SpringBoot中Async异步方法和定时任务介绍
1.功能说明
Spring提供了Async注解来实现方法的异步调用。
即当调用Async标识的方法时,调用线程不会等待被调用方法执行完成即返回继续执行以下操作,而被调用的方法则会启动一个独立线程来执行此方法。
这种异步执行的方式通常用于处理接口中不需要返回给用户的数据处理。比如当注册的时候,只需要将用户信息返回用户,而关于信息的保存操作可以使用异步执行。
Spring提供了Scheduled注解来实现定时任务的功能。
在异步方法和定时任务功能中都是开发这自己定义需要执行的方法,然后交给Spring容器管理线程,并执行相应的方法。在使用异步方法和定时任务的时候需要特别注意的是线程池的配置以及任务中异常的处理。下面对这两个功能进行简单介绍。
2.关键注解和配置接口
功能开启注解:
EnableAsync和EnableScheduling
通过在Spring的配置类中添加这两个注解来开启Spring的异步方法和定时任务的功能。
异步方法标识注解Async,其定义为:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Async {
String value() default "";
}
在注解定义中可以看到此注解可以用于type和method,当此注解用于类的时候,表示此类中的所有方法都为异步方法。此注解中的value属性可用于指定执行此异步方法的线程池。线程池的具体确定方法下面具体分析。
定时任务标识注解Scheduled,定义如下:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled {
定时任务
String cron() default "";
String zone() default "";
//上次执行结束到下次执行开始
long fixedDelay() default -1;
String fixedDelayString() default "";
上次执行开始到本次执行开始
long fixedRate() default -1;
fixedRate或者fixedDelay的时候第一次的延迟时间
long initialDelay() default -1;
}
3.Spring线程池的选择和自定义配置线程池
在项目中我们通常不会自己手动创建线程,而是通过统一的线程池来执行task或者异步方法,使用这种方法来避免多人团队中由于自定义线程导致的资源耗尽的问题。在自定义线程池之前首先要了解Spring在执行异步任务或者方法的时候是怎么选择线程池的。
3.1 Async对于线程池的选择顺序
Async线程池的选择顺序如下图所示:
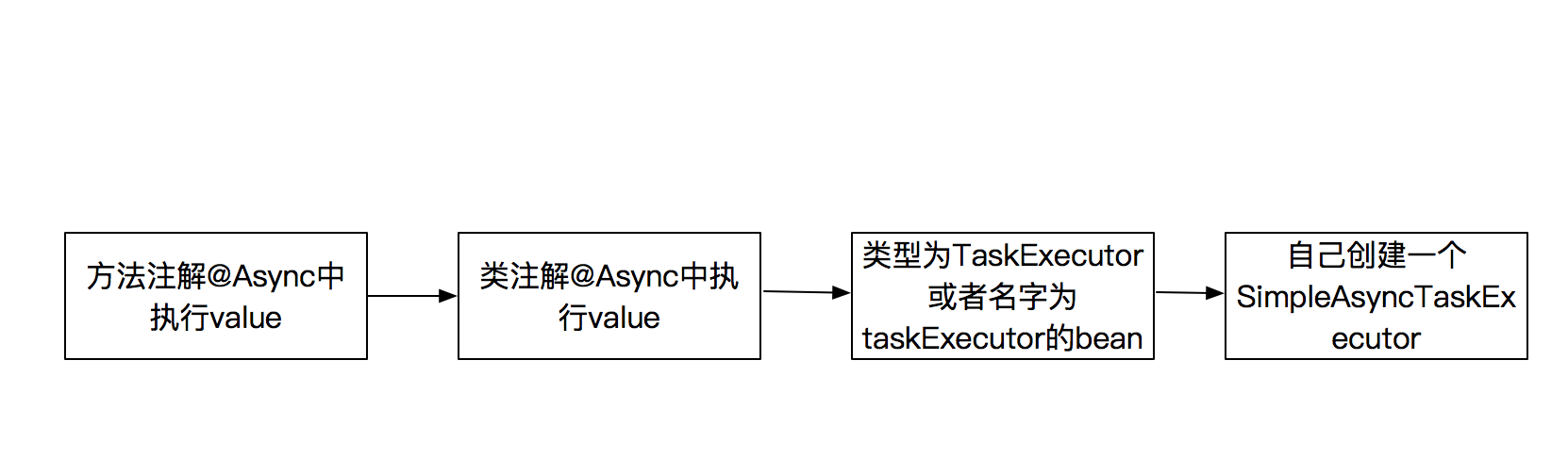
Spring在执行async标识的异步方法的时候首先会在Spring的上下文中搜索类型为TaskExecutor或者名称为“taskExecutor”的bean,当可以找到的时候,就将任务提交到此线程池中执行。当不存在以上线程池的时候,Spring会手动创建一个SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor执行异步任务。
另外当标识async注解的时候指定了,value值,Spring会使用指定的线程池执行。比如以下:
@Async(value = "asyncTaskThreadPool")
这个时候Spring会去上下文中找名字为asyncTaskThreadPool的bean,并执行异步任务,找不到,会抛出异常。
3.2 Scheduled对于线程池的选择顺序
Scheduled对于线程池的选择顺序如下图所示:
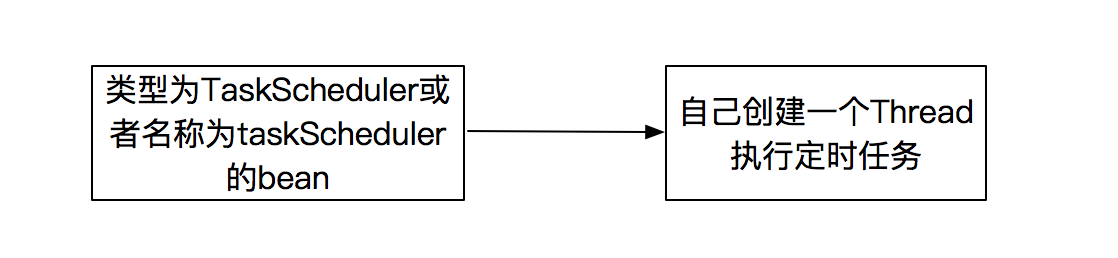
当Spring执行定时任务的时候,首先会在上下文中找类型为TaskScheduler或者名称为taskScheduler的bean,找不到的时候会手动创建一个线程执行此task。
3.3 自定义线程池和异常处理
在了解了Spring对于线程池的选择后,我们需要自定义线程池。自定义Async线程池有三种方式。
方法一:首先配置接口,重写获取线程池的方法。
配置Async方法的线程池需要继承AsyncConfigurerSupport类,或者实现AsyncConfigurer接口,并重写getAsyncExecutor方法,代码如下:
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class ThreadPoolBeanFactory extends AsyncConfigurerSupport{
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncTaskThreadPool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
asyncTaskThreadPool.setCorePoolSize(100);
asyncTaskThreadPool.setMaxPoolSize(200);
asyncTaskThreadPool.setQueueCapacity(11);
asyncTaskThreadPool.setThreadFactory(new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicLong index = new AtomicLong(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "Async-override-task-pool-thread-" + index.getAndIncrement());
}
});
asyncTaskThreadPool.initialize();
return asyncTaskThreadPool;
}
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
//返回值为void的异步方法不会传递异常,当方法中出现异常的时候只会打印日志,重写此方法来自定义异常处理方法
return null;
}
}
这种定义的方法缺点是没有定义bean。
方法二:自定义相应类型的线程池bean。
第二种方法是基于Spring对线程选择的原理来实现的,定义一个类型为TaskExecutor的bean,定义方式如下:
@Bean
public TaskExecutor asyncTaskThreadPool() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor asyncTaskThreadPool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
asyncTaskThreadPool.setCorePoolSize(100);
asyncTaskThreadPool.setMaxPoolSize(200);
asyncTaskThreadPool.setThreadFactory(new ThreadFactory() {
private final AtomicLong index = new AtomicLong(1);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "Async-task-pool-thread-" + index.getAndIncrement());
}
});
// asyncTaskThreadPool.initialize();//当为bean的时候不需要调用此方法,装载容器的时候回自动调用
return asyncTaskThreadPool;
}
以上两种方式定义线程池的时候在定义异步方法可以不执行线程池。定义如下:
@Async
public void test(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
此时Spring会自动使用以上定义的线程池执行此方法。使用以上两种配置输出结果依次是:
Async-task-pool-thread-1
Async-task-override-pool-thread-1
方法三 在Async注解中执行线程池名称
异步任务定义如下:
@Async(value = "asyncTaskThreadPool")
public void asyncTask2() {
LOGGER.info("AsyncTask2 start.");
LOGGER.info(Thread.currentThread().getName());
LOGGER.info("AsyncTask2 finished.");
}
此时Spring会在上下文中找名称为asyncTaskThreadPool的线程池来执行此任务。
类似的可以自定义Scheduled的线程池,需要实现的配置接口为:SchedulingConfigurer。方法类似。
4.Async返回操作结果
异步任务可以通过定义返回类型为Future来实现返回值,定义如下:
@Async
public Future<String> asyncTaskWithResult() {
LOGGER.info("AsyncTaskWithResult start.");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 10);
} catch (Exception e) {
return new AsyncResult<>("error" + e.getMessage());
}
LOGGER.info("AsyncTaskWithResult finished.");
return new AsyncResult<>("success");
}
5.编写单元测试测试功能
单元测试代码如下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class AsyncApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private AsyncTaskService asyncTaskService;
@Test
public void asyncTest() throws Exception{
Future<String> future = asyncTaskService.asyncTaskWithResult();
while (!future.isDone()) {
System.out.println("Wait asyncTaskWithResult.");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
System.out.println("asyncTaskWithResult result is:" + future.get());
System.out.println("asyncTask finished.");
}
}
输出内容如下:
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
Wait asyncTaskWithResult.
AsyncTaskWithResult finished.
asyncTaskWithResult result is:success
asyncTask finished.
SpringBoot中Async异步方法和定时任务介绍的更多相关文章
- 定时任务-----Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务----http://www.cnblogs.com/lirenqing/p/6596557.html
Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务---http://www.cnblogs.com/lirenqing/p/6596557.html 已经验证的方案: pom文件加入依赖 < ...
- SpringBoot中使用@Scheduled创建定时任务
SpringBoot中使用@Scheduled创建定时任务 定时任务一般会在很多项目中都会用到,我们往往会间隔性的的去完成某些特定任务来减少服务器和数据库的压力.比较常见的就是金融服务系统推送回调,一 ...
- SpringBoot中使用Scheduling执行定时任务
SpringBoot自带的 Schedule,可以将它看成一个轻量级的Quartz,而且使用起来比Quartz简单许多 以下任务都是在单线程下执行的 第一步 创建SpringBoot项目 第二步 外汇 ...
- SpringBoot中使用task实现定时任务
定时任务实现的几种方式: Timer:这是java自带的java.util.Timer类,这个类允许你调度一个java.util.TimerTask任务.使用这种方式可以让你的程序按照某一个频度执行, ...
- Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务
在开发中,定时任务是常见的功能,在spring boot 下开发定时任务其实很简单,具体代码如下: 1.配置依赖包pom.xml 由于默认的maven仓库经常访问不了,这里采用了阿里云的maven仓库 ...
- Springboot中定时任务的使用
在springboot中已经集成了定时任务,只需要在启动类上加注解@EnableScheduling即可 例如: 添加类加上@Component注解,添加方法加上@Scheduler即可
- SpringBoot中并发定时任务的实现、动态定时任务的实现(看这一篇就够了)
原创不易,如需转载,请注明出处https://www.cnblogs.com/baixianlong/p/10659045.html,否则将追究法律责任!!! 一.在JAVA开发领域,目前可以通过以下 ...
- 在SpringBoot中配置定时任务
前言 之前在spring中使用过定时任务,使用注解的方式配置很方便,在SpringBoot中的配置基本相同,只是原来在spring中的xml文件的一些配置需要改变,在SpringBoot中也非常简单. ...
- SpringBoot 中常用注解@PathVaribale/@RequestParam/@GetMapping介绍
SpringBoot 中常用注解@PathVaribale/@RequestParam/@GetMapping介绍 本篇博文将介绍几种如何处理url中的参数的注解@PathVaribale/@Requ ...
随机推荐
- 一篇文章读懂JSON
什么是json? W3C JSON定义修改版: JSON 指的是 JavaScript 对象表示法(JavaScript Object Notation) JSON 是轻量级的文本数据交换格式,并不是 ...
- LeetCode Valid Anagram (简单题)
题意: 给出两个字符串s和t,判断串t是否为s打乱后的串. 思路: 如果返回的是true,则两个串的长度必定相等,所有字符出现的次数一样.那么可以统计26个字母的次数来解决,复杂度O(n).也可以排序 ...
- AOJ 558 Cheese(bfs)
题意:网格图,老鼠吃奶酪,吃完奶酪体力值会增加,只能吃硬度不大于体力值的,问最小步数. 思路:按硬度从小到大的吃起,依次求最短路. 我用曼哈顿距离估价的A*,和普通bfs的time没区别啊,还把优先级 ...
- python_23_tuple
#元组只能统计和获取下表,不能插入之类的.元组和列表差不多,也是存一组数,只是它一旦创建,便不能再修改,所以又叫只读列表 names=('QiZhiguang','LiuGuannan','Liang ...
- CopyOnWriteArrayList分析——能解决什么问题
CopyOnWriteArrayList主要可以解决的问题是并发遍历读取无锁(通过Iterator) 对比CopyOnWriteArrayList和ArrayList 假如我们频繁的读取一个可能会变化 ...
- 1.redis 安装
1.https://redis.io/download. 2. $ wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-3.2.9.tar.gz $ .tar.g ...
- jquery淡入淡出轮播图
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 散列表的ASL计算
题目: 已知关键字序列为{30,25,72,38,8,17,59},设散列表表长为15.散列函数是H(key)=key MOD 13,处理冲突的方法为二次探测法Hi= ( H(key) + di )m ...
- 洛谷P3374树状数组1
下有彩蛋(from https://www.cnblogs.com/wuwangchuxin0924/p/5921130.html)树状数组的blog写的最好的是这位//https://www.cnb ...
- PAT 乙级 1024
题目 题目地址:PAT 乙级 1024 题解 模拟题,重点需要考虑到各种不同情况:简单来说一下: 因为输入格式固定,所以把不同的部分分别存储和处理可以在很大程度上简化运算:其中需要考虑最多的就是小数部 ...
