springboot整合视图层之Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf中有自己的表达式,和自己的语法,可以把数据取出来后再进行判断,遍历等操作,另外它还封装了strings,dates....对象,可以利用这些对象对已有的数据进行简单的逻辑处理;
1.pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.mr.li</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot_005</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <!-- 修改jdk版本 -->
<properties>
<java.version>1.7</java.version>
<!-- 将thymeleaf的版本升级一下,好处是:不会限制自动生成的html中编码标签结束没有结束符的错误 -->
<thymeleaf.version>3.0.2.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.0.4</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
</properties> <dependencies>
<!-- springBoot引入web启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springBoot引入thymeleaf视图模板启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
2.启动类
package com.mr.li; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @SpringBootApplication
public class App { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
3.MyController:各个方法的演示,方法的返回值都是对应的html名称
package com.mr.li.controller; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map; import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import com.mr.li.pojo.User; @Controller
public class MyController { /**
* 使用thymeleaf获取字符串:str是html的名字。
* 将字符串添加到model属性中,而model对象是springboot封装过的,在这里用于HTML中获取。
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/strs")
public String show1(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("str", "heLLLlo world");
return "str";
} /**
* 演示:在html中遍历取出list中的内容
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/lists")
public String show2(Model model) {
List<User> list = new ArrayList<User>();
list.add(new User(1, "小明", 15));
list.add(new User(2, "小刚", 16));
list.add(new User(3, "小丽", 14));
model.addAttribute("list", list);
return "list";
} /**
* 演示map:在html中取出map操作
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/maps")
public String show3(Model model) {
Map<String, User> map = new HashMap<String, User>();
map.put("user1", new User(1, "张三", 15));
map.put("user2", new User(2, "李四", 16));
map.put("user3", new User(3, "王五", 17));
model.addAttribute("map", map);
return "map";
} /**
* 演示使用thymeleaf在html中操作date类型
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/dates")
public String show4(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("date", new Date());
return "date";
} /**
* 演示作用域:在html中使用作用域
* @param request
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/scopes")
public String show5(HttpServletRequest request, Model model) {
request.setAttribute("req", "my is request!!!");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("session" , "my is httpsession");
ServletContext context = request.getSession().getServletContext();
context.setAttribute("application", "my is application!!!");
return "scope";
}
/**
* 演示在html判断数据
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/decides")
public String show6(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("id", 2);
model.addAttribute("sex", "男");
return "decide";
}
}
4.实体类,便于生成数据源,方便演示
package com.mr.li.pojo;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public User() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public User(int id, String name, int age) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
5.date.html 演示日期操作
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示Date类型</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- date值是controller中model对象的属性key名称 -->
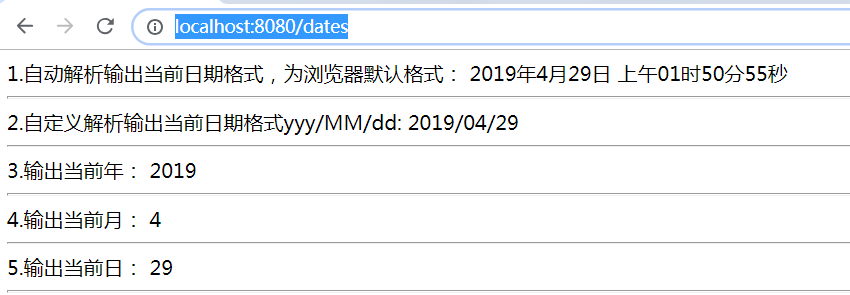
1.自动解析输出当前日期格式,为浏览器默认格式:
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date)}"></span>
<hr/>
2.自定义解析输出当前日期格式yyy/MM/dd:
<span th:text="${#dates.format(date, 'yyy/MM/dd')}"></span>
<hr/>
3.输出当前年:
<span th:text="${#dates.year(date)}"></span>
<hr/>
4.输出当前月:
<span th:text="${#dates.month(date)}"></span>
<hr/>
5.输出当前日:
<span th:text="${#dates.day(date)}"></span>
<hr/>
</body>
</html>
访问url: http://localhost:8080/dates
6.decide.html 用Thymeleaf演示判断
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示if、switch判断操作</title>
</head>
<body>
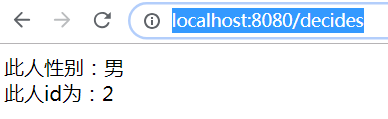
<span th:if = "${sex} == '男'">
此人性别:男
</span>
<span th:if = "${sex} == '女'">
此人性别:女
</span>
<div th:switch="${id}">
<span th:case="1">此人id为:1</span>
<span th:case="2">此人id为:2</span>
<span th:case="3">此人id为:3</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
url: http://localhost:8080/decides
7.list.html list处理数据演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示List类型</title>
</head>
<body>
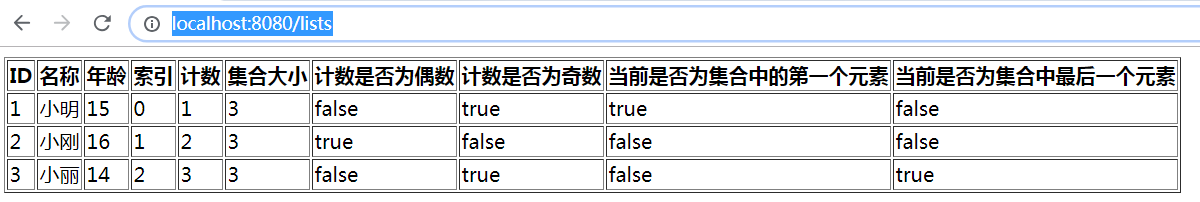
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>索引</th>
<th>计数</th>
<th>集合大小</th>
<th>计数是否为偶数</th>
<th>计数是否为奇数</th>
<th>当前是否为集合中的第一个元素</th>
<th>当前是否为集合中最后一个元素</th>
</tr>
<!-- u:是当前遍历的对象,var:是Thymeleaf帮我们封装的当前对象 -->
<tr th:each="u,var : ${list}">
<td th:text="${u.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.age}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.last}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
url : http://localhost:8080/lists
8.map.html map处理数据演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示Map类型</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>年龄</th>
</tr>
<!--遍历map方式一 -->
<!-- <tr th:each="maps : ${map}">
<td th:each="user : ${maps}" th:text="${user.value.id}"></td>
<td th:each="user : ${maps}" th:text="${user.value.name}"></td>
<td th:each="user : ${maps}" th:text="${user.value.age}"></td>
</tr> -->
<!-- 遍历map方式二:拿出map然后循环会拿出他的对象,输出每个对象,value为关键字 -->
<tr th:each="user : ${map}">
<td th:text="${user.value.id}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.value.name}"></td>
<td th:text="${user.value.age}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
url: http://localhost:8080/maps

9.str.html string类型处理数据演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示String类型</title>
</head>
<body>
演示输出:
<span th:text=" ${str}"></span>
<hr/>
1.检查此字符串是否为空:
<span th:text="${#strings.isEmpty(str)}"></span>
<hr/>
2.检查此str字符串送是否包含“h”:
<span th:text="${#strings.contains(str,'h')}"></span>
<hr/>
3.检查str中的第一个字符是否为“b”:
<span th:text="${#strings.startsWith(str,'b')}"></span>
<hr/>
4.检查str中最后一个字符是否为“s”:
<span th:text="${#strings.endsWith(str,'s')}"></span>
<hr/>
5.输出str的长度:
<span th:text="${#strings.length(str)}"></span>
<hr/>
6.截取str中某段字符的内容,包头不包尾,若只有一个值则从此值往后直到结束:
<span th:text="${#strings.substring(str,3,5)}"></span>
<hr/>
7.输出此字符“o”的索引值:
<span th:text="${#strings.indexOf(str,'o')}"></span>
<hr/>
8.将str所有字符转为大写:
<span th:text="${#strings.toUpperCase(str)}"></span>
<hr/>
9.将str所有字符转为小写:
<span th:text="${#strings.toLowerCase(str)}"></span>
<hr/>
</body>
</html>
url: http://localhost:8080/strs

10.scope.html 作用域演示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>使用Thymeleaf演示Request、HttpSession、Application(ServletContext)作用域类型</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- httpServletRequest对象是Thymeleaf提供的,方法也是,都不能错,req是controller中赋值时的key -->
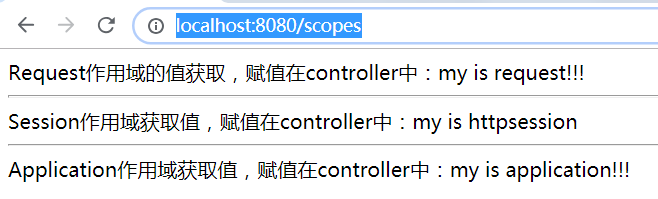
Request作用域的值获取,赋值在controller中:<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('req')}"></span>
<hr/>
<!-- 第一个session是Thymeleaf提供的,第二个session是controller中赋值的key -->
Session作用域获取值,赋值在controller中:<span th:text="${session.session}"></span>
<hr/>
<!-- 第一个application是Thymeleaf提供的,第二个application是controller中赋值的key -->
Application作用域获取值,赋值在controller中:<span th:text="${application.application}"></span>
</body>
</html>
url: http://localhost:8080/scopes
项目结构:
关于url:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf-URL</title>
</head>
<body>
<a th:href="@{http://www.baidu.com}">绝对路径</a><br/>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">绝对路径2</a>
<hr/>
<!-- 此时回去找名为show的这个controller -->
<a th:href="@{/show}">相对路径</a>
<hr/>
<a th:href="@{~/project2/resourcename}">相对于服务器的根</a>
<hr/>
<a th:href="@{/show(id=1,name=zhagnsan)}">相对路径-传参</a>
<hr/>
<a th:href="@{/path/{id}/show(id=1,name=zhagnsan)}">相对路径-传参-restful</a>
</body>
</html>
以上就是thymeleaf的简单应用
springboot整合视图层之Thymeleaf的更多相关文章
- springboot整合视图层之jsp
在springboot中不推荐视图层使用jsp展示,但是人们以前已经习惯使用jsp,所以对jsp也有支持,但是是解耦性的.也就是说并没有像其他组件一样直接集成到启动器中,所以像jsp引擎之类的需要额外 ...
- springboot整合视图层之freemarker
整合freemarker要求必须将视图文件放在 src/main/resources下的templates文件夹下,该文件夹是安全的不可直接访问的,必须由controller之类的接受请求类去跳转,因 ...
- Spring MVC视图层:thymeleaf vs. JSP
本文对比了同一Spring MVC工程中相同页面(一个订阅表单)分别采用Thymeleaf和JSP(包括JSP.JSTL.Spring tag lib)两种方式的实现. 本文的所有代码来自一个可运行的 ...
- SpringBoot整合freemarker 引用基础
原 ElasticSearch学习笔记Ⅲ - SpringBoot整合ES 新建一个SpringBoot项目.添加es的maven坐标如下: <dependency> <groupI ...
- springboot学习入门简易版四---springboot2.0静态资源访问及整合freemarker视图层
2.4.4 SpringBoot静态资源访问(9) Springboot默认提供静态资源目录位置需放在classpath下,目录名需要符合如下规则 /static /public /resourc ...
- SpringBoot整合Jsp和Thymeleaf (附工程)
前言 本篇文章主要讲述SpringBoot整合Jsp以及SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf,实现一个简单的用户增删改查示例工程.事先说明,有三个项目,两个是单独整合的,一个是将它们整合在一起的 ...
- 【Springboot】Springboot整合Thymeleaf模板引擎
Thymeleaf Thymeleaf是跟Velocity.FreeMarker类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代JSP,相较与其他的模板引擎,它主要有以下几个特点: 1. Thymeleaf在有网络和无 ...
- Springboot整合thymeleaf模板
Thymeleaf是个XML/XHTML/HTML5模板引擎,可以用于Web与非Web应用. Thymeleaf的主要目标在于提供一种可被浏览器正确显示的.格式良好的模板创建方式,因此也可以用作静态建 ...
- SpringBoot:2.SpringBoot整合Thymeleaf模板引擎渲染web视图
在Web开发过程中,Spring Boot可以通过@RestController来返回json数据,那如何渲染Web页面?Spring Boot提供了多种默认渲染html的模板引擎,主要有以下几种: ...
随机推荐
- Swift DispatchQueue
延迟2s执行 DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now()+2)
- django 中session的存储和获取
- 1283: 骨牌铺方格(zzuli)
Problem Description 在2×n的一个长方形方格中,用一个1× 2的骨牌铺满方格,输入n ,输出铺放方案的总数.例如n=3时,为2× 3方格,骨牌的铺放方案有三种,如下图: Input ...
- django----常用功能
request.path_info 获取url地址
- CSS3媒体查询的部分重要属性
width:视口宽度 height:视口高度 device-width:渲染表面的宽度,就是设备屏幕的宽度 device-height:渲染表面的高度,就是设备屏幕的高度 orientation:检查 ...
- poj1236 SCC+缩点
/* 强连通分量内的点可以互相传送,可以直接缩点 缩点后得到一棵树 第一问的答案是零入度点数量, 第二问: 加多少边后变成强连通图 树上入度为0的点有p个,出度为0的点为q,那么答案就是max(p,q ...
- 在lnmp环境下,将原来的PHP7.0升级到PHP7.2
基础环境: 系统:centos6.8 环境:lnmp 停止PHP7.0的版本,在做如下操作: 1.下载php-7.2.6.tar.bz2软件包放在/opt 路径下 mkdir /usr/local ...
- Oracle下载 OPatch
今天被朋友问及,如何下载OPatch ...我当时有些凌乱的.事后想想,人与人的思维是不同的,对待同一个问题,有人觉得很简单,有人觉得无从下手 . 乱不多说了.开始说明下吧. 1. 首先要有一个MOS ...
- 蓝桥杯 历届试题 幸运数 dfs
历届试题 幸运数 时间限制:1.0s 内存限制:256.0MB 问题描述 幸运数是波兰数学家乌拉姆命名的.它采用与生成素数类似的"筛法"生成 . 首先从1开始写出自然数1,2, ...
- 纯css3实现的switch开关按钮
效果如图 <p> <label><input class="mui-switch mui-switch-anim" type="checkb ...
