HDU 1890 Robotic Sort (splay tree)
Robotic Sort
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1640 Accepted Submission(s): 711
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
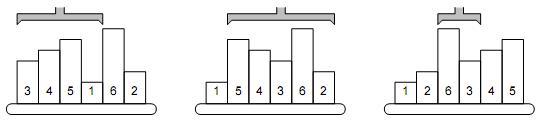
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
3 4 5 1 6 2
4
3 3 2 1
0
4 2 4 4
splay tree
旋转操作
/* ***********************************************
Author :kuangbin
Created Time :2013/8/24 23:28:43
File Name :F:\2013ACM练习\专题学习\splay_tree_2\HDU1890.cpp
************************************************ */ #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std; #define Key_value ch[ch[root][1]][0]
const int MAXN = ;
int pre[MAXN],ch[MAXN][],root,tot1;
int size[MAXN];//子树规模
int rev[MAXN];//反转标记
int s[MAXN],tot2;//内存池和容量 //debug部分**********************************
void Treavel(int x)
{
if(x)
{
Treavel(ch[x][]);
printf("结点:%2d: 左儿子 %2d 右儿子 %2d 父结点 %2d size = %2d rev = %2d\n",x,ch[x][],ch[x][],pre[x],size[x],rev[x]);
Treavel(ch[x][]);
}
}
void debug()
{
printf("root:%d\n",root);
Treavel(root);
}
//以上是debug部分************************************** void NewNode(int &r,int father,int k)
{
r = k;
pre[r] = father;
ch[r][] = ch[r][] = ;
size[r] = ;
rev[r] = ;
}
//反转的更新
void Update_Rev(int r)
{
if(!r)return;
swap(ch[r][],ch[r][]);
rev[r] ^= ;
}
inline void push_up(int r)
{
size[r] = size[ch[r][]] + size[ch[r][]] + ;
}
inline void push_down(int r)
{
if(rev[r])
{
Update_Rev(ch[r][]);
Update_Rev(ch[r][]);
rev[r] = ;
}
}
void Build(int &x,int l,int r,int father)
{
if(l > r)return;
int mid = (l+r)/;
NewNode(x,father,mid);
Build(ch[x][],l,mid-,x);
Build(ch[x][],mid+,r,x);
push_up(x);
}
int n;
void Init()
{
root = tot1 = tot2 = ;
ch[root][] = ch[root][] = pre[root] = size[root] = rev[root] = ;
NewNode(root,,n+);
NewNode(ch[root][],root,n+);
Build(Key_value,,n,ch[root][]);
push_up(ch[root][]);
push_up(root);
}
//旋转,0为左旋,1为右旋
inline void Rotate(int x,int kind)
{
int y = pre[x];
push_down(y);
push_down(x);//先把y的标记下传,在把x的标记下传
ch[y][!kind] = ch[x][kind];
pre[ch[x][kind]] = y;
if(pre[y])
ch[pre[y]][ch[pre[y]][]==y] = x;
pre[x] = pre[y];
ch[x][kind] = y;
pre[y] = x;
push_up(y);
}
//Splay调整,将r结点调整到goal下面
inline void Splay(int r,int goal)
{
push_down(r);
while(pre[r] != goal)
{
if(pre[pre[r]] == goal)
{
//有反转操作,需要先push_down,再判断左右孩子
push_down(pre[r]);
push_down(r);
Rotate(r,ch[pre[r]][]==r);
}
else
{
//有反转操作,需要先push_down
push_down(pre[pre[r]]);
push_down(pre[r]);
push_down(r);
int y = pre[r];
int kind = ch[pre[y]][]==y;
if(ch[y][kind] == r)
{
Rotate(r,!kind);
Rotate(r,kind);
}
else
{
Rotate(y,kind);
Rotate(r,kind);
}
}
}
push_up(r);
if(goal == ) root = r;
}
//得到第k个结点(需要push_down)
inline int Get_kth(int r,int k)
{
push_down(r);
int t = size[ch[r][]] + ;
if(t == k)return r;
if(t > k)return Get_kth(ch[r][],k);
else return Get_kth(ch[r][],k-t);
}
//找前驱(需要push_down)
inline int Get_pre(int r)
{
push_down(r);
if(ch[r][] == )return -;//不存在
r = ch[r][];
while(ch[r][])
{
r = ch[r][];
push_down(r);
}
return r;
}
//找后继(需要push_down)
inline int Get_next(int r)
{
push_down(r);
if(ch[r][] == )return -;
r = ch[r][];
while(ch[r][])
{
r = ch[r][];
push_down(r);
}
return r;
} struct Node
{
int id,val;
}node[MAXN];
bool cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
if(a.val != b.val)return a.val < b.val;
else return a.id < b.id;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
//freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
while(scanf("%d",&n) == && n)
{
for(int i = ;i <= n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&node[i].val);
node[i].id = i;
}
sort(node+,node+n+,cmp);
Init();
for(int i = ; i <= n;i++)
{
Splay(node[i].id,);
printf("%d",size[ch[root][]]);
if(i < n)printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
Splay(Get_kth(root,i),);
Splay(Get_next(node[i].id),root);
Update_Rev(Key_value);
}
}
return ;
}
HDU 1890 Robotic Sort (splay tree)的更多相关文章
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort(splay)
[题目链接] http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 [题意] 给定一个序列,每次将i..P[i]反转,然后输出P[i],P[i]定义为当前数字i ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic SortI(splay区间旋转操作)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 题解:splay又一高级的功能,区间旋转这个是用线段树这些实现不了的,这题可以学习splay的旋 ...
- HDU 1890--Robotic Sort(Splay Tree)
题意:每次找出第i大的数的位置p输出,然后将i~p之间的数反转. 题解:每次把要的区间转成一棵子树,然后更新.因为每次将第i小的数转到了了i,所以k次操作后,可知前k个数一定是最小的那k个数,所以以后 ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- 伸展树(Splay Tree)进阶 - 从原理到实现
目录 1 简介 2 基础操作 2.1 旋转 2.2 伸展操作 3 常规操作 3.1 插入操作 3.2 删除操作 3.3 查找操作 3.4 查找某数的排名.查找某排名的数 3.4.1 查找某数的排名 3 ...
- 数据结构(二) --- 伸展树(Splay Tree)
文章图片和代码来自邓俊辉老师课件 概述 伸展树(Splay Tree),也叫分裂树,是一种二叉排序树,它能在O(log n)内完成插入.查找和删除操作.它由丹尼尔·斯立特Daniel Sleator ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort | Splay
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) [Pr ...
- 数据结构(Splay平衡树):HDU 1890 Robotic Sort
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- 纸上谈兵:伸展树(splay tree)
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 我们讨论过,树的搜索效率与树的深度有关.二叉搜索树的深度可能为n,这种情况下,每次 ...
随机推荐
- redis tutorail
命令 set get incr expire 秒 ttl -1 不会过期 list : lpush rpush lpop rpop lrange llen se ...
- Python3中的yield from语法
Python3中的yield from语法 by Kay Zheng Tags: python, 协程, generator 30 March 2014 2016-2-23 更新 這篇文章是兩年前寫的 ...
- linux 101 hacks 5PS1
PS1——默认提示符 看完这一章,我心里若干个卧槽.. 如下所示, 可以通过修改 Linux 下的默认提示符,使其更加实用.在下面的例子中,默认的 PS1的值是“ \s-\v\$”,显示出了 shel ...
- 【Java】 参数的传递:值传递与引用传递讨论
内容稍多,可直接看第4点的讨论结果 前言 在涉及到传递参数给方法时,容易出现一些参数传递错误的问题,这就涉及到了参数的传递问题,必须搞清楚:参数是如何传递到方法中的?一般来说,参数的传递可以分为两种: ...
- Ubuntu16.04下Hive的安装与配置
一.系统环境 os : Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 64bit jdk : 1.8.0_161 hadoop : 2.6.4mysql : 5.7.21 hive : 2.1.0 在配置hive ...
- hdoj1879 继续畅通工程(Prime || Kruskal)
题目链接 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1879 思路 这题和hdoj1102很像,图中的有一些路已经修好了,对于这些已经修好的路,我们令还需要修 ...
- Python 爬虫个人笔记【目录】
个人笔记,仅供参考 目录 Python爬虫笔记(一) Python 爬虫笔记(二) Python 爬虫笔记(三) Scrapy 笔记(一) Scrapy 笔记(二) Scrapy 笔记(三) Pyth ...
- 【知了堂学习笔记】java 接口与抽象类
本次主角:抽象类 .接口. 对于皮皮潇这样一类的Java初学者来说,接口和抽象类如果不去花大量的精力与时间是很难弄清楚的,而我也是在最近这周的项目学习中感觉到了我对这两个概念不熟悉,所以导致对一些问题 ...
- python面向对象中类对象、实例对象、类变量、实例变量、类方法、实例方法、静态方法
1. 类对象和实例对象 Python中一切皆对象,Python类本身也是一种对象,类定义完成后,会在当前作用域中定义一个以类名为名字的命名空间.类对象具有以下两种操作: 可以通过“类名()”的方式实例 ...
- ubuntu下安装和破解navicat的方法
ubuntu下安装和破解navicat的方法 之前我也在苦苦搜寻ubuntu完美破解navicat的方法,但是大家都说是删除掉~/.Navicat,就可以续用,的确是这样,但是很麻烦. 于是我找到了一 ...