D. Happy Tree Party CodeForces 593D【树链剖分,树边权转点权】
Codeforces Round #329 (Div. 2)
D. Happy Tree Party
time limit per test
3 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Bogdan has a birthday today and mom gave him a tree consisting of n vertecies. For every edge of the tree i, some number x**i was written on it. In case you forget, a tree is a connected non-directed graph without cycles. After the present was granted, m guests consecutively come to Bogdan's party. When the i-th guest comes, he performs exactly one of the two possible operations:
- Chooses some number y**i, and two vertecies a**i and b**i. After that, he moves along the edges of the tree from vertex a**i to vertex b**i using the shortest path (of course, such a path is unique in the tree). Every time he moves along some edge j, he replaces his current number y**i by
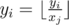 , that is, by the result of integer division y**i div x**j.
, that is, by the result of integer division y**i div x**j. - Chooses some edge p**i and replaces the value written in it xpi by some positive integer c**i < xpi.
As Bogdan cares about his guests, he decided to ease the process. Write a program that performs all the operations requested by guests and outputs the resulting value y**i for each i of the first type.
Input
The first line of the input contains integers, n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertecies in the tree granted to Bogdan by his mom and the number of guests that came to the party respectively.
Next n - 1 lines contain the description of the edges. The i-th of these lines contains three integers u**i, v**i and x**i (1 ≤ u**i, v**i ≤ n, u**i ≠ v**i, 1 ≤ x**i ≤ 1018), denoting an edge that connects vertecies u**i and v**i, with the number x**i initially written on it.
The following m lines describe operations, requested by Bogdan's guests. Each description contains three or four integers and has one of the two possible forms:
- 1 a**i b**i y**i corresponds to a guest, who chooses the operation of the first type.
- 2 p**i c**i corresponds to a guests, who chooses the operation of the second type.
It is guaranteed that all the queries are correct, namely ,1 ≤ p**i ≤ n - 1 , wherexpirepresents a number written on edgep**iat this particular moment of time that is not necessarily equal to the initial valuexpi
Output
For each guest who chooses the operation of the first type, print the result of processing the value y**i through the path from a**i to b**i.
Examples
input
Copy
6 61 2 11 3 71 4 42 5 52 6 21 4 6 172 3 21 4 6 171 5 5 202 4 11 5 1 3
output
Copy
24203
input
Copy
5 41 2 71 3 33 4 23 5 51 4 2 1001 5 4 12 2 21 1 3 4
output
Copy
202
Note
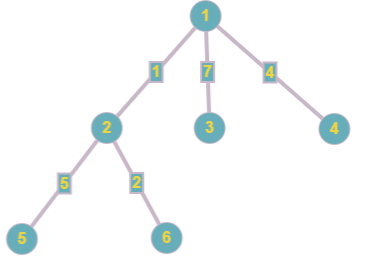
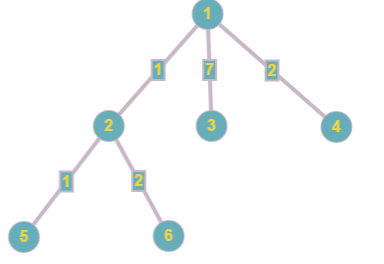
Initially the tree looks like this:
The response to the first query is: 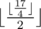 = 2
= 2
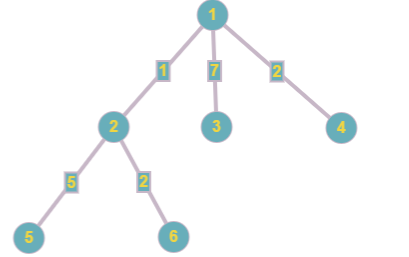
After the third edge is changed, the tree looks like this:
The response to the second query is: 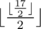 = 4
= 4
In the third query the initial and final vertex coincide, that is, the answer will be the initial number 20.
After the change in the fourth edge the tree looks like this:
In the last query the answer will be: 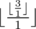 = 3
= 3
题意:
可以去这个链接阅读中文题意:
https://vjudge.net/problem/CodeForces-593D#author=AwayWithCorrect
思路:
1:边权转为点权建树:
确定一个root后,在dfs过程中,把边权值放在深度较大的节点的点权上。
这样建树的话,询问路径\(x->y\)的时候的边权sum和,实际求的过程中,点权只需要计算从(x到y路径的中的下一个节点z)到y节点的点权sum和。因为x的点权是root到x中的x上方的边权,并不在x到y的路径中。
2:树链剖分,同时用线段树维护连续点权的累乘积。
3:当线段树中的一个线段权值>1e18后,给该线段加个标记,或者权值定为0,因为询问是<=1e18的,那么如果询问包括了这个权值,答案一定是0.
4:更新边的权值时,直接用线段树更新那条边中深度更大的点权即可。
5:在树链剖分询问路径的过程中,别忘记1中讲到了去掉x节点点权,可以直接在最后的一个query中把id[x](x的dfs序)改为id[x]+1,因为一条链中dfs序时连续的。
判定x*y是否会超过1e18可以用这个函数的写法来求:
long long mul(long long aaa,long long bbb)
{
if(aaa==0||bbb==0)
return 0;
if(INF/aaa<bbb)
{
return 0;
}
else
return aaa*bbb;
}
AC代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <iomanip>
#define ALL(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define sz(a) int(a.size())
#define all(a) a.begin(), a.end()
#define rep(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<n;i++)
#define repd(i,x,n) for(int i=x;i<=n;i++)
#define pii pair<int,int>
#define pll pair<long long ,long long>
#define gbtb ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define MS0(X) memset((X), 0, sizeof((X)))
#define MSC0(X) memset((X), '\0', sizeof((X)))
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define eps 1e-6
#define gg(x) getInt(&x)
#define chu(x) cout<<"["<<#x<<" "<<(x)<<"]"<<endl
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
ll lcm(ll a, ll b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
ll powmod(ll a, ll b, ll MOD) {ll ans = 1; while (b) {if (b % 2)ans = ans * a % MOD; a = a * a % MOD; b /= 2;} return ans;}
inline void getInt(int* p);
const int maxn = 600010;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
/*** TEMPLATE CODE * * STARTS HERE ***/
int n, m;
int root;
ll a[maxn];// 初始点权
ll wt[maxn];// 新建编号点权。
int cnt;// 编号用的变量
int top[maxn];// 所在重链的顶点编号
int id[maxn];//节点的新编号。
typedef pair<int, ll> pil;
std::vector<pil> son[maxn];
int SZ[maxn];// 子数大小
int wson[maxn];// 重儿子
int fa[maxn];// 父节点
int dep[maxn];// 节点的深度
void dfs1(int id, int pre, int step) // 维护出sz,wson,fa,dep
{
dep[id] = step;
fa[id] = pre;
SZ[id] = 1;
int maxson = -1;
for (auto x : son[id])
{
if (x.fi != pre)
{
a[x.fi] = x.se;
dfs1(x.fi, id, step + 1);
SZ[id] += SZ[x.fi];
if (SZ[x.fi] > maxson)
{
maxson = SZ[x.fi];
wson[id] = x.fi;
}
}
}
}
//处理出top[],wt[],id[]
void dfs2(int u, int topf)
{
id[u] = ++cnt;
wt[cnt] = a[u];
top[u] = topf;
if (!wson[u]) // 没儿子时直接结束
{
return ;
}
dfs2(wson[u], topf); // 先处理重儿子
for (auto x : son[u])
{
if (x.fi == wson[u] || x.fi == fa[u]) //只处理轻儿子
{
continue;
}
dfs2(x.fi, x.fi); // 每个轻儿子以自己为top
}
}
struct node
{
int l, r;
ll sum;
} segment_tree[maxn << 2];
int getwei(ll x)
{
int res = 0;
while (x)
{
res++;
x /= 10;
}
return res;
}
ll num_1e18 = 1e18;
ll getcheng(ll v1, ll v2)
{
if (v1 == 0ll || v2 == 0ll)
{
return 0ll;
}
int x1 = getwei(v1);
int x2 = getwei(v2);
ll res;
if (x1 + x2 > 20)
{
res = 0ll;
} else if (x1 + x2 == 20 && num_1e18 / v2 == v2)
{
res = 0ll;
} else
{
res = (v1 * v2);
}
return res;
}
void pushup(int rt)
{
segment_tree[rt].sum = getcheng(segment_tree[rt << 1].sum, segment_tree[rt << 1 | 1].sum);
}
void build(int rt, int l, int r)
{
segment_tree[rt].l = l;
segment_tree[rt].r = r;
if (l == r)
{
segment_tree[rt].sum = wt[l];
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(rt << 1, l, mid);
build(rt << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(rt);
}
void update(int rt, int pos, ll val)
{
if (segment_tree[rt].l == pos && segment_tree[rt].r == pos)
{
segment_tree[rt].sum = min(segment_tree[rt].sum, val);
return ;
}
int mid = (segment_tree[rt].l + segment_tree[rt].r) >> 1;
if (mid >= pos)
{
update(rt << 1, pos, val);
}
if (mid < pos)
{
update(rt << 1 | 1, pos, val);
}
pushup(rt);
}
ll query(int rt, int l, int r)
{
if (l > r)
{
return 1ll;
}
if (segment_tree[rt].l >= l && segment_tree[rt].r <= r)
{
return segment_tree[rt].sum;
}
int mid = (segment_tree[rt].l + segment_tree[rt].r) >> 1;
ll res = 1ll;
if (mid >= l)
{
res = getcheng(res, query(rt << 1, l, r));
}
if (mid < r)
{
res = getcheng(res, query(rt << 1 | 1, l, r));
}
return res;
}
void uprange(int x, int y, ll k)
{
if (dep[x] < dep[y]) // 使x的top深度较大
{
swap(x, y);
}
update(1, id[x], k);
}
ll qrange(int x, int y)
{
ll ans = 1ll;
while (top[x] != top[y])
{
if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
{
swap(x, y);
}
ans = getcheng(ans, query(1, id[top[x]], id[x]));
x = fa[top[x]];
}
if (dep[x] > dep[y])
swap(x, y);
ans = getcheng(ans, query(1, id[x] + 1, id[y]));
return ans;
}
pii info[maxn];
int main()
{
// freopen("D:\\common_text\\code_stream\\in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("D:\\common_text\\code_stream\\out.txt","w",stdout);
gbtb;
// chu(getwei(1e9));
cin >> n >> m;
root = 1;
int u, v;
ll val;
repd(i, 1, n - 1)
{
cin >> u >> v >> val;
son[u].pb(mp(v, val));
son[v].pb(mp(u, val));
info[i] = mp(u, v);
}
dfs1(root, 0, 1);
dfs2(root, root);
build(1, 1, n);
int op, x, y;
ll z;
int isok = 0;
if (info[1].fi == 7610 && info[1].se == 132654)
{
isok = 1;
}
while (m--)
{
cin >> op;
if (op == 1)
{
cin >> x >> y >> z;
val = qrange(x, y);
// if (isok)
// {
// cout << " 1: " << val << endl;
// }
if (val == 0)
{
cout << val << endl;
} else
{
cout << z / val << endl;
}
} else if (op == 2)
{
cin >> x >> z;
uprange(info[x].fi, info[x].se, z);
}
}
return 0;
}
inline void getInt(int* p) {
char ch;
do {
ch = getchar();
} while (ch == ' ' || ch == '\n');
if (ch == '-') {
*p = -(getchar() - '0');
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 - ch + '0';
}
}
else {
*p = ch - '0';
while ((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
*p = *p * 10 + ch - '0';
}
}
}
D. Happy Tree Party CodeForces 593D【树链剖分,树边权转点权】的更多相关文章
- 4.12 省选模拟赛 LCA on tree 树链剖分 树状数组 分析答案变化量
LINK:duoxiao OJ LCA on Tree 题目: 一道树链剖分+树状数组的神题. (直接nQ的暴力有50. 其实对于树随机的时候不难想到一个算法 对于x的修改 暴力修改到根. 对于儿子的 ...
- hdu 3966 Aragorn's Story(树链剖分+树状数组/线段树)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3966 题意: 给出一棵树,并给定各个点权的值,然后有3种操作: I C1 C2 K: 把C1与C2的路 ...
- Aragorn's Story 树链剖分+线段树 && 树链剖分+树状数组
Aragorn's Story 来源:http://www.fjutacm.com/Problem.jsp?pid=2710来源:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.p ...
- 洛谷 P3384 【模板】树链剖分-树链剖分(点权)(路径节点更新、路径求和、子树节点更新、子树求和)模板-备注结合一下以前写的题目,懒得写很详细的注释
P3384 [模板]树链剖分 题目描述 如题,已知一棵包含N个结点的树(连通且无环),每个节点上包含一个数值,需要支持以下操作: 操作1: 格式: 1 x y z 表示将树从x到y结点最短路径上所有节 ...
- (简单) POJ 3321 Apple Tree,树链剖分+树状数组。
Description There is an apple tree outside of kaka's house. Every autumn, a lot of apples will grow ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) Problem D Misha, Grisha and Underground (Codeforces 832D) - 树链剖分 - 树状数组
Misha and Grisha are funny boys, so they like to use new underground. The underground has n stations ...
- Codeforces Round #425 (Div. 2) D 树链剖分 + 树状数组维护区间
一看就知道 可以LCA判断做 也可以树链剖分拿头暴力 然而快速读入和线段树维护区间会T70 于是只能LCA? 线段树的常数不小 于是需要另外一种办法来进行区间加减和查询区间和 就是使用树状数组 这个题 ...
- dsu+树链剖分+树分治
dsu,对于无修改子树信息查询,并且操作支持undo的问题 暴力dfs,对于每个节点,对所有轻儿子dfs下去,然后再消除轻儿子的影响 dfs重儿子,然后dfs暴力恢复轻儿子们的影响,再把当前节点影响算 ...
- HDU 3966 /// 树链剖分+树状数组
题意: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=3966 给一棵树,并给定各个点权的值,然后有3种操作: I x y z : 把x到y的路径上的所有点权值加 ...
- 7.18 NOI模拟赛 树论 线段树 树链剖分 树的直径的中心 SG函数 换根
LINK:树论 不愧是我认识的出题人 出的题就是牛掰 == 他好像不认识我 考试的时候 只会写42 还有两个subtask写挂了 拿了37 确实两个subtask合起来只有5分的好成绩 父亲能转移到自 ...
随机推荐
- 【Python】机器学习之单变量线性回归 利用正规方程找到合适的参数值
[Python]机器学习之单变量线性回归 利用正规方程找到合适的参数值 本次作业来自吴恩达机器学习. 你是一个餐厅的老板,你想在其他城市开分店,所以你得到了一些数据(数据在本文最下方),数据中包括不同 ...
- Had I not seen the Sun(如果我不曾见过太阳)
Had I not seen the Sun by Emily Dickinson Had I not seen the Sun I could have borne the shade But Li ...
- win10配置Keras及GPU环境
今天搭建了Keras深度学习的环境 详细记录一下 安装Anaconda3 Anaconda指的是一个开源的Python发行版本,其包含了conda.Python等180多个科学包及其依赖项. Anac ...
- 开发者福利!请及时领取您的SpreadJS临时部署授权码
SpreadJS 于2015年发布,至今已有4年历史,作为一款基于 HTML5 的纯前端电子表格控件,在短短四年间,即在财税.金融.计算机软件与服务.工业制造.大数据应用.电力能源.交通.物流运输.医 ...
- 关于springboot的日志logging.file和logging.path的配置问题
springboot日志配置 logging.path logging.file 它们俩不会同时生效,so只配置其中一个就好了. eg1: 单独一个path配置 logging.path=E:/lo ...
- java--键盘输入任意数字进行求和
思路,我将键盘输入的数放入数组,然后便利数组进行求和 package com.test.day01; import java.util.Scanner; public class Test { pub ...
- python 基础(十七)--hashlib加密模块
hashlib加密模块 两种方式使用 字符串是中文时需要先编码成utf-8 常用加密算法:md5,sha1(已被破解)等... >>> a= hashlib.md5() >&g ...
- python+django学习三
在这个网站看https://sshwsfc.github.io/xadmin/ xadmin结果一堆的坑,文档找不到界面,dome登陆就报错permission denied for rela ...
- 微信小程序异步回调
场景如下:现有一个方法需要等待其他N个异步函数执行完毕后执行,callback麻烦的头大,翻了一波API原来小程序已经支持 async函数,那一切就好办了. 废话不多说,直接开始撸... 第一步:打开 ...
- Linux下mysql不区分大小写设置
Linux环境下的MySQL数据库的表名默认是区分大小写的 Windows环境下的MySQL数据库的表名默认是不区分大小写的 所以Linux下想mysql不区分下大写可以查看/etc/my.cnf文件 ...
