Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#(转载)
Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#
The primary problems that arise when rendering semi-transparent 3d objects in Windows Presentation Foundation have to do with false z-buffer occlusions. Specifically, when a transparent surface or polygon is rendered, it sets the z-buffer depth values to block objects that are behind it from being rendered, even though they should show through the transparent layer.
In WPF with C#, the z-buffer is not accessible. So, it can not be disabled during transparent rendering. Instead, we must render the transparent objects last so that they are layered over the rest of the scene and the objects behind them show through.
Below, I have a program for the single code file that I used to generate the spinning, transparent tetrahedron shown above. The C# project that I used is a simple Console Application project with the libraries PresentationCore,PresentationFramework, and WindowsBase references added to it as I showed in a prior post: Using WPF in a C# Console Application. The Main() function creates the Window for the program and calls TransparentScene() to do all of the rendering.
Inside the function TransparentScene(), I create the camera, the light, the animated rotation transformation, the tetrahedron geometry, and then use that geometry to specify three tetrahedrons. The first tetrahedron is called the Inner Tetrahedronbecause it is scaled to fit inside the others. The second tetrahedron is called the Outer Tetrahedron and is semi-transparent. The third tetrahedron is also part of the Outer Tetrahedron, but consists of the opaque back faces. Note that it only makes sense to render the back faces because the front faces are semi-transparent. Otherwise, the back would not be visible.
At the end the code, I use the following lines to add the tetrahedrons to the scene:
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qBackGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qInnerGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qOuterGeometry);
Notice that the transparent “Outer Geometry” layer is added last. This is necessary to avoid false occlusions.
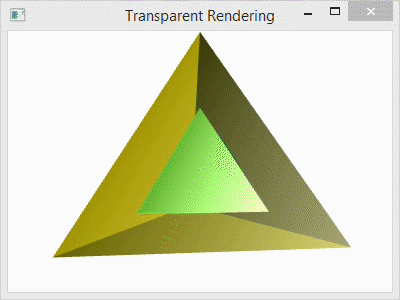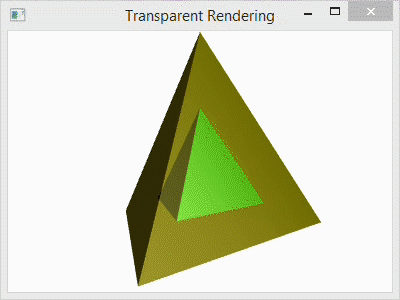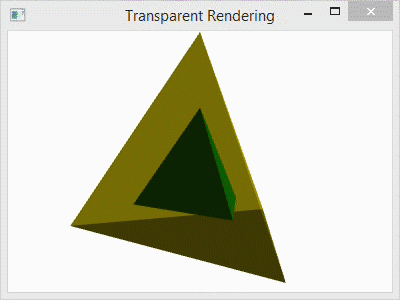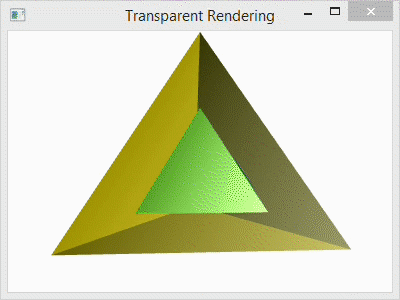
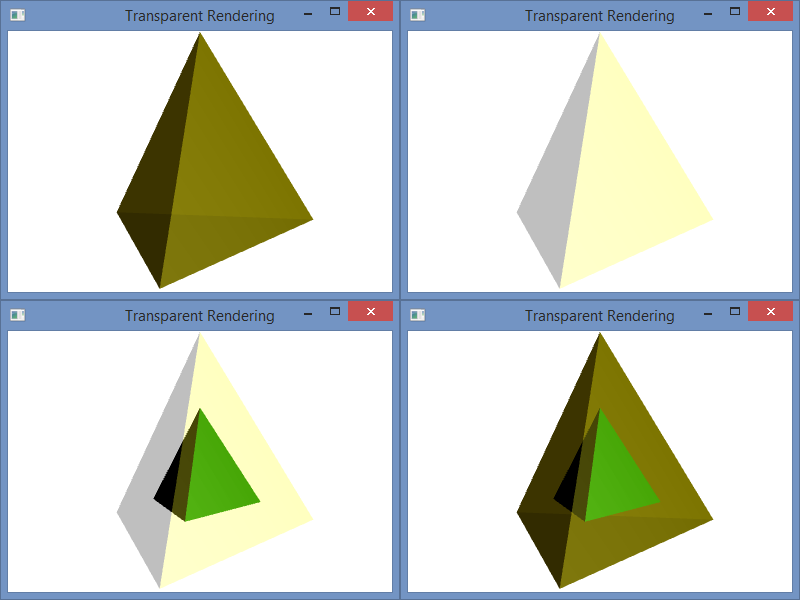
For comparison, I have included the image below with four different arrangements. The first (top-left) shows the scene with the transparent outer layer added before the inner and after the back. The second (top-right) shows the transparent outer layer added before both the inner and the back layers. The third (bottom-left) shows the transparent layer added before the back and after the inner layer. The last (bottom-right) shows the scene with the transparent layer added last as it is in the code.
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Media3D;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation; namespace WpfTransparent {
class Program {
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args) {
Window qWindow = new Window();
qWindow.Title = "Transparent Rendering";
qWindow.Width = 400;
qWindow.Height = 300;
qWindow.Content = TransparentScene();
qWindow.ShowDialog();
} static Viewport3D TransparentScene() {
// Define the camera
PerspectiveCamera qCamera = new PerspectiveCamera();
qCamera.Position = new Point3D(0, .25, 2.25);
qCamera.LookDirection = new Vector3D(0, -.05, -1);
qCamera.UpDirection = new Vector3D(0, 1, 0);
qCamera.FieldOfView = 60; // Define a lighting model
DirectionalLight qLight = new DirectionalLight();
qLight.Color = Colors.White;
qLight.Direction = new Vector3D(-0.5, -0.25, -0.5); // Define the animated rotation transformation
RotateTransform3D qRotation =
new RotateTransform3D(new AxisAngleRotation3D(new Vector3D(0, 1, 0), 1));
DoubleAnimation qAnimation = new DoubleAnimation();
qAnimation.From = 1;
qAnimation.To = 361;
qAnimation.Duration = new Duration(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5000));
qAnimation.RepeatBehavior = RepeatBehavior.Forever;
qRotation.Rotation.BeginAnimation(AxisAngleRotation3D.AngleProperty, qAnimation); // Define the geometry
const double kdSqrt2 = 1.4142135623730950488016887242097;
const double kdSqrt6 = 2.4494897427831780981972840747059;
// Create a collection of vertex positions
Point3D[] qaV = new Point3D[4]{
new Point3D(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
new Point3D(2.0 * kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, 0.0),
new Point3D(-kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, -kdSqrt6 / 3.0),
new Point3D(-kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, kdSqrt6 / 3.0)};
Point3DCollection qPoints = new Point3DCollection();
// Designate Vertices
// My Scheme (0, 1, 2), (1, 0, 3), (2, 3, 0), (3, 2, 1)
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i) {
if ((i/3) % 2 == 0) {
qPoints.Add(qaV[i%4]);
} else {
qPoints.Add(qaV[(i*3)%4]);
}
}
// Designate Triangles
Int32Collection qTriangles = new Int32Collection();
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i ) {
qTriangles.Add(i);
}
Int32Collection qBackTriangles = new Int32Collection();
// Designate Back Triangles in the opposite orientation
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i) {
qBackTriangles.Add(3 * (i / 3) + (2 * (i % 3) % 3));
} // Inner Tetrahedron: Define the mesh, material and transformation.
MeshGeometry3D qFrontMesh = new MeshGeometry3D();
qFrontMesh.Positions = qPoints;
qFrontMesh.TriangleIndices = qTriangles;
GeometryModel3D qInnerGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qInnerGeometry.Geometry = qFrontMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffGreen =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 0, 128, 0)));
SpecularMaterial qSpecWhite = new
SpecularMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 255, 255, 255)), 30.0);
MaterialGroup qInnerMaterial = new MaterialGroup();
qInnerMaterial.Children.Add(qDiffGreen);
qInnerMaterial.Children.Add(qSpecWhite);
qInnerGeometry.Material = qInnerMaterial;
// *** Transformation ***
ScaleTransform3D qScale = new ScaleTransform3D(new Vector3D(.5, .5, .5));
Transform3DGroup myTransformGroup = new Transform3DGroup();
myTransformGroup.Children.Add(qRotation);
myTransformGroup.Children.Add(qScale);
qInnerGeometry.Transform = myTransformGroup; // Outer Tetrahedron (semi-transparent) : Define the mesh, material and transformation.
GeometryModel3D qOuterGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qOuterGeometry.Geometry = qFrontMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffTransYellow =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(64, 255, 255, 0)));
SpecularMaterial qSpecTransWhite =
new SpecularMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(128, 255, 255, 255)), 30.0);
MaterialGroup qOuterMaterial = new MaterialGroup();
qOuterMaterial.Children.Add(qDiffTransYellow);
qOuterMaterial.Children.Add(qSpecTransWhite);
qOuterGeometry.Material = qOuterMaterial;
// *** Transformation ***
qOuterGeometry.Transform = qRotation; // Outer Tetrahedron (solid back) : Define the mesh, material and transformation.
MeshGeometry3D qBackMesh = new MeshGeometry3D();
qBackMesh.Positions = qPoints;
qBackMesh.TriangleIndices = qBackTriangles;
GeometryModel3D qBackGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qBackGeometry.Geometry = qBackMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffBrown =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 200, 175, 0)));
qBackGeometry.Material = qDiffBrown;
// *** Transformation ***
qBackGeometry.Transform = qRotation; // Collect the components
Model3DGroup qModelGroup = new Model3DGroup();
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qLight);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qBackGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qInnerGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qOuterGeometry);
ModelVisual3D qVisual = new ModelVisual3D();
qVisual.Content = qModelGroup;
Viewport3D qViewport = new Viewport3D();
qViewport.Children.Add(qVisual);
qViewport.Camera = qCamera; return qViewport;
}
}
}
Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#(转载)的更多相关文章
- WPF拖动总结[转载]
WPF拖动总结 这篇博文总结下WPF中的拖动,文章内容主要包括: 1.拖动窗口 2.拖动控件 Using Visual Studio 2.1thumb控件 2.2Drag.Drop(不连续,没有中 ...
- WPF阴影效果(DropShadowEffect)(转载)
<TextBlock Text="阴影效果" FontSize="32"> <TextBlock.Effect> <DropSha ...
- WPF 3D 知识点大全以及实例
引言 现在物联网概念这么火,如果监控的信息能够实时在手机的客服端中以3D形式展示给我们,那种体验大家可以发挥自己的想象. 那生活中我们还有很多地方用到这些,如上图所示的Kinect 在医疗上的应用,当 ...
- 3D开发基础知识和简单示例
引言 现在物联网概念这么火,如果监控的信息能够实时在手机的客服端中以3D形式展示给我们,那种体验大家可以发挥自己的想象. 那生活中我们还有很多地方用到这些,如上图所示的Kinect 在医疗上的应用,当 ...
- 优化WPF 3D性能
Maximize WPF 3D Performance .NET Framework 4.5 As you use the Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF ...
- WPF 3D 常用类(1)
原文:WPF 3D 常用类(1) 几何数据相关类 Geometry3D 抽象类, 用于定义物体的几何数据, 可用于计算HitTest和BoundingBox MeshGeometry3D Geomet ...
- WPF中反转3D列表项
原文:WPF中反转3D列表项 WPF中反转3D列表项 周银辉记得在苹果电脑中有一个很酷的 ...
- WPF 3D 小小小小引擎 - ·WPF 3D变换应用
原文:WPF 3D 小小小小引擎 - ·WPF 3D变换应用 WPF可以提供的3D模型使我们可以轻松地创建3D实体,虽然目前来看还很有一些性能上的问题,不过对于一些简单的3D应用应该是可取的,毕竟其开 ...
- WPF换肤之八:创建3D浏览效果
原文:WPF换肤之八:创建3D浏览效果 上节中,我们展示了WPF中的异步以及界面线程交互的方式,使得应用程序的显示更加的流畅.这节我们主要讲解如何设计一个具有3D浏览效果的天气信息浏览器. 效果显示 ...
随机推荐
- 利用Dnspod api批量更新添加DNS解析【python脚本】 - 推酷
利用Dnspod api批量更新添加DNS解析[python脚本] - 推酷 undefined
- yii快速入门与参考
Yii 权威指南 http://www.yiichina.com/guide/ http://www.yiiframework.com/doc/guide/1.1/zh_cn/ Ⅰ.基本概念一.入口文 ...
- Junit初体验
JUnit是一个开源的Java单元测试框架,由 Erich Gamma 和 Kent Beck 开发完成. 主要是为了方便开发人员在自己开发的过程中能够及时的发现和解决bug用的,一方面自己可以通过单 ...
- 把谷歌等webkit内核浏览器变为输入文本编辑器的方法
只需要在地址栏输入 data:text/html, <html contenteditable> 回车后即可看到效果
- 系统的启动模式(启动级别)的改动---使用upstart启动机制的
/********************************************************************* * Author : Samson * Date ...
- JAVA中toString方法的作用(转)
因为它是Object里面已经有了的方法,而所有类都是继承Object,所以“所有对象都有这个方法”. 它通常只是为了方便输出,比如System.out.println(xx),括号里面的“xx”如果不 ...
- Performance Tuning of Spring/Hibernate Applications---reference
http://java.dzone.com/articles/performance-tuning For most typical Spring/Hibernate enterprise appli ...
- 聊聊 iOS 中的网络加密
介绍下 公司的接口一般会两种协议的,一种HTTP,一种HTTPS的,HTTP 只要请求,服务器就会响应,如果我们不对请求和响应做出加密处理,所有信息都是会被检测劫持到的,是很不安全的,客户端加密可以使 ...
- MySQL查询
DQL 操作 DQL 数据查询语言(重要) 数据库执行DQL语句不会对数据做出任何改变,而是让数据库发送结果集给客户端. 查询返回的结果是一张虚拟表. 查询关键字:SELECT ...
- js中跨域请求原理及2种常见解决方案
一.同源策略: 说到跨域请求,首先得说说同源策略: 1995年,同源政策是由 Netscape 公司引入浏览器的.目前,所有浏览器都实行了这个政策. 同源策略是浏览器的一种安全策略,所谓同源是指,域名 ...
