1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
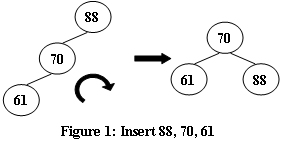

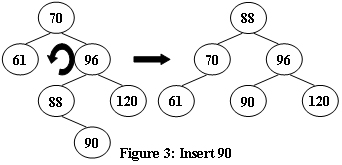
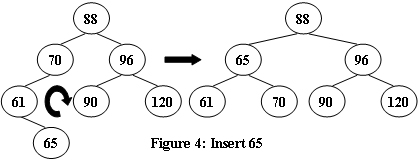
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print ythe root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7
88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
#include<stdio.h>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std; struct node
{
node(int v):left(NULL),right(NULL),high(),val(v){}
node* left,* right;
int val,high;
}; int gethigh(node* root)
{
int a = , b = ;
if(root->left!= NULL)
a = root->left->high;
if(root->right!= NULL)
b = root->right->high;
return a > b ? a+:b+;
} void R(node* & root)
{
node* tem = root->left;
root->left = tem->right;
tem->right = root;
root->high = gethigh(root);
tem->high = gethigh(tem);
root = tem;
} void L(node* & root)
{
node* tem = root->right;
root->right = tem->left;
tem->left = root;
root->high = gethigh(root);
tem->high = gethigh(tem);
root = tem;
} void insert(node*& root,int val)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
root = new node(val);
return;
} if(val < root->val)
{
insert(root->left,val);
root->high = gethigh(root);
int a = root->left == NULL ? : root->left->high;
int b = root->right == NULL ? : root->right->high;
if(a - b == )
{
int c = root->left->left == NULL ? :root->left->left->high;
int d = root->left->right == NULL ? :root->left->right->high;
if(c - d == )
{
R(root);
}
else if(c - d == -)
{
L(root->left);
R(root);
}
}
}
else
{
insert(root->right,val);
root->high = gethigh(root);
int a = root->left == NULL ? : root->left->high;
int b = root->right == NULL ? : root->right->high;
if(a - b == -)
{
int c = root->right->right == NULL ? :root->right->right->high;
int d = root->right->left == NULL ? :root->right->left->high;
if(c - d == )
{
L(root);
}
else if(c - d == -)
{
R(root->right);
L(root);
}
}
}
} int main()
{
int n,tem;
scanf("%d",&n);
node* Tree = NULL;
for(int i = ;i < n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&tem);
insert(Tree,tem);
}
printf("%d\n",Tree->val);
return ;
}
1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)的更多相关文章
- pat 甲级 1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
1066. Root of AVL Tree (25) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue An A ...
- PAT 甲级 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分)(快速掌握平衡二叉树的旋转,内含代码和注解)***
1066 Root of AVL Tree (25 分) An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, t ...
- PAT甲级:1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)
PAT甲级:1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分) 题干 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL t ...
- PAT 1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- PAT Advanced 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25) [平衡⼆叉树(AVL树)]
题目 An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child ...
- 1066 Root of AVL Tree (25分)(AVL树的实现)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child sub ...
- PAT (Advanced Level) 1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
AVL树的旋转.居然1A了.... 了解旋转方式之后,数据较小可以当做模拟写. #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<c ...
- PAT甲级题解-1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)-AVL树模板题
博主欢迎转载,但请给出本文链接,我尊重你,你尊重我,谢谢~http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxiwenruo/p/6803291.html特别不喜欢那些随便转载别人的原创文章又不给 ...
随机推荐
- Java实现深克隆的两种方式
序列化和依次克隆各个可变的引用类型都可以实现深克隆,但是序列化的效率并不理想 下面是两种实现深克隆的实例,并且测试类对两种方法进行了对比: 1.重写clone方法使用父类中的clone()方法实现深克 ...
- uva 10252 - Common Permutation 字符串水题
题意:給定兩個小寫的字串a與b,請印出皆出現在兩字串中的字母,出現的字母由a~z的順序印出,若同字母出現不只一次,請重複印出但不能超過任一字串中出現的次數.(from Ruby兔) 很水,直接比较输出 ...
- web前端开发(5)
CSS的一些问题: 一般情况下,尽量使用class选择器 解决点击超链接后hover 样式不出现多次问题:a:visited a:hover 的顺序是问题所在,记住 love hate L(lin ...
- js将人民币金额转换为大写
function upDigit(n) { var fraction = ['角', '分']; var digit = ['零', '壹', '贰', '叁', '肆', '伍', '陆', '柒' ...
- POJ 2492 A Bug's Life (并查集)
A Bug's Life Time Limit: 10000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 30130 Accepted: 9869 De ...
- [转]移动App测试中的最佳做法
Daniel Knott 用过各种不同编程语言和软件质量保证工具.他在软件开发和测试方面干了七年,自2010年起,他一直在德国汉堡的XING AG公司就职,几个项目里,比如XING调查和XING建议, ...
- 转载事务在C#方法里的应用
问题:一个系统的数据库更新或者插入的时候若遭遇到断电等能引起数据库不能正常工作的情况的话,其更新或插入的将是不完整的数据,或者是错误的数据.故需要引入事务处理. 实例:数据更新的事务处理. 解决方案: ...
- HttpContext 讲解
HttpContext类:封装有关个别HTTP请求的所有HTTP特定的信息,又叫上下文.看到这个解释,我觉得有些抽象,Http特定信息具体又是什么?看了下备注:为继承 IHttpModule 和 IH ...
- LinearLayout和RelativeLayout
LinearLayout和RelativeLayout 共有属性:java代码中通过btn1关联次控件android:id="@+id/btn1" 控件宽度android:layo ...
- C# 线程抛异常
异常抛出 异常抛出要在线程代码中抛出,否则捕获不到 using System; using System.Threading; namespace testthread_keyword_lock { ...
