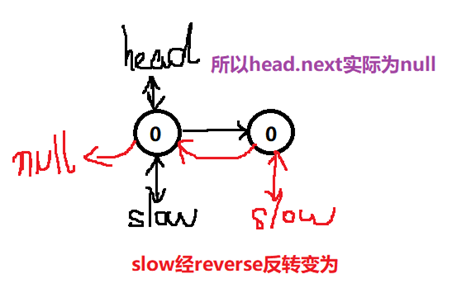
slow=reverse(slow.next);//此处如果是show的话,将从中点的前一个匹配,比较难理解,后面附图说明
while (slow!=null) {
if (head.val!=slow.val) {//到这里,head短的话会成为空指针而报错!!!
return false;
}
head=head.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return true;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead=reverse(head.next);
head.next.next=head;
head.next=null;
return newHead;
}
}
说明:如果测试样例输入0,0的话,黄色标记为什么会报错!
环形链表
我的解法:利用hashset
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return false;
}
Set<ListNode> set=new HashSet<>();
int n=0;
ListNode x=head;
while (set.size()>=n) {
set.add(x);
x=x.next;
n++;
if (x==null) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
大神解法:
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head==null) {
return false;
}
ListNode l1=head,l2=head.next;
while (l1!=null&&l2!=null&&l2.next!=null) {
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next.next;
if (l1==l2) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
递归解法,更为简洁
class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return false;
if(head.next==head)return true;
ListNode l=head.next;
head.next=head;
boolean isCycle=hasCycle(l);
return isCycle;
}
}
算法练习LeetCode初级算法之链表的更多相关文章
- 【LeetCode算法】LeetCode初级算法——字符串
在LeetCode初级算法的字符串专题中,共给出了九道题目,分别为:反转字符串,整数反转,字符串中的第一个唯一字符,有效的字母异位词,验证回文字符串,字符串转换整数,实现strStr(),报数,最 ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之字符串
反转字符串 我的解法比较low,利用集合的工具类Collections.reverse反转,用时过长 class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之数组
删除数组中的重复项 官方解答: 旋转数组 存在重复元素 只出现一次的数 官方解答: 同一个字符进行两次异或运算就会回到原来的值 两个数组的交集 II import java.util.Arr ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之其他
位1的个数 解法一: class Solution { // you need to treat n as an unsigned value public int hammingWeight(int ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之数学
Fizz Buzz class Solution { public List<String> fizzBuzz(int n) { List<String> list=new L ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之设计问题
打乱数组 不断的让第一个与后面随机选择的数交换 class Solution { private int[] nums; private int[] initnums; public Solution ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之动态规划
爬楼梯:斐波那契数列 假设你正在爬楼梯.需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶. 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶.你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢? 注意:给定 n 是一个正整数. 非递归解法 class S ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之排序和搜索
合并两个有序数组 class Solution { public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) { System.arrayco ...
- 算法练习LeetCode初级算法之树
二叉树的前序遍历 我的解法:利用递归,自底向下逐步添加到list,返回最终的前序遍历list class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderT ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript中DOM(第二天)
DOM document object model,文档对象模型,也叫dom树:dom是由节点组成的.html标签称为标签节点,属性称为属性节点: console.log(docment);即可输出d ...
- python------面向对象进阶 Socket网络编程
一.Socket网络编程 1.七层模型,亦称OSI(Open System Interconnection)参考模型,是参考模型是国际标准化组织(ISO)制定的一个用于计算机或通信系统间互联的标准体系 ...
- 添加一个pv到vg后,误删新加入的pv,报 pv * not found or rejected by a filter
问题如下 将某一pv加入vg vgextend cl /dev/xvdb1 然后进入fdisk将xvdb1分区删掉,重新创建pv 使用lvdisplay报警告 [root@localhost ~]# ...
- python 保存对象文件
之前用 R 语言一直感觉 .Rdata 格式的文件很好用,可以把每次执行的中间文件保存便于下次调用,刚熟悉 Python 还没接触这块知识,所以有时候做项目不太顺手,索性上网搜了下,整理如下: 模型存 ...
- go环境变量与sublime Text3开发工具
环境:win7 1:下载安装包 (下载太慢了,上传至百度网盘了) 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/10wHOR01mW-kjdkynqu1F-g 密码:kv71 2:安装 ...
- chrome's developer console
原文链接: https://medium.freecodecamp.org/10-tips-to-maximize-your-javascript-debugging-experience-b69a7 ...
- autoit3编辑器SCITE字体设置
选项→打开全局设置文件,就是SciTEGlobal.properties,修改下面的部分即可,保存之后立刻生效.如果不行,就打开用户设置文件SciTEUser.properties进行修改: font ...
- Kong管理UI -kong-dashboard
本文仍然是在ubuntu18的环境下进行 https://github.com/PGBI/kong-dashboard kong dashboart如果要正常使用管理UI,前提为kong已经正常run ...
- Grafana介绍
Grafana是一个开源的度量分析与可视化套件.纯 Javascript 开发的前端工具,通过访问库(如InfluxDB),展示自定义报表.显示图表等.大多使用在时序数据的监控方面,如同Kibana类 ...
- Group Pathfinding & Movement in RTS Style Games
转自:http://gamasutra.com/blogs/AndrewErridge/20180522/318413/Group_Pathfinding__Movement_in_RTS_Style ...
