POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines (判断直线位置关系)
题目链接:POJ 1269
Problem Description
We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane defines a line and that a pair of lines on a plane will intersect in one of three ways: 1) no intersection because they are parallel, 2) intersect in a line because they are on top of one another (i.e. they are the same line), 3) intersect in a point. In this problem you will use your algebraic knowledge to create a program that determines how and where two lines intersect.
Your program will repeatedly read in four points that define two lines in the x-y plane and determine how and where the lines intersect. All numbers required by this problem will be reasonable, say between -1000 and 1000.
Input
The first line contains an integer N between 1 and 10 describing how many pairs of lines are represented. The next N lines will each contain eight integers. These integers represent the coordinates of four points on the plane in the order x1y1x2y2x3y3x4y4. Thus each of these input lines represents two lines on the plane: the line through (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) and the line through (x3,y3) and (x4,y4). The point (x1,y1) is always distinct from (x2,y2). Likewise with (x3,y3) and (x4,y4).
Output
There should be N+2 lines of output. The first line of output should read INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT. There will then be one line of output for each pair of planar lines represented by a line of input, describing how the lines intersect: none, line, or point. If the intersection is a point then your program should output the x and y coordinates of the point, correct to two decimal places. The final line of output should read "END OF OUTPUT".
Sample Input
5
0 0 4 4 0 4 4 0
5 0 7 6 1 0 2 3
5 0 7 6 3 -6 4 -3
2 0 2 27 1 5 18 5
0 3 4 0 1 2 2 5
Sample Output
INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT
POINT 2.00 2.00
NONE
LINE
POINT 2.00 5.00
POINT 1.07 2.20
END OF OUTPUT
Solution
题意
\(n\) 组样例。每组样例给定两条直线,判断直线是平行,重合还是相交。若相交求交点。
题解
叉积
- 判断共线:
若 \(\boldsymbol{ab}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{cd}\) 共线,则 \(\boldsymbol{ab} \times \boldsymbol{cd} = 0\)。
- 判断重合:
若 \(\boldsymbol{ab}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{cd}\) 重合,则 \(\boldsymbol{bc} \times \boldsymbol{ad} = 0\)。
- 判断平行:
共线且不重合。
- 求交点:
首先要满足相交。
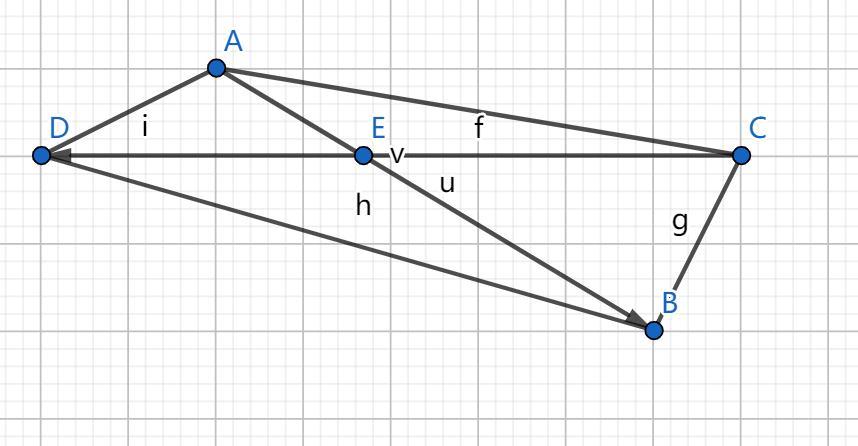
如上图,求 \(\boldsymbol{AB}\) 与 \(\boldsymbol{CD}\) 的交点 \(E\)。
\]
\]
设原点为 \(O\),则
\]
\(\boldsymbol{OE}\) 即为点 \(E\) 的坐标。
Code
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef double db;
const db eps = 1e-10;
const db pi = acos(-1.0);
const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const ll maxn = 1e5 + 10;
inline int dcmp(db x) {
if(fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
return x > 0? 1: -1;
}
class Point {
public:
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {}
void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
bool operator<(const Point &a) const {
return (!dcmp(x - a.x))? dcmp(y - a.y) < 0: x < a.x;
}
bool operator==(const Point &a) const {
return dcmp(x - a.x) == 0 && dcmp(y - a.y) == 0;
}
db dis2(const Point a) {
return pow(x - a.x, 2) + pow(y - a.y, 2);
}
db dis(const Point a) {
return sqrt(dis2(a));
}
db dis2() {
return x * x + y * y;
}
db dis() {
return sqrt(dis2());
}
Point operator+(const Point a) {
return Point(x + a.x, y + a.y);
}
Point operator-(const Point a) {
return Point(x - a.x, y - a.y);
}
Point operator*(double p) {
return Point(x * p, y * p);
}
Point operator/(double p) {
return Point(x / p, y / p);
}
db dot(const Point a) {
return x * a.x + y * a.y;
}
db cross(const Point a) {
return x * a.y - y * a.x;
}
};
typedef Point Vector;
class Line {
public:
Point s, e;
Line() {}
Line(Point s, Point e) : s(s), e(e) {}
void input() {
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &s.x, &s.y, &e.x, &e.y);
}
int toLeftTest(Point p) {
if((e - s).cross(p - s) > 0) return 1;
else if((e - s).cross(p - s) < 0) return -1;
return 0;
}
// 共线
bool collinear(Line l) {
if(dcmp((e - s).cross(l.e - l.s)) == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 同线
bool same(Line l) {
if(dcmp((l.s - e).cross(l.e - s)) == 0) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// 平行
bool parallel(Line l) {
return collinear(l) && (!same(l));
}
// 直线与直线交点
Point crosspoint(Line l) {
double a1 = (l.e - l.s).cross(s - l.s);
double a2 = (l.e - l.s).cross(e - l.s);
Point ans = s + (e - s) * (-a1) / (a2 - a1);
if(dcmp(ans.x) == 0) ans.x = 0;
if(dcmp(ans.y) == 0) ans.y = 0;
return ans;
}
// 直线与直线位置关系 0-重合 1-平行 2-相交
int linecrossline (Line l) {
if(dcmp((e - s).cross(l.e - l.s)) == 0) {
if(dcmp((l.s - e).cross(l.e - s)) == 0) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
return 2;
}
};
Line l1, l2;
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
printf("INTERSECTING LINES OUTPUT\n");
while(T--) {
l1.input();
l2.input();
if(l1.linecrossline(l2) == 0) {
printf("LINE\n");
} else if(l1.linecrossline(l2) == 1) {
printf("NONE\n");
} else {
Point ans = l1.crosspoint(l2);
printf("POINT %.2lf %.2lf\n", ans.x, ans.y);
}
}
printf("END OF OUTPUT\n");
return 0;
}
POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines (判断直线位置关系)的更多相关文章
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(直线相交判断,求交点)
Intersecting Lines Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 8342 Accepted: 378 ...
- poj 1269 Intersecting Lines(判断两直线关系,并求交点坐标)
Intersecting Lines Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 12421 Accepted: 55 ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(直线求交点)
Description We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane defines a line and that a pair of ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines 判断两直线关系
用的是初中学的方法 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <al ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines(判断两直线位置关系)
题目传送门:POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines Description We all know that a pair of distinct points on a plane ...
- 判断两条直线的位置关系 POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines
两条直线可能有三种关系:1.共线 2.平行(不包括共线) 3.相交. 那给定两条直线怎么判断他们的位置关系呢.还是用到向量的叉积 例题:POJ 1269 题意:这道题是给定四个点p1, ...
- 简单几何(直线位置) POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines
题目传送门 题意:判断两条直线的位置关系,共线或平行或相交 分析:先判断平行还是共线,最后就是相交.平行用叉积判断向量,共线的话也用叉积判断点,相交求交点 /********************* ...
- POJ 1269 Intersecting Lines【判断直线相交】
题意:给两条直线,判断相交,重合或者平行 思路:判断重合可以用叉积,平行用斜率,其他情况即为相交. 求交点: 这里也用到叉积的原理.假设交点为p0(x0,y0).则有: (p1-p0)X(p2-p0) ...
- POJ 1269 - Intersecting Lines 直线与直线相交
题意: 判断直线间位置关系: 相交,平行,重合 include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; str ...
随机推荐
- leetcode上回溯法的使用
17 93 131 46(全排列) class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> permute(vector<int> ...
- VTemplate模板引擎的使用--高级篇
VTemplate模板引擎的使用--高级篇 在网站中,经常会有某个栏目的数据在多个页面同时使用到.比如新闻网站或电子商务网站的栏目列表,几乎在很多页面都会显示栏目导航.对于这种多个页面同时使用到的“数 ...
- Android 发布自动版本号方案
以前看到一些自动化版本号打包的文章.如果您的项目是用 Git 管理的,并且恰巧又是使用 Gradle 编译(应该绝大部分都是这样的了吧?),本文试图找到一种更加优雅的自动版本管理方法. 背景 我们都知 ...
- table td 溢出隐藏
需要给table加一个属性:table-layout:fixed;
- Cocos2d-x 发布 Android
Cocos2d-x 发布 Android 前置需求: Android NDK Android SDK OR Eclipse ADT Bundle Android AVD target installe ...
- 三、函数 (SUM、MIN、MAX、COUNT、AVG)
第八章 使用数据处理函数 8.1 函数 SQL支持利用函数来处理数据.函数一般是在数据上执行的,给数据的转换和处理提供了方便. 每一个DBMS都有特定的函数.只有少数几个函数被所有主要的DBMS等同的 ...
- [已解决]报错: No module named pip
cmd中敲命令: python -m ensurepip 更新升级pip命令: python -m pip install --upgrade pip
- Pytest参数传递
import pytest@pytest.fixture()def login_r(open_browser):#调用login时,发现需要先打开浏览器,所以改成先打开浏览器,在登陆 print('输 ...
- SpringData 完全入门指南
SpringData 笔记 1. 配置项目 1.pom.xml <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> < ...
- CSS3 新特性(box-sizing盒模型,背景线性渐变,filter滤镜,calc函数,transition过渡)
1.盒子模型(box-sizing) CSS3 中可以通过 box-sizing 来指定盒模型,有两个值:即可指定为 content-box.border-box,这样我们计算盒子大小的方式就发生了改 ...
