Eat the Trees hdu 1693
Problem Description
Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable, e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat the trees?
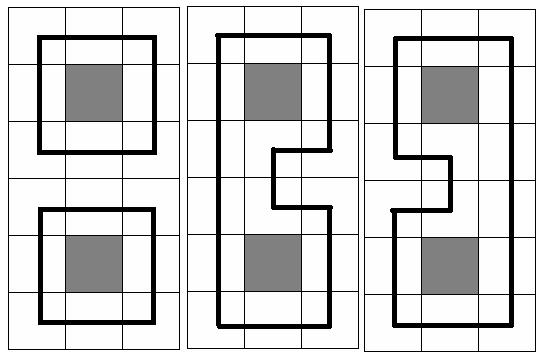
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M = 3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the chosen circuit(s))
Input
The input consists of several test cases. The first line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10 cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M, 1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1) separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1 means a cell that has exactly one tree.
Output
For each case, you should print the desired number of ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263 – 1. Use the format in the sample.
Sample Input
2
6 3
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case 1: There are 3 ways to eat the trees.
Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
最简单的插头dp
题目大意
给出一个M*N的地图,部分格子是障碍。
现把所有非障碍格子连起来,要求每个格子有且仅有有两个相邻格子与之相连,
问有多少种方案。
(N,M<=11)
插头dp的两个重要元素就是插头和决策线(这个还是去看论文吧)
主要就是讨论换行的情况和不换行的情况
然后就是讨论那个凸角的情况,还有当前决策的格子是不是障碍物,仔细一点就没问题了
被hdu坑了,pascal不能用<<,忘记用int64结果WA了,还好测了一下大数据发现了
var
f:array[..,..,..]of int64;
a:array[..,..]of longint;
n,m,time,t:longint; procedure init;
var
i,j:longint;
begin
fillchar(f,sizeof(f),);
fillchar(a,sizeof(a),);
read(n,m);
for i:= to n do
for j:= to m do
read(a[i,j]);
f[,m,]:=;
end; procedure work;
var
i,j,k:longint;
begin
for i:= to n do
for j:= to m do
if j= then
begin
if a[i,j]= then
for k:= to shl m- do
if k and = then inc(f[i,j,k shl +],f[i-,m,k])
else
begin
inc(f[i,j,k shl ],f[i-,m,k]);
inc(f[i,j,k shl -],f[i-,m,k]);
end
else
for k:= to shl m- do
if k and = then inc(f[i,j,k shl ],f[i-,m,k]);
end
else
begin
if a[i,j]= then
for k:= to shl (m+)- do
if k and( shl (j-))> then
if k and( shl j)> then inc(f[i,j,k- shl (j-)],f[i,j-,k])
else
begin
inc(f[i,j,k],f[i,j-,k]);
inc(f[i,j,k+ shl (j-)],f[i,j-,k]);
end
else
if k and( shl j)> then
begin
inc(f[i,j,k],f[i,j-,k]);
inc(f[i,j,k- shl (j-)],f[i,j-,k]);
end
else inc(f[i,j,k+ shl (j-)],f[i,j-,k])
else
for k:= to shl (m+)- do
if k and( shl (j-))= then inc(f[i,j,k],f[i,j-,k]);
end;
writeln('Case ',time,': There are ',f[n,m,],' ways to eat the trees.');
end; begin
read(t);
for time:= to t do
begin
init;
work;
end;
end.
Eat the Trees hdu 1693的更多相关文章
- 【HDU】1693 Eat the Trees
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1693 题意:n×m的棋盘求简单回路(可以多条)覆盖整个棋盘的方案,障碍格不许摆放.(n,m<=11) #i ...
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees——插头DP
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1693 第一道插头 DP ! 直接用二进制数表示状态即可. #include<cstdio> # ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿回路数)+ URAL 1519 Formula 1(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿单回路数)
插头DP基础题的样子...输入N,M<=11,以及N*M的01矩阵,0(1)表示有(无)障碍物.输出哈密顿回路(可以多回路)方案数... 看了个ppt,画了下图...感觉还是挺有效的... 参考 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP)
题目链接 USACO 第6章,第一题是一个插头DP,无奈啊.从头看起,看了好久的陈丹琦的论文,表示木看懂... 大体知道思路之后,还是无法实现代码.. 此题是插头DP最最简单的一个,在一个n*m的棋盘 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees
第一道(可能也是最后一道)插头dp.... 总算是领略了它的魅力... #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstr ...
- HDU - 1693 Eat the Trees(多回路插头DP)
题目大意:要求你将全部非障碍格子都走一遍,形成回路(能够多回路),问有多少种方法 解题思路: 參考基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题 - 陈丹琦 下面为代码 #include<cstdio> ...
- 【HDU】1693:Eat the Trees【插头DP】
Eat the Trees Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP,入门题)
Problem Description Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a ...
- Eat the Trees(hdu 1693)
题意:在n*m的矩阵中,有些格子有树,没有树的格子不能到达,找一条或多条回路,吃完所有的树,求有多少中方法. 第一道真正意义上的插头DP,可参考陈丹琦的<基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题> ...
随机推荐
- CSS3—三角形
话不多说看效果:演示效果,runjs 1.加了宽高和border,边用不同颜色显示,每条边都是一个梯形 2.去掉宽高,每条边都是三角形 3.只显示其中一条边就是不同的三角形了,是不是很简单,改变bor ...
- Java Concurrency - Phaser, Controlling phase change in concurrent phased tasks
The Phaser class provides a method that is executed each time the phaser changes the phase. It's the ...
- Spring(3.2.3) - Beans(12): 属性占位符
使用属性占位符可以将 Spring 配置文件中的部分元数据放在属性文件中设置,这样可以将相似的配置(如 JDBC 的参数配置)放在特定的属性文件中,如果只需要修改这部分配置,则无需修改 Spring ...
- DOS批处理命令-if语句
IF语句是批处理中执行的条件分歧处理. 批处理中,IF分歧的写法有好几种,接下来,我们来一个一个的分析IF语法的结构. 1.IF [NOT] ERRORLEVEL 番号 批处理命令 当ERRORLEV ...
- struts2文件上传(保存为BLOB格式)
html文件:提供上传文件的入口 <input type="file" name="upload"><!-- name很重要,与后面actio ...
- Tomcat上配置连接池{ connect error=Name [jdbc/OracleDB] is not bound in this Context. Unable to find [jdbc]}
. 在学习期间,从未实践过在tomcat上配置连接池,今天终于实现一次,在tomcat玩了一把,不知道你是否现在有和我一样的困境.废话少说直接上代码 java public static Con ...
- Bootstrap学习笔记(二) 表单
在Bootstrap学习笔记(一) 排版的基础上继续学习Bootstrap的表单,编辑器及head内代码不变. 3-1 基础表单 单中常见的元素主要包括:文本输入框.下拉选择框.单选按钮.复选按钮.文 ...
- 04_例子讲解:rlViewDemo.exe
参考资料:http://www.roboticslibrary.org/tutorials/first-steps-windows 使用rlViewDemo对应的快捷方式启动程序,可以看到如下界面: ...
- Windows Phone开发之”给我好评“
课余时间搞了一年的Windows phone开发,最近又开始重拾C#编程之道,之前下载许多应用都有"给我好评"的界面,那个时候自己的应用都没有这个界面,于是到处百度谷歌,却 ...
- mysql 主从同步 Last_SQL_Error
参考文章: http://kerry.blog.51cto.com/172631/277414/ http://hancang2010.blog.163.com/blog/static/1824602 ...