Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发——注解
源码:https://gitee.com/kszsa/dchart
一, AspectJ的概述:
AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,它扩展了Java语言。AspectJ定义了AOP语法所以它有一个专门的编译器用来生成遵守Java字节编码规范的Class文件。
Spring为了简化自身的AOP的开发,将AspectJ拿过来作为Spring自身一个AOP的开发.
二, Spring AspectJ开发实例
2.1 开发所需jar包
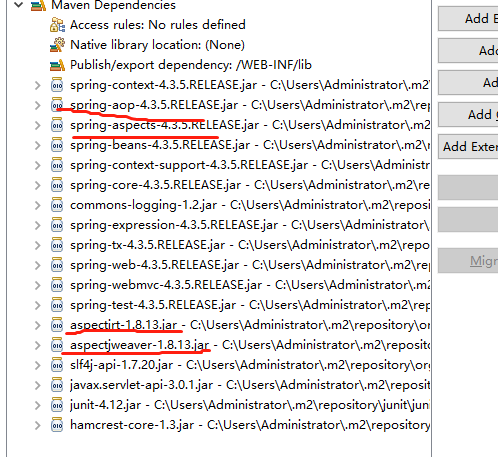
maven中相关包引入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- aspectJ依赖包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>${aspectj.version}</version>
</dependency>
2.2 AspectJ 注解开发规范
2.2.1 AspectJ的切入点:
//统一管理切入点的表达式.
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.find(..))")
private void myPointcut1(){}//这个类没有实际用途, 只是为了@Pointcut 注解
2.2.2 @AspectJ提供不同的通知类型
@Before 前置通知,相当于BeforeAdvice
在执行目标方法之前完成一个操作,获得到切入点信息.
@Before(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.save(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("前置通知============"+joinPoint);
}
@AfterReturning 后置通知,相当于AfterReturningAdvice
在目标方法执行之后完成一个操作,获得方法的返回值.
@AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.update(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturn(Object result){
System.out.println("后置通知============"+result);
}
@Around 环绕通知,相当于MethodInterceptor
在目标方法执行的前和执行后完成一个操作,阻止目标方法执行.
@Around(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.delete(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前通知==========");
Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕后通知==========");
return obj;
}
@AfterThrowing抛出通知,相当于ThrowAdvice
在目标方法出现异常的时候,完成一个操作.获得异常信息.
@AfterThrowing(value="CustomerServiceAspect.myPointcut1()",throwing="e")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable e){
System.out.println("异常抛出通知========="+e.getMessage());
}
@After 最终final通知,不管是否异常,该通知都会执行
在目标方法任何情况下都会执行的操作.相当于finally中的代码.
@After(value="CustomerServiceAspect.myPointcut1()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知===========");
}
2.2.3 通过配置启用@AspectJ切面
1、开启AspectJ的自动代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 开启AspectJ自动代理 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
2、对应的切面类添加注解
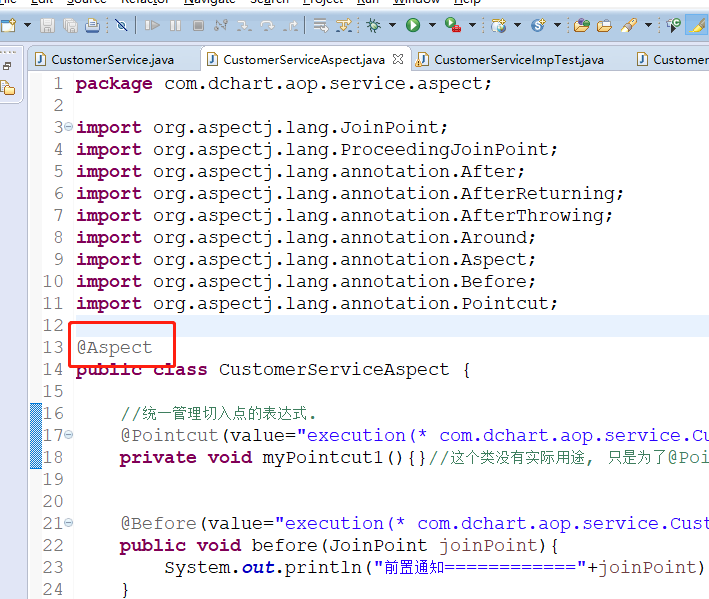
2.2.4 Aspect和Advisor的区别:
Advisor :传统的切面.传统切面一般都是由一个切入点和一个通知的组合.
Aspect :真正意义上的切面.由多个切入点和多个通知的组合.
2.2.5 在通知中通过value属性定义切点
通过execution函数,可以定义切点的方法切入
语法:
execution(<访问修饰符>?<返回类型><方法名>(<参数>)<异常>)
例如
匹配所有类public方法 execution(public * *(..))
匹配指定包下所有类方法 execution(* cn.itcast.dao.*(..)) 不包含子包
execution(* cn.itcast.dao..*(..)) ..*表示包、子孙包下所有类
匹配指定类所有方法 execution(* cn.itcast.service.UserService.*(..))
匹配实现特定接口所有类方法 execution(* cn.itcast.dao.GenericDAO+.*(..))
匹配所有save开头的方法 execution(* save*(..))
2.3 Spring AspctJ 基于注解模式的开发例子
定义接口CustomerService.java
package com.dchart.aop.service;
public interface CustomerService {
public void save();
public Integer update();
public void delete();
public void find();
}
接口实现
CustomerServiceImp.java
package com.dchart.aop.service.imp;
import com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService;
public class CustomerServiceImp implements CustomerService {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("保存客户...");
}
@Override
public Integer update() {
System.out.println("修改客户...");
return 100;
}
@Override
public void delete() {
System.out.println("删除客户...");
}
@Override
public void find() {
System.out.println("查询客户...");
// int d = 1 / 0;
}
}
编写切面类
CustomerServiceAspect.java
package com.dchart.aop.service.aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Aspect
public class CustomerServiceAspect { //统一管理切入点的表达式.
@Pointcut(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.find(..))")
private void myPointcut1(){}//这个类没有实际用途, 只是为了@Pointcut 注解 @Before(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.save(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("前置通知============"+joinPoint);
} @AfterReturning(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.update(..))",returning="result")
public void afterReturn(Object result){
System.out.println("后置通知============"+result);
} @Around(value="execution(* com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService+.delete(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前通知==========");
Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕后通知==========");
return obj;
} @AfterThrowing(value="CustomerServiceAspect.myPointcut1()",throwing="e")
public void afterThrowing(Throwable e){
System.out.println("异常抛出通知========="+e.getMessage());
} @After(value="CustomerServiceAspect.myPointcut1()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("最终通知===========");
} }
单元测试类CustomerServiceImpTest.java
package com.dchart.aop.service.imp; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import com.dchart.aop.service.CustomerService; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring_aop.xml")
public class CustomerServiceImpTest { @Resource(name="customerService")
private CustomerService customerService; @Test
public void test() {
customerService.save();
customerService.update();
customerService.delete();
customerService.find();
} }
Spring 配置文件:spring_aop.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 开启AspectJ自动代理 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
<!-- 目标对象 -->
<bean id="customerService" class="com.dchart.aop.service.imp.CustomerServiceImp" />
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<bean id="myAspectAnno" class="com.dchart.aop.service.aspect.CustomerServiceAspect" /> </beans>
运行结果:
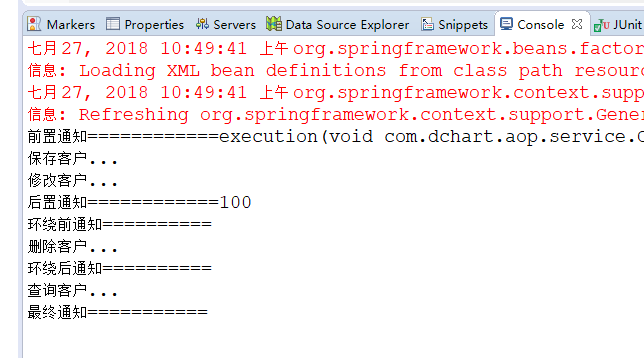
源码:https://gitee.com/kszsa/dchart
参考地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wang-meng/p/5641687.html
Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发——注解的更多相关文章
- [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结二:Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发.
前言: 在上一篇中: [Spring框架]Spring AOP基础入门总结一. 中 我们已经知道了一个Spring AOP程序是如何开发的, 在这里呢我们将基于AspectJ来进行AOP 的总结和学习 ...
- Spring 基于 AspectJ 的 AOP 开发
Spring 基于 AspectJ 的 AOP 开发 在 Spring 的 aop 代理方式中, AspectJ 才是主流. 1. AspectJ 简介 AspectJ 是一个基于 java 语言的 ...
- (转)Spring使用AspectJ进行AOP的开发:注解方式
http://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/69790950 Spring使用AspectJ进行AOP的开发:注解方式 之前我已讲过Sprin ...
- Spring基于AspectJ的AOP的开发之AOP的相关术语
1. Joinpoint(连接点) -- 所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点.在spring中,这些点指的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点(任何一个方法都可以称为连接点) 2. Pointc ...
- Spring整合AspectJ的AOP
学而时习之,不亦说乎! --<论语> 看这一篇之前最好先看前面关于AOP的两篇. http://www.cnblogs.com/z ...
- 利用基于@AspectJ的AOP实现权限控制
一. AOP与@AspectJ AOP 是 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,意思是面向方面的编程.我们在系统开发中可以提取出很多共性的东西作为一个 Aspect,可以理 ...
- Spring学习之旅(八)Spring 基于AspectJ注解配置的AOP编程工作原理初探
由小编的上篇博文可以一窥基于AspectJ注解配置的AOP编程实现. 本文一下未贴出的相关代码示例请关注小编的上篇博文<Spring学习之旅(七)基于XML配置与基于AspectJ注解配置的AO ...
- Spring框架学习09——基于AspectJ的AOP开发
1.基于注解开发AspectJ (1)AspectJ注解 基于注解开发AspectJ要比基于XML配置开发AspectJ便捷许多,所以在实际开发中推荐使用注解方式.关于注解的相关内容如下: @Aspe ...
- 基于aspectj的aop注解操作
随机推荐
- java----八种排序算法
1.直接插入排序 经常碰到这样一类排序问题:把新的数据插入到已经排好的数据列中. 将第一个数和第二个数排序,然后构成一个有序序列 将第三个数插入进去,构成一个新的有序序列. 对第四个数.第五个数……直 ...
- spring4笔记----spring4构造注入
与设值注入有以下不同,颜色标出 package com.ij34.web; import com.ij34.servce.people; import com.ij34.servce.root; pu ...
- 单纯linux系统下hadoop2.7.3 eclipse,记一次成功的运行wordcount的注意事项
hadoop要正确安装好 hadoop eclipse plugin要对应相应的eclipse版本 define hadoop location mr master:9000 另一个9001 下面的 ...
- CSS实现三列布局
三列布局指的是两边两列定宽,中间的宽度自适应. 常用三种方法: 定位 浮动 弹性盒布局 定位方式 最直观和容易理解的一种方法,左右两栏选择绝对定位,固定于页面的两侧,中间的主体选择用margin确定位 ...
- Django 2.1.3 文档
https://blog.csdn.net/lengfengyuyu/article/details/83342553#3_23
- AI学习---基于TensorFlow的案例[实现线性回归的训练]
线性回归原理复习 1)构建模型 |_> y = w1x1 + w2x2 + -- + wnxn + b 2)构造损失函数 | ...
- js实现的省市联动
最近工作,要用到省市联动的功能.网上搜了一下,发现有很多这样的例子,看了不少实例,把觉得写得不错的代码穿上来,好给大家分享一下. <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W ...
- Python爬虫-02:HTTPS请求与响应,以及抓包工具Fiddler的使用
目录 1. HTTP和HTTPS 1.1. HTTP的请求和响应流程:打开一个网页的过程 1.2. URL 2. 客户端HTTP请求 3. Fiddler抓包工具的使用 3.1. 工作原理 3.2. ...
- vue使用JS的形式进行路由导航
// 注意: 一定要区分 this.$route 和 this.$router 这两个对象, // 其中: this.$route 是路由[参数对象],所有路由中的参数, params, query ...
- PHP 缓存技术(一)
移除光盘
