chapter3——逻辑回归手动+sklean版本
1 导入numpy包
import numpy as np
2 sigmoid函数
def sigmoid(x):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
demox = np.array([1,2,3])
print(sigmoid(demox))
#报错
#demox = [1,2,3]
# print(sigmoid(demox))
结果:
[0.73105858 0.88079708 0.95257413]
3 定义逻辑回归模型主体
### 定义逻辑回归模型主体
def logistic(x, y, w, b):
# 训练样本量
num_train = x.shape[0]
# 逻辑回归模型输出
y_hat = sigmoid(np.dot(x,w)+b)
# 交叉熵损失
cost = -1/(num_train)*(np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat)+(1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)))
# 权值梯度
dW = np.dot(x.T,(y_hat-y))/num_train
# 偏置梯度
db = np.sum(y_hat- y)/num_train
# 压缩损失数组维度
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
return y_hat, cost, dW, db
4 初始化函数
def init_parm(dims):
w = np.zeros((dims,1))
b = 0
return w ,b
5 定义逻辑回归模型训练过程
### 定义逻辑回归模型训练过程
def logistic_train(X, y, learning_rate, epochs):
# 初始化模型参数
W, b = init_parm(X.shape[1])
cost_list = []
for i in range(epochs):
# 计算当前次的模型计算结果、损失和参数梯度
a, cost, dW, db = logistic(X, y, W, b)
# 参数更新
W = W -learning_rate * dW
b = b -learning_rate * db
if i % 100 == 0:
cost_list.append(cost)
if i % 100 == 0:
print('epoch %d cost %f' % (i, cost))
params = {
'W': W,
'b': b
}
grads = {
'dW': dW,
'db': db
}
return cost_list, params, grads
6 定义预测函数
def predict(X,params):
y_pred = sigmoid(np.dot(X,params['W'])+params['b'])
y_preds = [1 if y_pred[i]>0.5 else 0 for i in range(len(y_pred))]
return y_preds
7 生成数据
# 导入matplotlib绘图库
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 导入生成分类数据函数
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# 生成100*2的模拟二分类数据集
x ,label = make_classification(
n_samples=100,# 样本个数
n_classes=2,# 样本类别
n_features=2,#特征个数
n_redundant=0,#冗余特征个数(有效特征的随机组合)
n_informative=2,#有效特征,有价值特征
n_repeated=0, # 重复特征个数(有效特征和冗余特征的随机组合)
n_clusters_per_class=2 ,# 簇的个数
random_state=1,
)
print("x.shape =",x.shape)
print("label.shape = ",label.shape)
print("np.unique(label) =",np.unique(label))
print(set(label))
# 设置随机数种子
rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
# 对生成的特征数据添加一组均匀分布噪声https://blog.csdn.net/vicdd/article/details/52667709
x += 2*rng.uniform(size=x.shape)
# 标签类别数
unique_label = set(label)
# 根据标签类别数设置颜色
print(np.linspace(0,1,len(unique_label)))
colors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0,1,len(unique_label)))
print(colors)
# 绘制模拟数据的散点图
for k,col in zip(unique_label , colors):
x_k=x[label==k]
plt.plot(x_k[:,0],x_k[:,1],'o',markerfacecolor=col,markeredgecolor="k",
markersize=14)
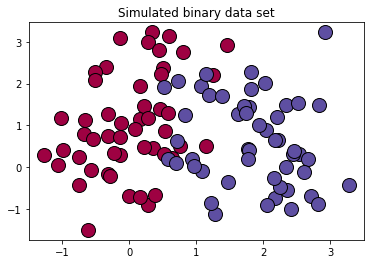
plt.title('Simulated binary data set')
plt.show();
结果:
x.shape = (100, 2)
label.shape = (100,)
np.unique(label) = [0 1]
{0, 1}
[0. 1.]
[[0.61960784 0.00392157 0.25882353 1. ]
[0.36862745 0.30980392 0.63529412 1. ]]
复习
# 复习
mylabel = label.reshape((-1,1))
data = np.concatenate((x,mylabel),axis=1)
print(data.shape)
结果:
(100, 3)
8 划分数据集
offset = int(x.shape[0]*0.7)
x_train, y_train = x[:offset],label[:offset].reshape((-1,1))
x_test, y_test = x[offset:],label[offset:].reshape((-1,1))
print(x_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape)
print(y_test.shape)
结果:
(70, 2)
(70, 1)
(30, 2)
(30, 1)
9 训练
cost_list, params, grads = logistic_train(x_train, y_train, 0.01, 1000)
print(params['b'])
结果:
epoch 0 cost 0.693147
epoch 100 cost 0.568743
epoch 200 cost 0.496925
epoch 300 cost 0.449932
epoch 400 cost 0.416618
epoch 500 cost 0.391660
epoch 600 cost 0.372186
epoch 700 cost 0.356509
epoch 800 cost 0.343574
epoch 900 cost 0.332689
-0.6646648941379839
10 准确率计算
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,classification_report
y_pred = predict(x_test,params)
print("y_pred = ",y_pred)
print(y_pred)
print(y_test.shape)
print(accuracy_score(y_pred,y_test)) #不需要都是1维的,貌似会自动squeeze()
print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred))
结果:
y_pred = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
(30, 1)
0.9333333333333333
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.92 0.92 0.92 12
1 0.94 0.94 0.94 18 accuracy 0.93 30
macro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 30
weighted avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 30
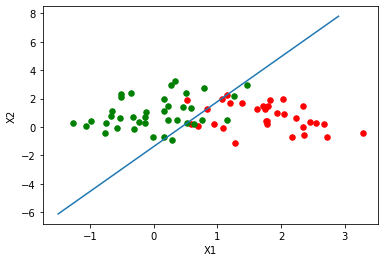
11 绘制逻辑回归决策边界
### 绘制逻辑回归决策边界
def plot_logistic(X_train, y_train, params):
# 训练样本量
n = X_train.shape[0]
xcord1,ycord1,xcord2,ycord2 = [],[],[],[]
# 获取两类坐标点并存入列表
for i in range(n):
if y_train[i] == 1:
xcord1.append(X_train[i][0])
ycord1.append(X_train[i][1])
else:
xcord2.append(X_train[i][0])
ycord2.append(X_train[i][1])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,s = 30,c = 'red')
ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,s = 30,c = 'green')
# 取值范围
x =np.arange(-1.5,3,0.1)
# 决策边界公式
y = (-params['b'] - params['W'][0] * x) / params['W'][1]
# 绘图
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlabel('X1')
plt.ylabel('X2')
plt.show()
plot_logistic(x_train, y_train, params)
结果:
11 sklearn实现
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0).fit(x_train,y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print(y_pred)
accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
结果:
[0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0]
0.9333333333333333
chapter3——逻辑回归手动+sklean版本的更多相关文章
- numpy+sklearn 手动实现逻辑回归【Python】
逻辑回归损失函数: from sklearn.datasets import load_iris,make_classification from sklearn.model_selection im ...
- 逻辑回归原理_挑战者飞船事故和乳腺癌案例_Python和R_信用评分卡(AAA推荐)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&a ...
- 逻辑回归算法的原理及实现(LR)
Logistic回归虽然名字叫"回归" ,但却是一种分类学习方法.使用场景大概有两个:第一用来预测,第二寻找因变量的影响因素.逻辑回归(Logistic Regression, L ...
- Theano3.3-练习之逻辑回归
是官网上theano的逻辑回归的练习(http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/logreg.html#logreg)的讲解. Classifying MNIST digits ...
- PRML读书会第四章 Linear Models for Classification(贝叶斯marginalization、Fisher线性判别、感知机、概率生成和判别模型、逻辑回归)
主讲人 planktonli planktonli(1027753147) 19:52:28 现在我们就开始讲第四章,第四章的内容是关于 线性分类模型,主要内容有四点:1) Fisher准则的分类,以 ...
- Spark Mllib逻辑回归算法分析
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/3816289.html 本文以spark 1.0.0版本MLlib算法为准进行分析 一.代码结构 逻辑回归 ...
- Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 机器学习算法与Pyth ...
- 学习Machine Leaning In Action(四):逻辑回归
第一眼看到逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)这个词时,脑海中没有任何概念,读了几页后,发现这非常类似于神经网络中单个神经元的分类方法. 书中逻辑回归的思想是用一个超平面将数据集分为两部 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week3(逻辑回归&正则化参数)
Logistic Regression 一.内容概要 Classification and Representation Classification Hypothesis Representatio ...
随机推荐
- Orcale
oracleoracle中不存在引擎的概念,数据处理大致可以分成两大类:联机事务处理OLTP(on-line transaction processing).联机分析处理OLAP(On-Line An ...
- CS5265/CS5267设计替代VL102+PS176 Typec转HDMI2.0音视频芯片
目前USB TYPEC转HDMI2.0转换方案或者TYPEC转HDMI2.0转换器方案都是用PS176加一个PD芯片来实现,其中VL102是一颗PD协议芯片,PS176是一款DP转HDMI2.0视频解 ...
- 【MySQL作业】SELECT 数据查询——美和易思MySQL运算符应用习题
点击打开所使用到的数据库>>> 1.查询指定姓名的客户(如"张晓静")的地址和电话号码. select address 地址, phone 电话号码 from c ...
- vue3获取当前路由
正解 使用useRouter: // router的 path: "/user/:uid" <template> <div>user</div> ...
- JSON生成Java实体类
https://www.bejson.com/json2javapojo/new/ 至于效果怎么样,自己试一下就知道了
- JS 数组的基本使用和案例
知识点汇总: 数组:就是一组数据的集合,存储在单个变量的方式 自变量创建数组 var 数组名字 = ['a','b'] // []里面的是数据的元素,可为任意字符类型 利用new创建数组 var 数组 ...
- Word合并多文档
图片如果损坏,点击链接: https://www.toutiao.com/i6489785099528176142/ 很多时候,我们需要将两个或者多个文档的内容,放到一起,而最直接的办法就是将多个文档 ...
- 学习笔记--Java中的变量
Java中的变量 /** * 关于 Java 语言当中的变量: * * 1. 什么是变量? * - 变量的本质上来说是内存空间,这块空间有(数据类型.名字.字面值) * - 变量包括三部分:数据类型. ...
- IK 分词器
目录 IK 分词器-介绍 IK 分词器-安装 环境准备:Maven 安装 IK 分词器 IK 分词器-使用 IK 分词器-介绍 现有问题:ES 默认对中文分词并不友好,实际上是把中文进行了每个字的分词 ...
- “老”的Flexbox和“新”的Flexbox
本文由大漠根据Chris Coyier的<"Old" Flexbox and "New" Flexbox>所译,整个译文带有我们自己的理解与思想,如 ...
