ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--ObstacleLayer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493676
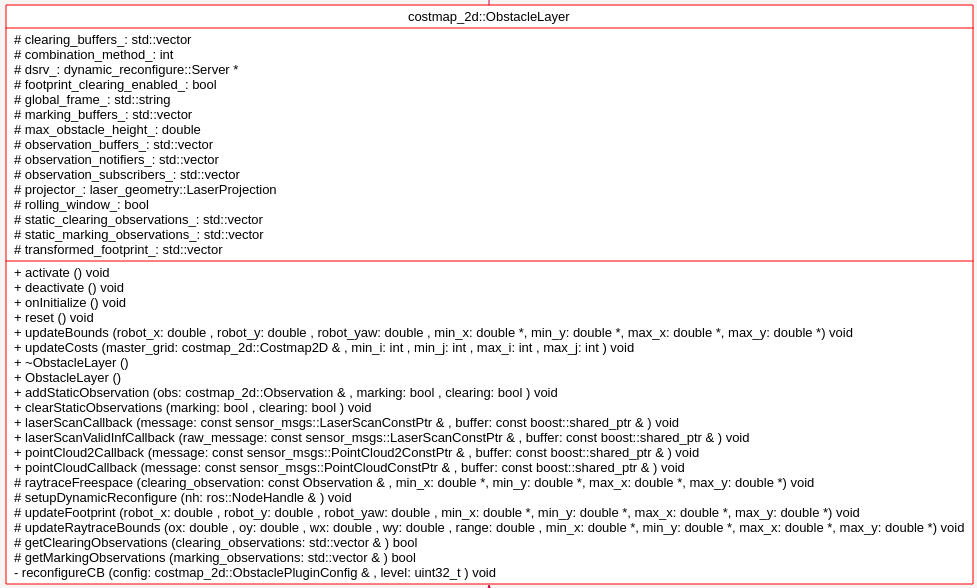
构造函数
ObstacleLayer()
{
costmap_ = NULL; // this is the unsigned char* member of parent class Costmap2D.这里指明了costmap_指针保存了Obstacle这一层的地图数据
}
对于ObstacleLater,首先分析其需要实现的Layer层的方法:
virtual void onInitialize();
virtual void updateBounds(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw, double* min_x, double* min_y,double* max_x, double* max_y);
virtual void updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i, int max_j); virtual void activate();
virtual void deactivate();
virtual void reset();
函数 onInitialize();:
首先获取参数设定的值,然后新建observation buffer
// create an observation buffer
observation_buffers_.push_back(boost::shared_ptr < ObservationBuffer>
(new ObservationBuffer(topic, observation_keep_time, expected_update_rate, min_obstacle_height,max_obstacle_height, obstacle_range, raytrace_range, *tf_, global_frame_,sensor_frame, transform_tolerance))); // check if we'll add this buffer to our marking observation buffers
if (marking)
marking_buffers_.push_back(observation_buffers_.back()); // check if we'll also add this buffer to our clearing observation buffers
if (clearing)
clearing_buffers_.push_back(observation_buffers_.back());
然后分别对不同的sensor类型如LaserScan PointCloud PointCloud2,注册不同的回调函数。这里选LaserScan 分析其回调函数:
void ObstacleLayer::laserScanCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScanConstPtr& message,
const boost::shared_ptr<ObservationBuffer>& buffer)
{
// project the laser into a point cloud
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloud;
cloud.header = message->header; // project the scan into a point cloud
try
{
projector_.transformLaserScanToPointCloud(message->header.frame_id, *message, cloud, *tf_);
}
catch (tf::TransformException &ex)
{
ROS_WARN("High fidelity enabled, but TF returned a transform exception to frame %s: %s", global_frame_.c_str(),
ex.what());
projector_.projectLaser(*message, cloud);
} // buffer the point cloud
buffer->lock();
buffer->bufferCloud(cloud);
buffer->unlock();
}
其中buffer->bufferCloud(cloud)实际上是sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 >>>pcl::PCLPointCloud2 >>> pcl::PointCloud < pcl::PointXYZ > ; 然后才调用void ObservationBuffer::bufferCloud(const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& cloud)
void ObservationBuffer::bufferCloud(const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& cloud)
{
Stamped < tf::Vector3 > global_origin; // create a new observation on the list to be populated
observation_list_.push_front(Observation()); // check whether the origin frame has been set explicitly or whether we should get it from the cloud
string origin_frame = sensor_frame_ == "" ? cloud.header.frame_id : sensor_frame_; try
{
// given these observations come from sensors... we'll need to store the origin pt of the sensor
Stamped < tf::Vector3 > local_origin(tf::Vector3(0, 0, 0),
pcl_conversions::fromPCL(cloud.header).stamp, origin_frame);
tf_.waitForTransform(global_frame_, local_origin.frame_id_, local_origin.stamp_, ros::Duration(0.5));
tf_.transformPoint(global_frame_, local_origin, global_origin);
observation_list_.front().origin_.x = global_origin.getX();
observation_list_.front().origin_.y = global_origin.getY();
observation_list_.front().origin_.z = global_origin.getZ(); // make sure to pass on the raytrace/obstacle range of the observation buffer to the observations
observation_list_.front().raytrace_range_ = raytrace_range_;
observation_list_.front().obstacle_range_ = obstacle_range_; pcl::PointCloud < pcl::PointXYZ > global_frame_cloud; // transform the point cloud
pcl_ros::transformPointCloud(global_frame_, cloud, global_frame_cloud, tf_);
global_frame_cloud.header.stamp = cloud.header.stamp;
//上面的操作都是针对 observation_list_.front()的一些meta数据作赋值
下面的操作是对(observation_list_.front().cloud_)作赋值操作,
// now we need to remove observations from the cloud that are below or above our height thresholds
pcl::PointCloud < pcl::PointXYZ > &observation_cloud = *(observation_list_.front().cloud_);
unsigned int cloud_size = global_frame_cloud.points.size();
observation_cloud.points.resize(cloud_size);
unsigned int point_count = 0; // copy over the points that are within our height bounds
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud_size; ++i)
{
if (global_frame_cloud.points[i].z <= max_obstacle_height_
&& global_frame_cloud.points[i].z >= min_obstacle_height_)
{
observation_cloud.points[point_count++] = global_frame_cloud.points[i];
}
} // resize the cloud for the number of legal points
observation_cloud.points.resize(point_count);
observation_cloud.header.stamp = cloud.header.stamp;
observation_cloud.header.frame_id = global_frame_cloud.header.frame_id;
}
catch (TransformException& ex)
{
// if an exception occurs, we need to remove the empty observation from the list
observation_list_.pop_front();
ROS_ERROR("TF Exception that should never happen for sensor frame: %s, cloud frame: %s, %s", sensor_frame_.c_str(),
cloud.header.frame_id.c_str(), ex.what());
return;
} // if the update was successful, we want to update the last updated time
last_updated_ = ros::Time::now(); // we'll also remove any stale observations from the list
//这个操作会将timestamp较早的点都移除出observation_list_
purgeStaleObservations();
}
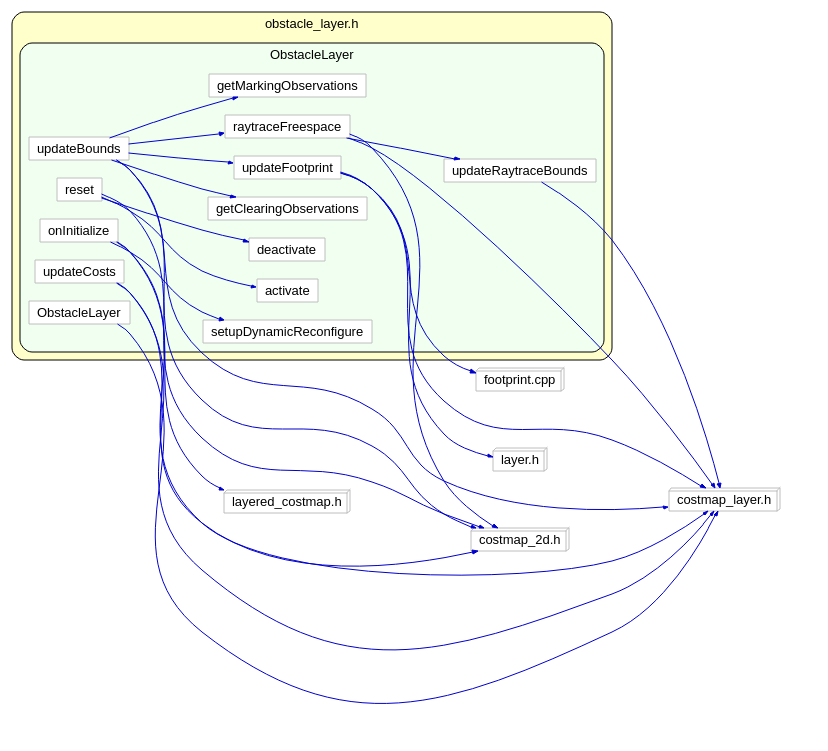
以下重点分析updateBounds:
void ObstacleLayer::updateBounds(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw, double* min_x,double* min_y, double* max_x, double* max_y)
{
if (rolling_window_)
updateOrigin(robot_x - getSizeInMetersX() / 2, robot_y - getSizeInMetersY() / 2);
if (!enabled_)
return;
useExtraBounds(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y); bool current = true;
std::vector<Observation> observations, clearing_observations; // get the marking observations
current = current && getMarkingObservations(observations);
// get the clearing observations
current = current &&getClearingObservations(clearing_observations); // update the global current status
current_ = current; // raytrace freespace
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < clearing_observations.size(); ++i)
{
raytraceFreespace(clearing_observations[i], min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);//首先清理出传感器到被测物之间的区域,标记为FREE_SPACE
} // place the new obstacles into a priority queue... each with a priority of zero to begin with
for (std::vector<Observation>::const_iterator it = observations.begin(); it != observations.end(); ++it)
{
const Observation& obs = *it;
const pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>& cloud = *(obs.cloud_);
double sq_obstacle_range = obs.obstacle_range_ * obs.obstacle_range_;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < cloud.points.size(); ++i)
{
double px = cloud.points[i].x, py = cloud.points[i].y, pz = cloud.points[i].z;
// if the obstacle is too high or too far away from the robot we won't add it
if (pz > max_obstacle_height_)
{
ROS_DEBUG("The point is too high");
continue;
}
// compute the squared distance from the hitpoint to the pointcloud's origin
double sq_dist =
(px - obs.origin_.x) * (px - obs.origin_.x) + (py - obs.origin_.y) * (py - obs.origin_.y)
+ (pz - obs.origin_.z) * (pz - obs.origin_.z); // if the point is far enough away... we won't consider it
if (sq_dist >= sq_obstacle_range)
{
ROS_DEBUG("The point is too far away");
continue;
}
// now we need to compute the map coordinates for the observation
unsigned int mx, my;
if (!worldToMap(px, py, mx, my))
{
ROS_DEBUG("Computing map coords failed");
continue;
}
unsigned int index = getIndex(mx, my);
costmap_[index] = LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
touch(px, py, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
}
} updateFootprint(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
}
函数raytraceFreespace:
会首先处理测量值越界的问题,然后调用
MarkCell marker(costmap_, FREE_SPACE);
// and finally... we can execute our trace to clear obstacles along that line
raytraceLine(marker, x0, y0, x1, y1, cell_raytrace_range);
updateRaytraceBounds(ox, oy, wx, wy, clearing_observation.raytrace_range_, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
最终raytraceLine(marker, x0, y0, x1, y1, cell_raytrace_range); 会将所有在(x0,y0) -> (x1,y1)之间的所有cell标记为FREE_SPACE。而updateRaytraceBounds 会根据测量的距离,更新扩张(min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y)。 updateBounds 在根据测量数据完成clear 操作之后,就开始了mark 操作,对每个测量到的点,标记为obstacle :
double px = cloud.points[i].x, py = cloud.points[i].y, pz = cloud.points[i].z;
// if the obstacle is too high or too far away from the robot we won't add it
if (pz > max_obstacle_height_)
{
ROS_DEBUG("The point is too high");
continue;
}
// compute the squared distance from the hitpoint to the pointcloud's origin
double sq_dist = (px - obs.origin_.x) * (px - obs.origin_.x) + (py - obs.origin_.y) * (py - obs.origin_.y)
+ (pz - obs.origin_.z) * (pz - obs.origin_.z);
// if the point is far enough away... we won't consider it
if (sq_dist >= sq_obstacle_range)
{
ROS_DEBUG("The point is too far away");
continue;
}
// now we need to compute the map coordinates for the observation
unsigned int mx, my;
if (!worldToMap(px, py, mx, my))
{
ROS_DEBUG("Computing map coords failed");
continue;
}
unsigned int index = getIndex(mx, my);
costmap_[index] = LETHAL_OBSTACLE;
touch(px, py, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);
}
函数 updateFootprint:
void ObstacleLayer::updateFootprint(double robot_x, double robot_y, double robot_yaw, double* min_x, double* min_y,
double* max_x, double* max_y)
{
if (!footprint_clearing_enabled_) return;
transformFootprint(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw, getFootprint(), transformed_footprint_);//这里获得了在当前机器人位姿(robot_x, robot_y, robot_yaw)条件下,机器人轮廓点在global坐标系下的值 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < transformed_footprint_.size(); i++)
{
touch(transformed_footprint_[i].x, transformed_footprint_[i].y, min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y);//再次保留或者扩张Bounds
}
}
函数 updateCosts:
void ObstacleLayer::updateCosts(costmap_2d::Costmap2D& master_grid, int min_i, int min_j, int max_i, int max_j)
{
if (!enabled_)
return; if (footprint_clearing_enabled_)
{
setConvexPolygonCost(transformed_footprint_, costmap_2d::FREE_SPACE);//设置机器人轮廓所在区域为FREE_SPACE
} switch (combination_method_)
{
case 0: // Overwrite调用的CostmapLayer提供的方法
updateWithOverwrite(master_grid, min_i, min_j, max_i, max_j);
break;
case 1: // Maximum
updateWithMax(master_grid, min_i, min_j, max_i, max_j);
break;
default: // Nothing
break;
}
}
ObstacleLayer 主要内容就是这些~~~接下来是InflationLayer
ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--ObstacleLayer的更多相关文章
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Costmap2DROS
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50485418 在上一篇文章中moveBase就有关于costmap_2d的使用: pl ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: move_base
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50483123 这是navigation的第一篇文章,主要通过分析ROS代码级实现,了解 ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--LayeredCostmap
博客转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50490490 在数据成员中,有两个重要的变量:Costmap2D costmap_和 s ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--StaticLayer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493246 从UML中能够看到,StaticLayer主要是在实现Layer层要求实 ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--CostmapLayer
博客转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493220 这个类是为ObstacleLayer StaticLayer voxelL ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Layer
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50493113 这个类中有一个LayeredCostmap* layered_costm ...
- ROS naviagtion analysis: costmap_2d--Costmap2D
博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/u013158492/article/details/50492506 Costmap2D是存储地图数据的父类.真正的地图数据就存储在数据成员u ...
- ROS探索总结(十三)——导航与定位框架
导航与定位是机器人研究中的重要部分. 一般机器人在陌生的环境下需要使用激光传感器(或者深度传感器转换成激光数据),先进行地图建模,然后在根据建立的地图进行导航.定位.在ROS中也有很多 ...
- ROS 教程之 navigation :在 catkin 环境下创建costmap layer plugin
在做机器人导航的时候,肯定见到过global_costmap和local_costmap.global_costmap是为了全局路径规划服务的,如从这个房间到那个房间该怎么走.local_costma ...
随机推荐
- 【解题报告】牡丹江现场赛之ABDIK ZOJ 3819 3820 3822 3827 3829
那天在机房做的同步赛,比现场赛要慢了一小时开始,直播那边已经可以看到榜了,所以上来就知道A和I是水题,当时机房电脑出了点问题,就慢了好几分钟,12分钟才A掉第一题... A.Average Score ...
- 深入理解java虚拟机-第八章
第8章 虚拟机字节码执行引擎 8.2 运行时栈帧结构 栈帧(Stack Frame)是用于支持虚拟机进行方法调用和方法执行的数据结构. 每一个栈帧包括了局部变量表.操作数栈.动态连接.方法返回地址和一 ...
- niosii boot过程
1 概述Nios II 的boot过程要经历两个过程. FPGA器件本身的配置过程.FPGA器件在外部配置控制器或自身携带的配置控制器的控制下配置FPGA的内部逻辑.如果内部逻辑中使用了Nios II ...
- java多线程:线程体往外抛出异常的处理机制实践
1当线程的线程体内部无捕获异常,将异常抛出线程体外,不同情况下,程序处理机制 测试类 package com.ehking.bankchannel.domesticremit.facade.impl; ...
- 浅谈Sql各种join的用法
1.left join.right join.inner join三者区别 left join(左联接) 返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中联结字段相等的记录 right join(右联接) 返回包括右 ...
- android多渠道打包牛B工具
http://www.orchidshell.com/ 兰贝壳儿:一个Eclipse插件,为Android开发提供了多渠道打包功能和一些工具类.
- oracle11g,安装失败,提示找不到文件,win7 64位下报错
提示: 未找到文件 E:\app\Administrator\product\11.2.0\dbhome_5\owb\external\oc4j_applications\applications\W ...
- 启用不安全的HTTP方法解决方案
启用不安全的HTTP方法解决方案 Web AppScan HTTP WebDAV 近期通过APPScan扫描程序,发现了不少安全问题,通过大量查阅和尝试最终还是解决掉了,于是整理了一下方便查阅. 1. ...
- 家谱处理(30 分)(字符串的处理substr)
家谱处理(30 分) 人类学研究对于家族很感兴趣,于是研究人员搜集了一些家族的家谱进行研究.实验中,使用计算机处理家谱.为了实现这个目的,研究人员将家谱转换为文本文件.下面为家谱文本文件的实例: Jo ...
- SE新手游操控创新:一个按键=五个技能
转自:http://www.gamelook.com.cn/2015/01/201299 GameLook报道 / 日本游戏厂商一向擅长搞发明创造,除了诞生了各种烧脑奇葩游戏以外,日本主流手机游戏的核 ...
