数据结构(Splay平衡树):HDU 1890 Robotic Sort
Robotic Sort
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3456 Accepted Submission(s): 1493
deep in the Czech Technical University buildings, there are
laboratories for examining mechanical and electrical properties of
various materials. In one of yesterday’s presentations, you have seen
how was one of the laboratories changed into a new multimedia lab. But
there are still others, serving to their original purposes.
In
this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in
such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a
running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause
troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we
need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering
is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number
of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order
is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order
of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort
the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse
the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample
to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse
the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
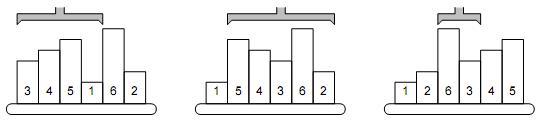
The
picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the
4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples.
The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation
will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step
will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find
the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples
using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same
height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given
first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final
order too.
input consists of several scenarios. Each scenario is described by two
lines. The first line contains one integer number N , the number of
samples, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100 000. The second line lists exactly N
space-separated positive integers, they specify the heights of
individual samples and their initial order.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note
that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should
output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi
and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
3 4 5 1 6 2
4
3 3 2 1
0
4 2 4 4
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=;
int n,fa[maxn],ch[maxn][],sz[maxn];
int flip[maxn],pos[maxn],rt;
struct Node{
int x,id;
}a[maxn]; void Flip(int x){
swap(ch[x][],ch[x][]);
flip[x]^=;
} void Push_down(int x){
if(flip[x]){
Flip(ch[x][]);
Flip(ch[x][]);
flip[x]=;
}
} int pd[maxn];
void P(int x){
int cnt=;
while(x){
pd[++cnt]=x;
x=fa[x];
}
while(cnt){
Push_down(pd[cnt--]);
}
} void Push_up(int x){
sz[x]=sz[ch[x][]]+sz[ch[x][]]+;
} void Rotate(int x){
int y=fa[x],g=fa[y],c=ch[y][]==x;
ch[y][c]=ch[x][c^];fa[ch[x][c^]]=y;
ch[x][c^]=y;fa[y]=x;fa[x]=g;
if(g)ch[g][ch[g][]==y]=x;
Push_up(y);
} void Splay(int x,int g=){
P(x);
for(int y;(y=fa[x])!=g;Rotate(x))
if(fa[y]!=g)
Rotate((ch[fa[y]][]==y)==(ch[y][]==x)?y:x);
Push_up(x);
if(!g)rt=x;
} int Build(int f,int l,int r){
if(l>r)return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>;fa[mid]=f;
ch[mid][]=Build(mid,l,mid-);
ch[mid][]=Build(mid,mid+,r);
sz[mid]=;
Push_up(mid);
return mid;
} bool cmp(Node a,Node b){
if(a.x!=b.x)
return a.x<b.x;
return a.id<b.id;
} int main(){
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n){
memset(flip,,sizeof(flip));
rt=Build(,,n+);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i].x);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
a[i].id=i;
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
pos[i+]=a[i].id+;
pos[]=;pos[n+]=n+;
for(int i=,p;i<n+;i++){
Splay(pos[]);
Splay(pos[i],pos[]);
printf("%d ",sz[ch[ch[rt][]][]]+);
Splay(pos[i]);
p=ch[pos[i]][];
while(ch[p][]){
Push_down(p);
p=ch[p][];
}
Push_down(p);
Splay(pos[i-]);
Splay(p,pos[i-]);
Flip(ch[ch[rt][]][]);
}
printf("%d\n",n);
}
return ;
}
数据结构(Splay平衡树):HDU 1890 Robotic Sort的更多相关文章
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort | Splay
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) [Pr ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort (splay tree)
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort(splay)
[题目链接] http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 [题意] 给定一个序列,每次将i..P[i]反转,然后输出P[i],P[i]定义为当前数字i ...
- HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][区间反转+删除根节点]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Li ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort
原题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 如下: #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib&g ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic SortI(splay区间旋转操作)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 题解:splay又一高级的功能,区间旋转这个是用线段树这些实现不了的,这题可以学习splay的旋 ...
- 【HDOJ】1890 Robotic Sort
伸展树伤不起啊,很容易wa,很容易T,很容易M. /* 1890 */ #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <m ...
- 数据结构(Splay平衡树):COGS 339. [NOI2005] 维护数列
339. [NOI2005] 维护数列 时间限制:3 s 内存限制:256 MB [问题描述] 请写一个程序,要求维护一个数列,支持以下 6 种操作:(请注意,格式栏 中的下划线‘ _ ’表示实际 ...
随机推荐
- linux进程地址空间详解(转载)
linux进程地址空间详解(转载) 在前面的<对一个程序在内存中的分析 >中很好的描述了程序在内存中的布局,这里对这个结果做些总结和实验验证.下面以Linux为例(实验结果显示window ...
- angularJS function
angular.bootstrap 启动Angular angular.element 相当于轻量的JQuery 使用方法: angular.element('#qq'); angular.eleme ...
- Android ListView 嵌套 ImageView,如何响应ImageView的点击和长按事件
http://www.tuicool.com/articles/EZv2Uv 1.先说下嵌套在ListView中的ImageView如何响应点击事件 方法:在imageView中设置onClick属性 ...
- 图论——读书笔记(基于BFS广度优先算法的广度优先树)
广度优先树 对于一个图G=(V,E)在跑过BFS算法的过程中会创建一棵广度优先树. 形式化一点的表示该广度 优先树的形成过程是这样的: 对于图G=(V,E)是有向图或是无向图, 和图中的源结点s, 我 ...
- jq 图片上传
1.html <input type="file" class="ImgInput" name="ImgInput"/> 2.j ...
- phpcms(3) V9 常用函数 及 代码整理(转)
转自http://www.cnblogs.com/Braveliu/p/5103918.html 常用函数 及 常用代码 总结如下 <;?php //转换字符串或者数组的编码 str_chars ...
- CentOS7下安装配置vncserver
之前试了xmanager,不过好像和在centos6有很大不同,居然没成功,然后找到了vncserver,试了下,成了 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/jiangliqing1234/ ...
- Android安装 sdk+jdk+Eclipse+Adt开发工具
根据别人提供的手册和安装过程体验加以更新和详细描述 安装Android开发工具 开发Android应用程序的门坎并不高,因为Google已经为Android应用程序开发提供了免费而且跨平台的集成开发环 ...
- QTP的DataTable操作整理(注---不知转载多少遍)
返回值:数字 示例: 以下示例使用 GetRowCount 方法查找 MySheet 运行时数据表中最长的列中的总行数,并将其写入报告. rowcount = DataTable.GetSheet(& ...
- echshop jquery与transpart冲突解决?
<script type="text/javascript">$(function() {window.__Object_toJSONString = Object.p ...