04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)
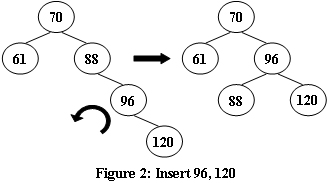
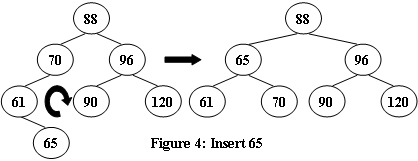
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
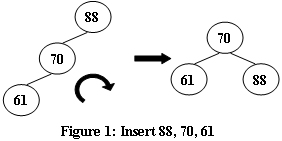
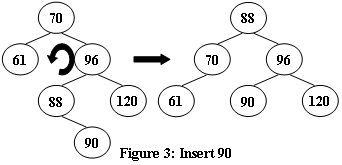
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; struct Node
{
int v;
int height;
Node *lchild, *rchild;
}*root; void Insert(Node* &root,int v);
Node* NewNode(int v);
void updateHeight(Node *root);
int getHeight(Node* root);
int getBalanceFactor(Node* root);
Node* R(Node* &root);
Node* L(Node* &root); int main()
{
int n;
int v;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
Insert(root,v);
}
printf("%d",root->v);
return ;
} void Insert(Node* &root, int v)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
root = NewNode(v);
return ;
} if (root->v > v)
{
Insert(root->lchild,v);
updateHeight(root);
if ( == getBalanceFactor(root))
{
if ( == getBalanceFactor(root->lchild))
{
R(root);
}
else if(- == getBalanceFactor(root->lchild))
{
L(root->lchild);
R(root);
}
}
}
else
{
Insert(root->rchild,v);
updateHeight(root);
if (- == getBalanceFactor(root))
{
if (- == getBalanceFactor(root->rchild))
{
L(root);
}
else if( == getBalanceFactor(root->rchild))
{
R(root->rchild);
L(root);
}
}
}
} Node* NewNode(int v)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->lchild = node->rchild = NULL;
node->v = v;
node->height = ;
return node;
} void updateHeight(Node *root)
{
root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeight(root->rchild)) + ; } int getHeight(Node* root)
{
if (NULL == root)
{
return ;
}
else
{
return root->height;
}
} int getBalanceFactor(Node* root)
{
return getHeight(root->lchild) - getHeight(root->rchild);
} Node* R(Node* &root)
{
Node *tmp = root->lchild;
root->lchild = tmp->rchild;
tmp->rchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(tmp);
root = tmp;
} Node* L(Node* &root)
{
Node *tmp = root->rchild;
root->rchild = tmp->lchild;
tmp->lchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(tmp);
root = tmp;
}
04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)的更多相关文章
- PTA 04-树5 Root of AVL Tree (25分)
题目地址 https://pta.patest.cn/pta/test/16/exam/4/question/668 5-6 Root of AVL Tree (25分) An AVL tree ...
- PAT甲级:1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)
PAT甲级:1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分) 题干 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL t ...
- PAT 甲级 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)(快速掌握平衡二叉树的旋转,内含代码和注解)***
1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分) An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, t ...
- 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)(AVL树的实现)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- 【PAT甲级】1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)(AVL树建树模板)
题意: 输入一个正整数N(<=20),接着输入N个结点的值,依次插入一颗AVL树,输出最终根结点的值. AAAAAccepted code: #define HAVE_STRUCT_TIMESP ...
- 04-树4. Root of AVL Tree (25)
04-树4. Root of AVL Tree (25) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue An A ...
- pat04-树4. Root of AVL Tree (25)
04-树4. Root of AVL Tree (25) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue An A ...
- pat 甲级 1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
1066. Root of AVL Tree (25) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue An A ...
- pat1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
1066. Root of AVL Tree (25) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue An A ...
随机推荐
- 使用HttpWebRequest POST上传文件
2019/10/27, .Net c#代码片段 摘要:使用HttpWebRequest向Api接口发送文件,multipart-form数据格式,POST方式 参考地址 /// <summary ...
- Java IO---序列化和反序列化
一.序列化和反序列化介绍 什么是序列化和反序列化? 序列化就是将对象转换为字节序列的过程. 反序列化就是将字节序列恢复为对象的过程. 序列化的用途在哪? 通常情况下,序列化有两个用途: 将对象 ...
- Spring Security 解析(五) —— Spring Security Oauth2 开发
Spring Security 解析(五) -- Spring Security Oauth2 开发 在学习Spring Cloud 时,遇到了授权服务oauth 相关内容时,总是一知半解,因此决 ...
- Myeclipse6.5迁移到IDEA
背景 myeclipse开发的javaweb项目用svn管理.现要转用idea开发.因为发现idea实在是太好用了.myeclipse6.5是个纯净版,用了两年,对于新手来说用myeclipse6.5 ...
- vue项目的一个package.json
{ "name": "projectName", "version": "1.0.1", "des ...
- jQuery选择器与过滤器(二)
一.jQuery选择器1.基本选择器:所有选择器 *标签选择器 标签名ID选择器 #ID类选择器 .className组合选择器 selector1,selector2 ...
- Ext.bind函数说明
bind( fn, [scope], [args], [appendArgs] ) : FunctionCreate a new function from the provided fn, chan ...
- ffmpeg 详解
来源:http://blog.itpub.net/9399028/viewspace-1242300/ FFMPEG详解 认识FFMPEG FFMPEG堪称自由软件中最完备的一套多媒体支持库,它几 ...
- JS案例 - 城市三级联动
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- Python装饰器与闭包
闭包是Python装饰器的基础.要理解闭包,先要了解Python中的变量作用域规则. 变量作用域规则 首先,在函数中是能访问全局变量的: >>> a = 'global var' & ...