Cookies Client Identification
HTTP The Definitive Guide
Cookies are the best current way to identify users and allow persistent sessions. They don't suffer
many of the problems of the previous techniques, but they often are used in conjunction with those
techniques for extra value. Cookies were first developed by Netscape but now are supported by all
major browsers.
Because cookies are important, and they define new HTTP headers, we're going to explore them in
more detail than we did the previous techniques. The presence of cookies also impacts caching, and
most caches and browsers disallow caching of any cookied content. The following sections present
more details.

11.6.1 Types of Cookies
You can classify cookies broadly into two types: session cookies and persistent cookies. A session
cookie is a temporary cookie that keeps track of settings and preferences as a user navigates a site. A
session cookie is deleted when the user exits the browser. Persistent cookies can live longer; they are
stored on disk and survive browser exits and computer restarts. Persistent cookies often are used to
retain a configuration profile or login name for a site that a user visits periodically.
The only difference between session cookies and persistent cookies is when they expire. As we will
see later, a cookie is a session cookie if its Discard parameter is set, or if there is no Expires or Max-
Age parameter indicating an extended expiration time.

11.6.2 How Cookies Work
Cookies are like "Hello, My Name Is" stickers stuck onto users by servers. When a user visits a web
site, the web site can read all the stickers attached to the user by that server.
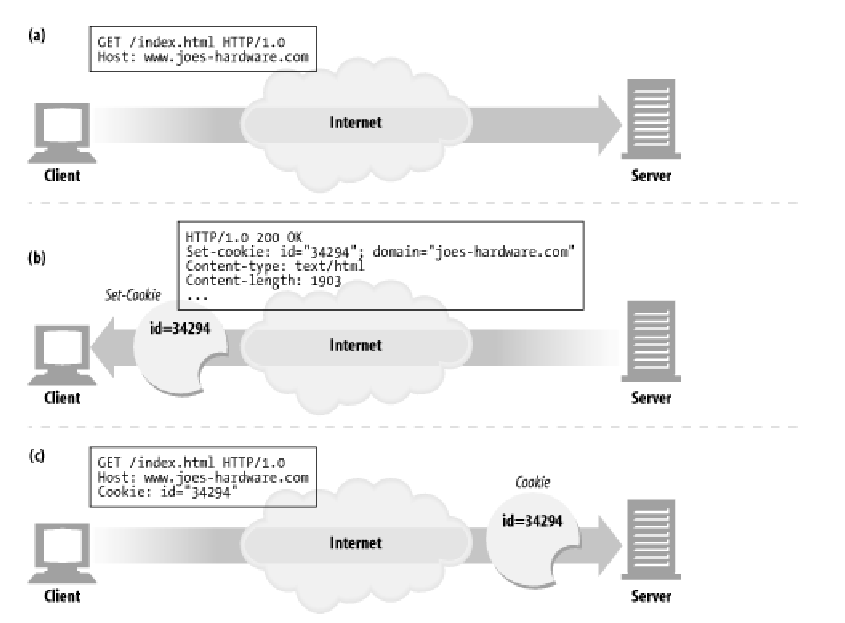
The first time the user visits a web site, the web server doesn't know anything about the user (Figure
11-3a). The web server expects that this same user will return again, so it wants to "slap" a unique
cookie onto the user so it can identify this user in the future. The cookie contains an arbitrary list of
name=value information, and it is attached to the user using the Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2 HTTP
response (extension) headers.
Cookies can contain any information, but they often contain just a unique identification number,
generated by the server for tracking purposes. For example, in Figure 11-3b, the server slaps onto the
user a cookie that says id="34294". The server can use this number to look up database information
that the server accumulates for its visitors (purchase history, address information, etc.).
However, cookies are not restricted to just ID numbers. Many web servers choose to keep information
directly in the cookies. For example:
Cookie: name="Brian Totty"; phone="555-1212"
The browser remembers the cookie contents sent back from the server in Set-Cookie or Set-Cookie2
headers, storing the set of cookies in a browser cookie database (think of it like a suitcase with stickers
from various countries on it). When the user returns to the same site in the future (Figure 11-3c), the
browser will select those cookies slapped onto the user by that server and pass them back in a Cookie
request header.

Figure 11-3. Slapping a cookie onto a user

Cookies Client Identification的更多相关文章
- Technical analysis of client identification mechanisms
http://www.chromium.org/Home/chromium-security/client-identification-mechanisms Chromium > Chro ...
- Cookies and Session Tracking Client Identification cookie与会话跟踪 客户端识别
w HTTP The Definitive Guide Cookies can be used to track users as they make multiple transactions to ...
- Cookies, Security, and Privacy Client Identification
w HTTP The Definitive Guide Cookies themselves are not believed to be a tremendous security risk, be ...
- Cookies and Caching Client Identification
w HTTP The Definitive Guide 11.6.9 Cookies and Caching You have to be careful when caching documents ...
- The Personal Touch Client Identification 个性化接触 客户识别
w服务器要知道和谁在交谈. HTTP The Definitive Guide Web servers may talk to thousands of different clients simul ...
- combined with the Referer header, to potentially build an exhaustive data set of user profiles and browsing habits Client Identification
w https://www.zhihu.com/question/35307626 w 0-客户端(附加用户信息)首次请求服务端--->服务端生成session(有唯一性).session_id ...
- Fat URLs Client Identification
w在每个URL后面都附加一个用户特有的标识码. HTTP The Definitive Guide Some web sites keep track of user identity by gene ...
- Client IP Address Client Identification
HTTP The Definitive Guide Early web pioneers tried using the IP address of the client as a form of i ...
- HTTP Headers Client Identification
用户信息通过HTTP头部承载:不能实现用户唯一性标识. w HTTP The Definitive Guide Table 11-1 shows the seven HTTP request head ...
随机推荐
- Linux系统(Ubuntu/Debian/RedHat/CentOS)超级简单的samba配置文件smb.conf
1.超简单的smb.conf 该配置文件对Ubuntu和CentOS都好用. #============== Global Settings ============== [global] ## Br ...
- TIM—基本定时器
本章参考资料:< STM32F4xx 参考手册>.< STM32F4xx 规格书>.库帮助文档< stm32f4xx_dsp_stdperiph_lib_um.chm&g ...
- hdu1331(记忆化搜索)
#include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> using namespace std; typed ...
- Unity3D学习(十):使用VideoPlayer在UI上播放视频
前言 每一款游戏往往启动的第一次都会播放CG动画之类的,Unity本身对于移动平台也提供了一个接口. Handheld.PlayFullScreenMovie("path") 过场 ...
- SQL select查询原理--查询语句执行原则<转>
1.单表查询:根据WHERE条件过滤表中的记录,形成中间表(这个中间表对用户是不可见的):然后根据SELECT的选择列选择相应的列进行返回最终结果. 1)简单的单表查询 SELECT 字段 FROM ...
- phpstorm 中文版 支持BUG调试 IDE
下载地址:http://dx2.7down.net/soft/P/phpstorm8_cn.zip
- 使用JAVASCRIPT进行数据完整性验证
页面输入完整性是编写BS经常遇到的问题,如果那里需要就到那里写,那可是要花不少的时候,并且造成不必要的浪费,下面是一个通过校验脚本,使用非常方便,通过传入FORM名就可以进行校验,通过在页面控件中增加 ...
- 数据库 数据库SQL语句四
多表查询 等值连接 --查询员工信息,员工号,姓名,月薪,部门名称 select e.empno,e.ename,d.dname from emp e,dept d where e.deptno=d. ...
- 指数族分布(Exponential Families of Distributions)
指数族分布是一大类分布,基本形式为: T(x)是x的充分统计量(能为相应分布提供足够信息的统计量) 为了满足归一化条件,有: 可以看出,当T(x)=x时,e^A(theta)是h(x)的拉普拉斯变换. ...
- Win10下安装MySQL总卡在write configuration的解决办法
先说结论 删除 C:\ProgramData 下的MySQL文件夹!!! 折腾过程 反复安装卸载,安装版.绿色版,都不行,清理注册表,清理安装文件夹,还是不行!!! 最后找到并删除 C:\Prog ...
