Seaborn分布数据可视化---散点分布图
散点分布图
综合表示散点图和直方分布图。
Jointplot()
绘制二变量或单变量的图形,底层是JointGrid()。
sns.jointplot(
x,
y,
data=None,
kind='scatter',
stat_func=None,
color=None,
height=6,
ratio=5,
space=0.2,
dropna=True,
xlim=None,
ylim=None,
joint_kws=None,
marginal_kws=None,
annot_kws=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Draw a plot of two variables with bivariate and univariate graphs.
This function provides a convenient interface to the :class:`JointGrid`
class, with several canned plot kinds. This is intended to be a fairly
lightweight wrapper; if you need more flexibility, you should use
:class:`JointGrid` directly.
Parameters
----------
x, y : strings or vectors
Data or names of variables in ``data``.
data : DataFrame, optional
DataFrame when ``x`` and ``y`` are variable names.
kind : { "scatter" | "reg" | "resid" | "kde" | "hex" }, optional
Kind of plot to draw.
stat_func : callable or None, optional
*Deprecated*
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color used for the plot elements.
height : numeric, optional
Size of the figure (it will be square).
ratio : numeric, optional
Ratio of joint axes height to marginal axes height.
space : numeric, optional
Space between the joint and marginal axes
dropna : bool, optional
If True, remove observations that are missing from ``x`` and ``y``.
{x, y}lim : two-tuples, optional
Axis limits to set before plotting.
{joint, marginal, annot}_kws : dicts, optional
Additional keyword arguments for the plot components.
kwargs : key, value pairings
Additional keyword arguments are passed to the function used to
draw the plot on the joint Axes, superseding items in the
``joint_kws`` dictionary.
Returns
-------
grid : :class:`JointGrid`
:class:`JointGrid` object with the plot on it.
See Also
--------
JointGrid : The Grid class used for drawing this plot. Use it directly if
you need more flexibility.
#综合散点分布图-jointplot
#创建DataFrame数组
rs = np.random.RandomState(3)
df = pd.DataFrame(rs.randn(200,2), columns=['A','B'])
#绘制综合散点分布图jointplot()
sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'], #设置x和y轴的数据
data=df, #设置数据
color='k',
s=50, edgecolor='w', linewidth=1, #散点大小、边缘线颜色和宽度(只针对scatter)
kind='scatter', #默认类型:“scatter”,其他有“reg”、“resid”、“kde”
space=0.2, #设置散点图和布局图的间距
height=8, #图表的大小(自动调整为正方形)
ratio=5, #散点图与布局图高度比率
stat_func= sci.pearsonr, #pearson相关系数
marginal_kws=dict(bins=15, rug=True)) #边际图的参数
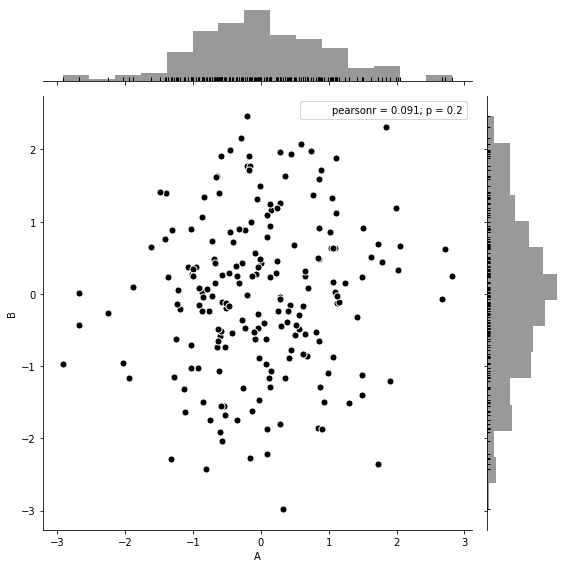
sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'],
data=df,
color='k',
kind='reg', #reg添加线性回归线
height=8,
ratio=5,
stat_func= sci.pearsonr,
marginal_kws=dict(bins=15, rug=True))
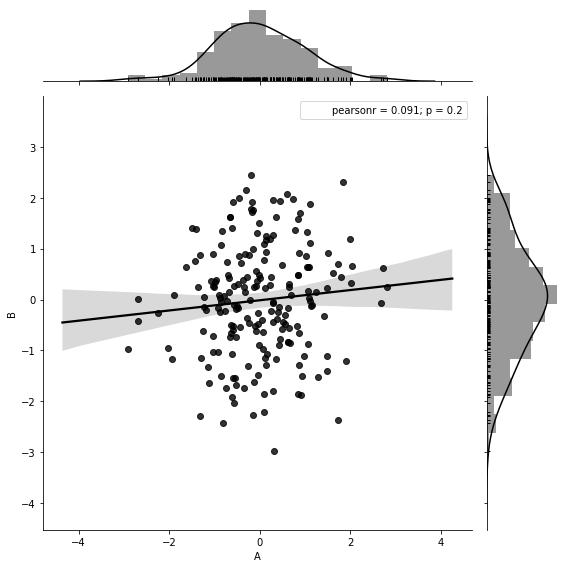
sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'],
data=df,
color='k',
kind='resid', #resid
height=8,
ratio=5,
marginal_kws=dict(bins=15, rug=True))
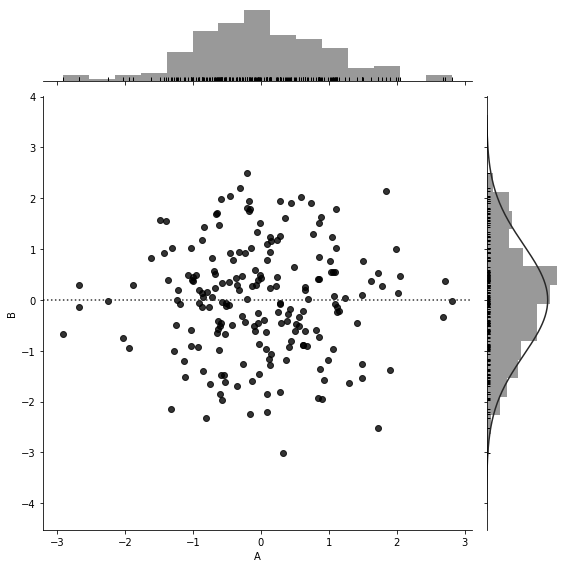
sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'],
data=df,
color='k',
kind='kde', #kde密度图
height=8,
ratio=5)
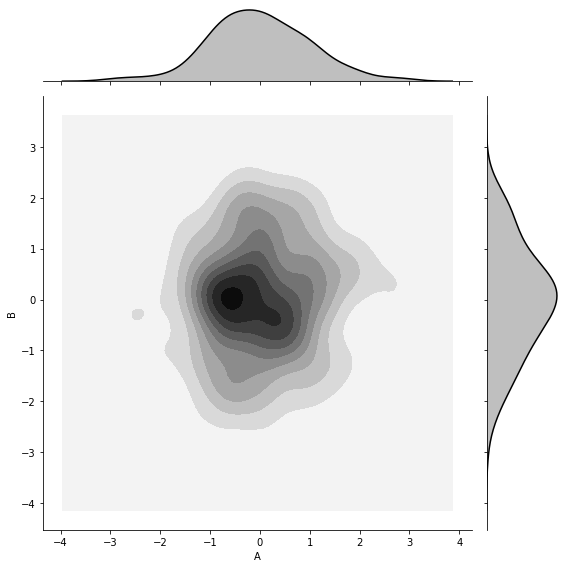
sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'],
data=df,
color='k',
kind='hex', #hex蜂窝图(六角形)
height=8,
ratio=5)
g = sns.jointplot(x=df['A'], y=df['B'],
data=df,
color='k',
kind='kde', #kde密度图
height=8,
ratio=5,
shade_lowest=False)
#添加散点图(c-->颜色,s-->大小)
g.plot_joint(plt.scatter, c='w', s=10, linewidth=1, marker='+')
JointGrid()
创建图形网格,用于绘制二变量或单变量的图形,作用和Jointplot()一样,不过比Jointplot()更灵活。
sns.JointGrid(
x,
y,
data=None,
height=6,
ratio=5,
space=0.2,
dropna=True,
xlim=None,
ylim=None,
size=None,
)
Docstring: Grid for drawing a bivariate plot with marginal univariate plots.
Init docstring:
Set up the grid of subplots.
Parameters
----------
x, y : strings or vectors
Data or names of variables in ``data``.
data : DataFrame, optional
DataFrame when ``x`` and ``y`` are variable names.
height : numeric
Size of each side of the figure in inches (it will be square).
ratio : numeric
Ratio of joint axes size to marginal axes height.
space : numeric, optional
Space between the joint and marginal axes
dropna : bool, optional
If True, remove observations that are missing from `x` and `y`.
{x, y}lim : two-tuples, optional
Axis limits to set before plotting.
See Also
--------
jointplot : High-level interface for drawing bivariate plots with
several different default plot kinds.
#设置风格
sns.set_style('white')
#导入数据
tip_datas = sns.load_dataset('tips', data_home='seaborn-data')
#绘制绘图网格,包含三部分:一个主绘图区域,两个边际绘图区域
g = sns.JointGrid(x='total_bill', y='tip', data=tip_datas)
#主绘图区域:散点图
g.plot_joint(plt.scatter, color='m', edgecolor='w', alpha=.3)
#边际绘图区域:x和y轴
g.ax_marg_x.hist(tip_datas['total_bill'], color='b', alpha=.3)
g.ax_marg_y.hist(tip_datas['tip'], color='r', alpha=.3,
orientation='horizontal')
#相关系数标签
from scipy import stats
g.annotate(stats.pearsonr)
#绘制表格线
plt.grid(linestyle='--')
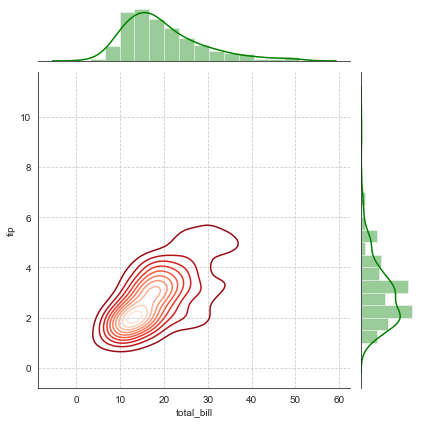
g = sns.JointGrid(x='total_bill', y='tip', data=tip_datas)
g = g.plot_joint(plt.scatter, color='g', s=40, edgecolor='white')
plt.grid(linestyle='--')
#两边边际图用统一函数设置统一风格
g.plot_marginals(sns.distplot, kde=True, color='g')
g = sns.JointGrid(x='total_bill', y='tip', data=tip_datas)
#主绘图设置密度图
g = g.plot_joint(sns.kdeplot, cmap='Reds_r')
plt.grid(linestyle='--')
#两边边际图用统一函数设置统一风格
g.plot_marginals(sns.distplot, kde=True, color='g')
Pairplot()
用于数据集的相关性图形绘制,如:矩阵图,底层是PairGrid()。
sns.pairplot(
data,
hue=None,
hue_order=None,
palette=None,
vars=None,
x_vars=None,
y_vars=None,
kind='scatter',
diag_kind='auto',
markers=None,
height=2.5,
aspect=1,
dropna=True,
plot_kws=None,
diag_kws=None,
grid_kws=None,
size=None,
)
Docstring:
Plot pairwise relationships in a dataset.
By default, this function will create a grid of Axes such that each
variable in ``data`` will by shared in the y-axis across a single row and
in the x-axis across a single column. The diagonal Axes are treated
differently, drawing a plot to show the univariate distribution of the data
for the variable in that column.
It is also possible to show a subset of variables or plot different
variables on the rows and columns.
This is a high-level interface for :class:`PairGrid` that is intended to
make it easy to draw a few common styles. You should use :class:`PairGrid`
directly if you need more flexibility.
Parameters
----------
data : DataFrame
Tidy (long-form) dataframe where each column is a variable and
each row is an observation.
hue : string (variable name), optional
Variable in ``data`` to map plot aspects to different colors.
hue_order : list of strings
Order for the levels of the hue variable in the palette
palette : dict or seaborn color palette
Set of colors for mapping the ``hue`` variable. If a dict, keys
should be values in the ``hue`` variable.
vars : list of variable names, optional
Variables within ``data`` to use, otherwise use every column with
a numeric datatype.
{x, y}_vars : lists of variable names, optional
Variables within ``data`` to use separately for the rows and
columns of the figure; i.e. to make a non-square plot.
kind : {'scatter', 'reg'}, optional
Kind of plot for the non-identity relationships.
diag_kind : {'auto', 'hist', 'kde'}, optional
Kind of plot for the diagonal subplots. The default depends on whether
``"hue"`` is used or not.
markers : single matplotlib marker code or list, optional
Either the marker to use for all datapoints or a list of markers with
a length the same as the number of levels in the hue variable so that
differently colored points will also have different scatterplot
markers.
height : scalar, optional
Height (in inches) of each facet.
aspect : scalar, optional
Aspect * height gives the width (in inches) of each facet.
dropna : boolean, optional
Drop missing values from the data before plotting.
{plot, diag, grid}_kws : dicts, optional
Dictionaries of keyword arguments.
Returns
-------
grid : PairGrid
Returns the underlying ``PairGrid`` instance for further tweaking.
See Also
--------
PairGrid : Subplot grid for more flexible plotting of pairwise
relationships.
#导入鸢尾花数据
i_datas = sns.load_dataset('iris', data_home='seaborn-data')
i_datas
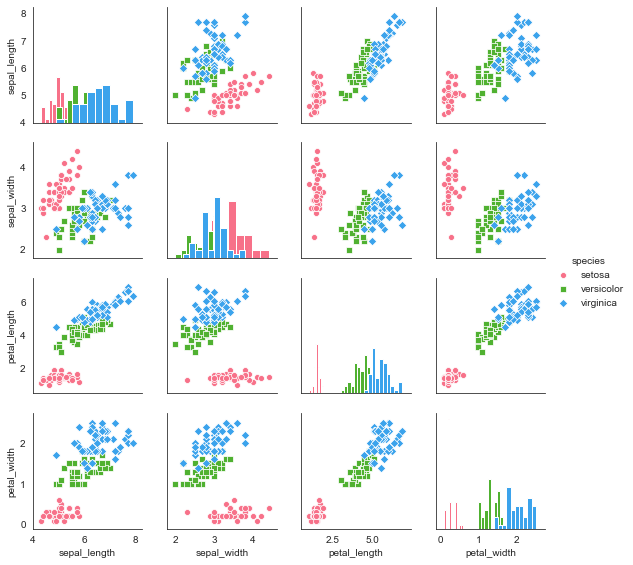
#矩阵散点图
sns.pairplot(i_datas,
kind='scatter', #图形类型(散点图:scatter, 回归分布图:reg)
diag_kind='hist', #对角线的图形类型(直方图:hist, 密度图:kde)
hue='species', #按照某一字段分类
palette='husl', #设置调色板
markers=['o','s','D'], #设置点样式
height=2) #设置图标大小
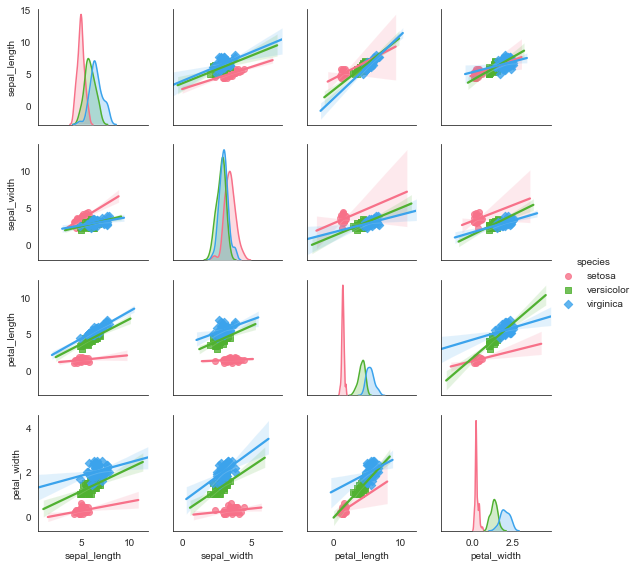
#矩阵回归分析图
sns.pairplot(i_datas,
kind='reg', #图形类型(散点图:scatter, 回归分布图:reg)
diag_kind='kde', #对角线的图形类型(直方图:hist, 密度图:kde)
hue='species', #按照某一字段分类
palette='husl', #设置调色板
markers=['o','s','D'], #设置点样式
height=2) #设置图标大小
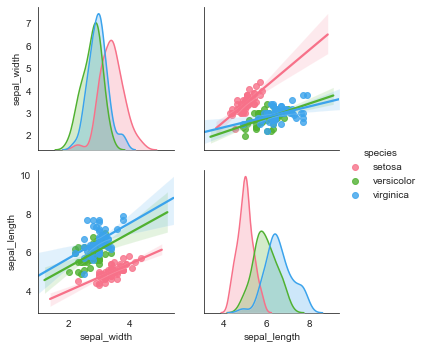
#局部变量选择,vars
g = sns.pairplot(i_datas, vars=['sepal_width', 'sepal_length'],
kind='reg', diag_kind='kde',
hue='species', palette='husl')
#综合参数设置
sns.pairplot(i_datas, diag_kind='kde', markers='+', hue='species',
#散点图的参数
plot_kws=dict(s=50, edgecolor='b', linewidth=1),
#对角线图的参数
diag_kws=dict(shade=True))
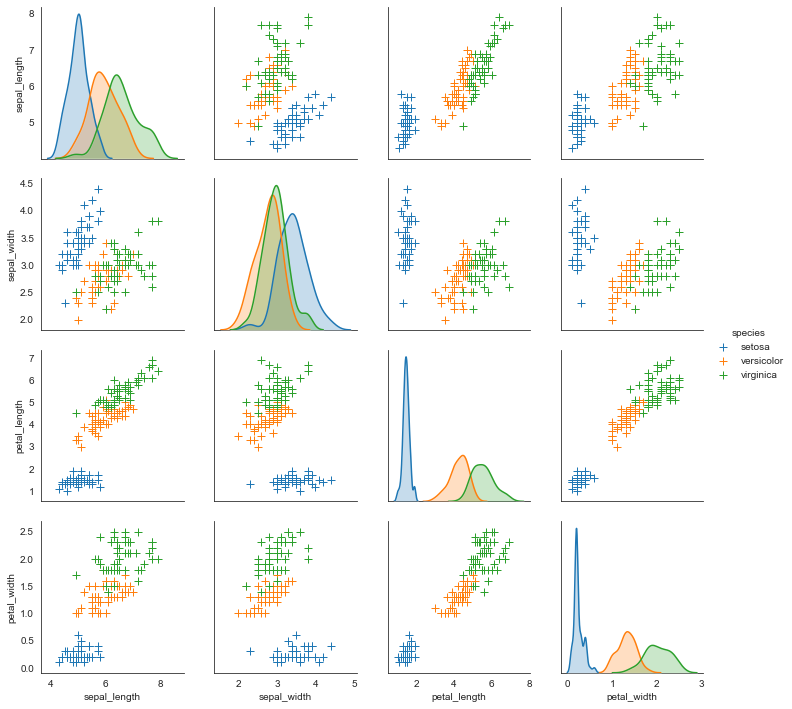
PairGrid()
用于数据集的相关性图形绘制,如:矩阵图。功能比Pairplot()更加灵活。
sns.PairGrid(
data,
hue=None,
hue_order=None,
palette=None,
hue_kws=None,
vars=None,
x_vars=None,
y_vars=None,
diag_sharey=True,
height=2.5,
aspect=1,
despine=True,
dropna=True,
size=None,
)
Docstring:
Subplot grid for plotting pairwise relationships in a dataset.
This class maps each variable in a dataset onto a column and row in a
grid of multiple axes. Different axes-level plotting functions can be
used to draw bivariate plots in the upper and lower triangles, and the
the marginal distribution of each variable can be shown on the diagonal.
It can also represent an additional level of conditionalization with the
``hue`` parameter, which plots different subets of data in different
colors. This uses color to resolve elements on a third dimension, but
only draws subsets on top of each other and will not tailor the ``hue``
parameter for the specific visualization the way that axes-level functions
that accept ``hue`` will.
See the :ref:`tutorial <grid_tutorial>` for more information.
Init docstring:
Initialize the plot figure and PairGrid object.
Parameters
----------
data : DataFrame
Tidy (long-form) dataframe where each column is a variable and
each row is an observation.
hue : string (variable name), optional
Variable in ``data`` to map plot aspects to different colors.
hue_order : list of strings
Order for the levels of the hue variable in the palette
palette : dict or seaborn color palette
Set of colors for mapping the ``hue`` variable. If a dict, keys
should be values in the ``hue`` variable.
hue_kws : dictionary of param -> list of values mapping
Other keyword arguments to insert into the plotting call to let
other plot attributes vary across levels of the hue variable (e.g.
the markers in a scatterplot).
vars : list of variable names, optional
Variables within ``data`` to use, otherwise use every column with
a numeric datatype.
{x, y}_vars : lists of variable names, optional
Variables within ``data`` to use separately for the rows and
columns of the figure; i.e. to make a non-square plot.
height : scalar, optional
Height (in inches) of each facet.
aspect : scalar, optional
Aspect * height gives the width (in inches) of each facet.
despine : boolean, optional
Remove the top and right spines from the plots.
dropna : boolean, optional
Drop missing values from the data before plotting.
See Also
--------
pairplot : Easily drawing common uses of :class:`PairGrid`.
FacetGrid : Subplot grid for plotting conditional relationships.
#绘制四个参数vars的绘图网格(subplots)
g = sns.PairGrid(i_datas, hue='species', palette='hls',
vars=['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width'])
#对角线图形绘制
g.map_diag(plt.hist,
histtype='step', #可选:'bar'\ 'barstacked'\'step'\'stepfilled'
linewidth=1)
#非对角线图形绘制
g.map_offdiag(plt.scatter, s=40, linewidth=1)
#添加图例
g.add_legend()

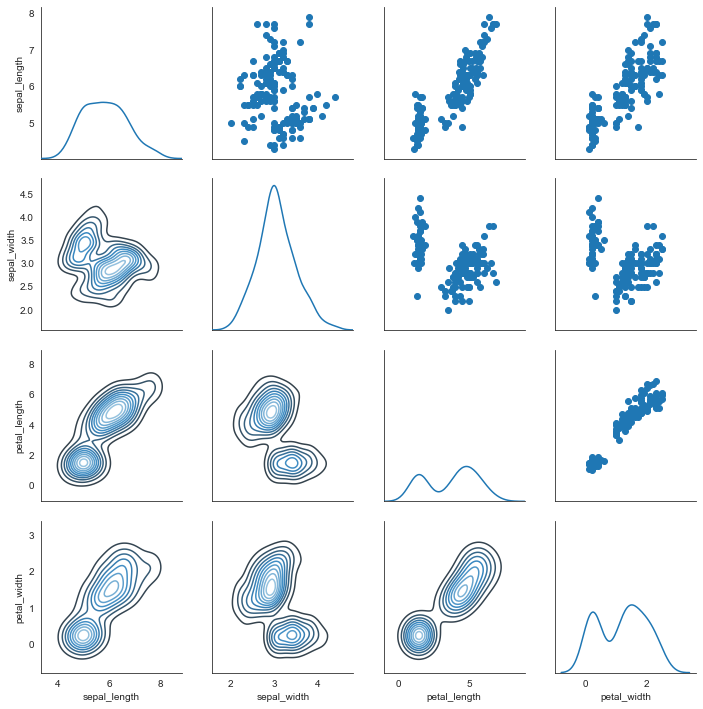
g = sns.PairGrid(i_datas)
#主对角线图形
g.map_diag(sns.kdeplot)
#上三角图形
g.map_upper(plt.scatter)
#下三角图形
g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot, cmap='Blues_d')
Seaborn分布数据可视化---散点分布图的更多相关文章
- seaborn分布数据可视化:直方图|密度图|散点图
系统自带的数据表格(存放在github上https://github.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data),使用时通过sns.load_dataset('表名称')即可,结果为一个Dat ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:1. 风格| 分布数据可视化-直方图| 密度图| 散点图
conda install seaborn 是安装到jupyter那个环境的 1. 整体风格设置 对图表整体颜色.比例等进行风格设置,包括颜色色板等调用系统风格进行数据可视化 set() / se ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化-分类散点图|分布图(箱型图|小提琴图|LV图表)|统计图(柱状图|折线图)
1. 分类数据可视化 - 分类散点图 stripplot( ) / swarmplot( ) sns.stripplot(x="day",y="total_bill&qu ...
- seaborn线性关系数据可视化:时间线图|热图|结构化图表可视化
一.线性关系数据可视化lmplot( ) 表示对所统计的数据做散点图,并拟合一个一元线性回归关系. lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, p ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化
转载:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1178368 seaborn针对分类型的数据有专门的可视化函数,这些函数可大致分为三种: 分类数据散点图 ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化:散点图|箱型图|小提琴图|lv图|柱状图|折线图
一.散点图stripplot( ) 与swarmplot() 1.分类散点图stripplot( ) 用法stripplot(x=None, y=None, hue=None, data=None, ...
- 用seaborn对数据可视化
以下用sns作为seaborn的别名 1.seaborn整体布局设置 sns.set_syle()函数设置图的风格,传入的参数可以是"darkgrid", "whiteg ...
- Python Seaborn综合指南,成为数据可视化专家
概述 Seaborn是Python流行的数据可视化库 Seaborn结合了美学和技术,这是数据科学项目中的两个关键要素 了解其Seaborn作原理以及使用它生成的不同的图表 介绍 一个精心设计的可视化 ...
- Seaborn数据可视化入门
在本节学习中,我们使用Seaborn作为数据可视化的入门工具 Seaborn的官方网址如下:http://seaborn.pydata.org 一:definition Seaborn is a Py ...
- seaborn教程4——分类数据可视化
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015310299 Seaborn学习大纲 seaborn的学习内容主要包含以下几个部分: 风格管理 绘图风格设置 颜色风格设置 绘 ...
随机推荐
- core-js/modules/es7.arrat......................报错
拉入代码之后出现如图提示,导致原因是因为core-js版本太高,可以用cnpm install core-js@2成功解决,安装一个项目前最后将node-moudel删除,重新安装
- 【Azure 存储服务】Storage Account Blob 使用REST API如何获取磁盘大小(Content-Length), IOPS信息
问题描述 1)关于使用Rest API获取非托管磁盘信息比如获取磁盘大小 2)关于使用Rest API获取非托管磁盘信息比如iops 问题答案 #1:关于使用Rest API获取非托管磁盘信息比如获取 ...
- Codeforces Round 914 (Div. 2)A~C
A 反过来考虑,由皇后和国王的位置去寻找骑士的位置,当一个点既可以被皇后找到,也可以被国王找到时就说明这个点是满足条件的 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ...
- web项目开发写接口时,为什么需要在关键位置打印日志-2022新项目
一.业务场景 最近在开发新功能,新功能主要就是写app的首页查询接口,接口比较多有十几个,首页会有各种查询,新增操作比较少.由于用户量 比较大,据说并发量不小,所以首页的很多查询都做了缓存处理,用来提 ...
- centos 养成计划
20220720 常用命令 pm2 list pm2 delete all 启动前端 cd /root/website && pm2 start http-server 启动后端 cd ...
- k8s中port-forward 、service的nodeport与ingress区别
在Kubernetes中,port-forward.Service的NodePort和Ingress都是用于将外部流量引入集群内部的方法,但它们在使用场景.实现方式和功能上有所不同. port-for ...
- 没有 Release 文件的解决方法
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44903509/article/details/108825738 sudo apt-get update 出现问题 E: 仓库 " ...
- IIS 修改配置 进行性能优化
1.修改线程池队列长度和启动模式 2.修改线程池最大工作进程数 --设置为0 目的是根据服务器核数 匹配最佳线程数 3.站点高级设置开启预加载
- 曲线艺术编程第一章 coding curves
原作:Keith Peters 原文:https://www.bit-101.com/blog/2022/11/coding-curves/ 译者:池中物王二狗(sheldon) blog: http ...
- day04-实现SpringBoot底层机制
实现SpringBoot底层机制 Tomcat底层启动分析+Spring容器初始化+Tomcat关联Spring容器 1.任务1-创建Tomcat,并启动 (1)创建一个Maven项目,修改pom.x ...
