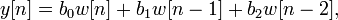Digital biquad filter
Direct Form 1
The most straightforward implementation is the Direct Form 1, which has the following difference equation:
or, if normalized:
Here the  ,
,  and
and  coefficients determine zeros, and
coefficients determine zeros, and  ,
,  determine the position of the poles.
determine the position of the poles.
Flow graph of biquad filter in Direct Form 1:

Direct Form 2
The Direct Form 1 implementation requires four delay registers. An equivalent circuit is the Direct Form 2 implementation, which requires only two delay registers:

The Direct Form 2 implementation is called the canonical form, because it uses the minimal amount of delays, adders and multipliers, yielding in the same transfer function as the Direct Form 1 implementation. The difference equations for DF2 are:
where
//ASM example
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// //
// Process the audio stream //
// //
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include <def21262.h>
#define SECTIONS 3 /* Number of second-order sections (biquads) */
.section /pm seg_pmco;
.global _Cascaded_IIR_Filter_SIMD;
.extern inbuf;
.extern outbuf;
.extern delaybuf;
.extern coefficients;
_Cascaded_IIR_Filter_SIMD:
/*****************************************************************************
The algorithm:
IIR Second order sections - The cannonic second-order section implemented as
"Direct Form II" biquads. Note that the SIMD architecture of the 2126x SHARC
family enables the two parallel execution units to filter the left and right
channel simultaneously. All register moves and memory reads implicitly apply
to the shadow processing element (PEy) as well as the primary computational
unit (PEx).
*****************************************************************************
Given the most general biquadratic (second order rational polynomial)
b0 + b1'*z^-1 + b2'*z^-2
H(z) = -------------------------- ,
a0 + a1'*z^-1 + a2'*z^-2
we may factor out the gain of the transfer function,
b0 (b1'/a0)*z^-1 + (b2'/a0)*z^-2
H(z) = ---- * -------------------------------
a0 (a1'/b0)*z^-1 + (a2'/b0)*z^-2
and normalize the coefficients, such that
a1*z^-1 + a2*z^-2
H(z) = A * -------------------
b1*z^-1 + b2*z^-2
where A = gain = b1'/a0
a1 = a1'/b0, a2 = a2'/b0, b1 = b1'/a0, b2 = b2'/a0
This leaves only four true filter coefficients. The gain values from
all of the sections may be combined into a single channel gain applied
apart from the inner computational loop. With the simplified coefficients,
the cannonic direct form II may be written as a pair of difference
equations:
w[n] = x[n] + a1*w[n-1] + a2*w[n-2]
y[n] = w[n] + b1*w[n-1] + b2*w[n-2]
which leads to the following pseudocode:
read(x[n])
f12=0, f2=w[n-1], read(a1)
--- Loop --------------------------------------------------------------------
f12=a1*w[n-1], f8=f8 + f12, f3=w[n-2], read(a2)
f12=a2*w[n-2], f8=x[n] + a1*w[n-2], w[n-1] -> w[n-2]', read(b1)
f12=b1*w[n-2], w[n]=x[n] + a1*w[n-2] + a2*w[n-1], f2=w[n-1], read(b2)
f12=b2*w[n-1], f8=w[n] + b1*w[n-2], w[n] -> w[n-1]', read(a1)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
y[n]=f8 + f12
**************************************************************************/
/* Subroutine that implements the pseudocode above */
cascaded_biquad:
bit set mode1 CBUFEN | PEYEN ; // Enable SIMD mode
b0 = delaybuf;
b1 = b0;
b3 = inbuf;
b4 = outbuf;
b9 = coefficients;
r0 = SECTIONS;
f8=dm(i3,m1); // read inbuf
r12=r12 xor r12, f2=dm(i0,m1), f4=pm(i8,m8);
lcntr=r0, do quads until lce;
f12=f2*f4, f8=f8+f12, f3=dm(i0,m1), f4=pm(i8,m8);
f12=f3*f4, f8=f8+f12, dm(i1,m1)=f3, f4=pm(i8,m8);
f12=f2*f4, f8=f8+f12, f2=dm(i0,m1), f4=pm(i8,m8);
quads:f12=f3*f4, f8=f8+f12, dm(i1,m1)=f8, f4=pm(i8,m8);
f8=f8+f12;
rts (db);
dm(i4,m1)=f8;
bit clr mode1 CBUFEN | PEYEN; // disable SIMD mode
_Cascaded_IIR_Filter_SIMD.end:
//--------------------------------------------
Digital biquad filter的更多相关文章
- biquad filter实现
原始频谱: LPF: HPF: 代码: #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<errno.h> #includ ...
- 转载:EQ--biquad filter
http://www.musicdsp.org/files/Audio-EQ-Cookbook.txt https://arachnoid.com/BiQuadDesigner/index.html ...
- H5的Web Audio Api
概述 研究Web Audio Api的主要原因是:工作中需要在ios中实现声音的淡出效果,主要是通过setInterval来改audio标签的volume属性实现的,但是ios上面volume属性是只 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.27
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about thi ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.26
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.24
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.23
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.22
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example 8.21
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about thi ...
随机推荐
- python - 装饰器+描述符(给类添加属性且属性类型审核)
装饰器+描述符 实现给一个类添加属性且对添加的时,对属性进行类型审核: def zsq(**kwargs): def fun(obj): for i,j in kwargs.items(): seta ...
- SpringBoot三种配置Dubbo的方式
*必须首先导入dubbo-starter (1).使用SpringBoot配置文件(application.properties或application.yml) dubbo.application. ...
- V4L2文档翻译(一)【转】
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/airk000/article/details/23218903 相关资料 https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentat ...
- Kernel 3.0.8 内存管理函数【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/7208777 1. 内存分配函数 相关代码如下: #define alloc_pages(gfp_ma ...
- 【转】C++的const类成员函数
我们知道,在C++中,若一个变量声明为const类型,则试图修改该变量的值的操作都被视编译错误.例如, const char blank=' '; blank='\n'; //错误 面向对象程序设计中 ...
- Oracle数据库修改LISTENER的监听端口
背景 这又是个不作不会死的事情,自己不懂,硬搞,端口换了,后来竟然捣鼓好了.尽量少搞这些事情. 注意点 http://wallimn.iteye.com/blog/1163614 修改配置文件后,需修 ...
- css 悬浮框
<style> .xfk { display: block; position: fixed; top: 150px; lef ...
- centos6.5系统bash损坏之救援模式修复
1.模拟bash被损坏的情况 # mv /bin/bash /tmp [root@localhost ~]# sync [root@localhost ~]# shutdown -r now 2.挂载 ...
- zabbix安装及简单配置
Zabbix基本介绍: zabbix是一个基于WEB界面的提供分布式系统监视以及网络监视功能的企业级的开源解决方案.它能监视各种网络参数,保证服务器系统的安全运营:并提供柔软的通知机制以让系统管理员快 ...
- 转载:Linux内核参数的优化(1.3.4)《深入理解Nginx》(陶辉)
原文:https://book.2cto.com/201304/19615.html 由于默认的Linux内核参数考虑的是最通用的场景,这明显不符合用于支持高并发访问的Web服务器的定义,所以需要修改 ...