《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.12


上代码:
b = [0, 1, 1]; a = [1, -0.9, 0.81]; % [R, p, C] = residuez(b,a); Mp = (abs(p))'
Ap = (angle(p))'/pi %% ----------------------------------------------
%% START a determine H(z) and sketch
%% ----------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.12 H(z) its pole-zero plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title('pole-zero plot'); grid on; %% ----------------------------------------------
%% END
%% ---------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 1st form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
[H,w] = freqz(b,a,100); % 1st form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
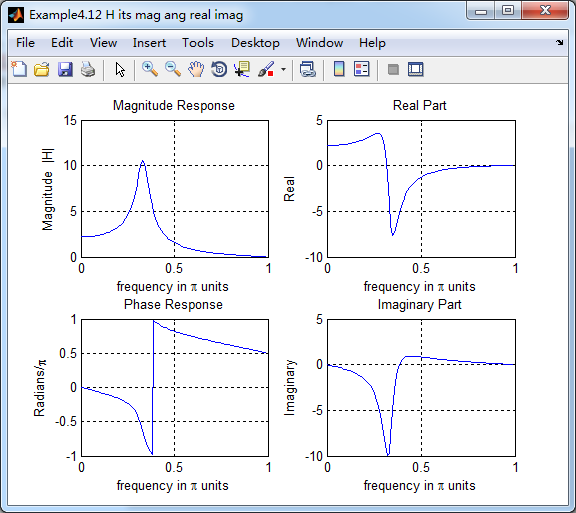
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.12 H its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 3rd form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
w = [0:1:100]*pi/100; H = freqz(b,a,w);
%[H,w] = freqz(b,a,200,'whole'); % 3rd form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
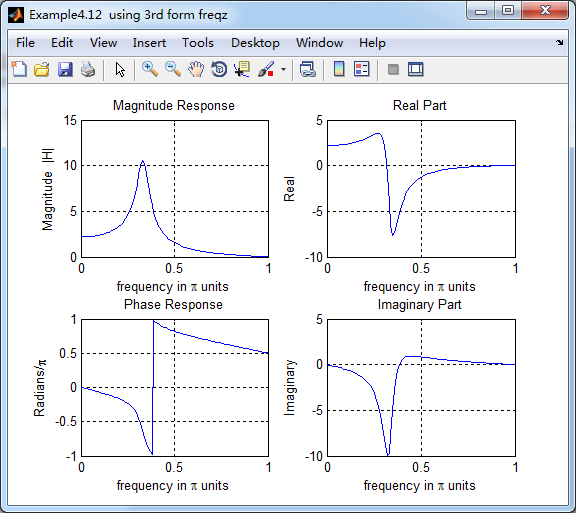
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.12 using 3rd form freqz ');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------
结果:

《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.12的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example2.12
代码: b = [1]; a = [1, -0.9]; n = [-5:50]; h = impz(b,a,n); set(gcf,'Color','white'); %subplot(2,1,1); ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)) + j * rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
随机推荐
- eclipse修改jdk后版本冲突问题
将安装的jdk1.8改为1.7之后出现了很淡疼的问题 修改工程下.setting/ org.eclipse.jdt.core.prefs eclipse.preferences.version=1or ...
- App主界面Tab实现方法
ViewPager + FragmentPagerAdapter 这里模仿下微信APP界面的实现 国际惯例,先看下效果图: activity_main.xml 布局文件: <?xml ver ...
- 【leetcode】Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II (middle)
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numb ...
- RAD Studio/Delphi 2010 3615下载+破解
RAD Studio/Delphi 2010 3615下载+破解 官方下载地址: http://altd.embarcadero.com/download/RADStudio2010/delphicb ...
- Java自定义注解开发
一.背景 最近在自己搞一个项目时,遇到可需要开发自定义注解的需求,对于没有怎么关注这些java新特性的来说,比较尴尬,索性就拿出一些时间,来进行研究下自定义注解开发的步骤以及使用方式.今天在这里记下, ...
- 假期(codevs 3622)
题目描述 Description 经过几个月辛勤的工作,FJ决定让奶牛放假.假期可以在1-N天内任意选择一段(需要连续),每一天都有一个享受指数W.但是奶牛的要求非常苛刻,假期不能短于P天,否则奶牛不 ...
- 矿场搭建(codevs 1996)
题目描述 Description 煤矿工地可以看成是由隧道连接挖煤点组成的无向图.为安全起见,希望在工地发生事故时所有挖煤点的工人都能有一条出路逃到救援出口处.于是矿主决定在某些挖煤点设立救援出口,使 ...
- 双栈排序(codevs 1170)
题目描述 Description Tom最近在研究一个有趣的排序问题.如图所示,通过2个栈S1和S2,Tom希望借助以下4种操作实现将输入序列升序排序. 操作a 如果输入序列不为空,将第一个元素压入栈 ...
- 关于each
1种 通过each遍历li 可以获得所有li的内容 <!-- 1种 --> <ul class="one"> <li>11a</li> ...
- TCP/IP的Socket编程
1. TCP/IP.UDP的基本概念 TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)即传输控制协议/网间协议,他是一个工业标准的协议集, ...
