《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.15
代码:
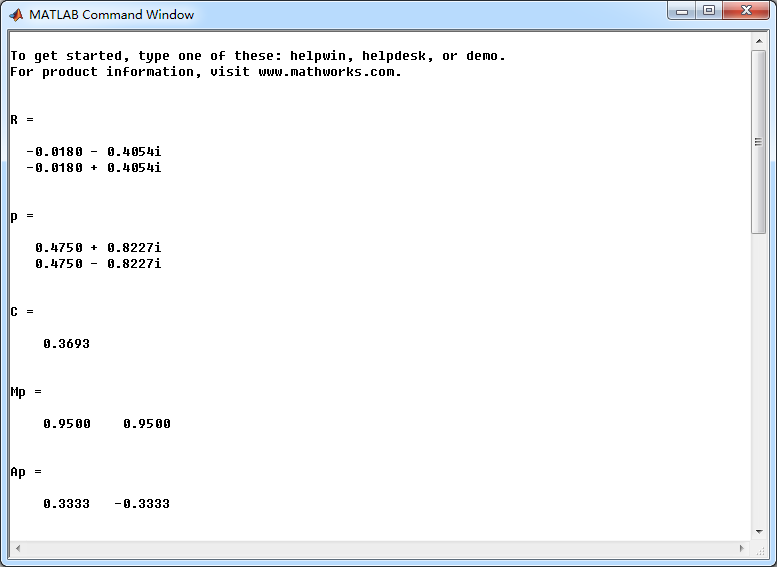
b = [1/3, 1/3, 1/3]; a = [1, -0.95, 0.9025]; % x(n) y(n) coefficient [R, p, C] = residuez(b,a) Mp = (abs(p))', Ap = (angle(p))'/pi % polar form Y = [-2, -3]; X =[1, 1]; xic = filtic(b,a,Y,X); %% ----------------------------------------------
%% START a determine H(z) and sketch
%% ----------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.15 H(z) its pole-zero plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title('pole-zero plot'); grid on; %% ----------------------------------------------
%% END
%% ---------------------------------------------- bxplus = [1, -0.5]; axplus = [1, -1, 1]; % X(z) transform coeff
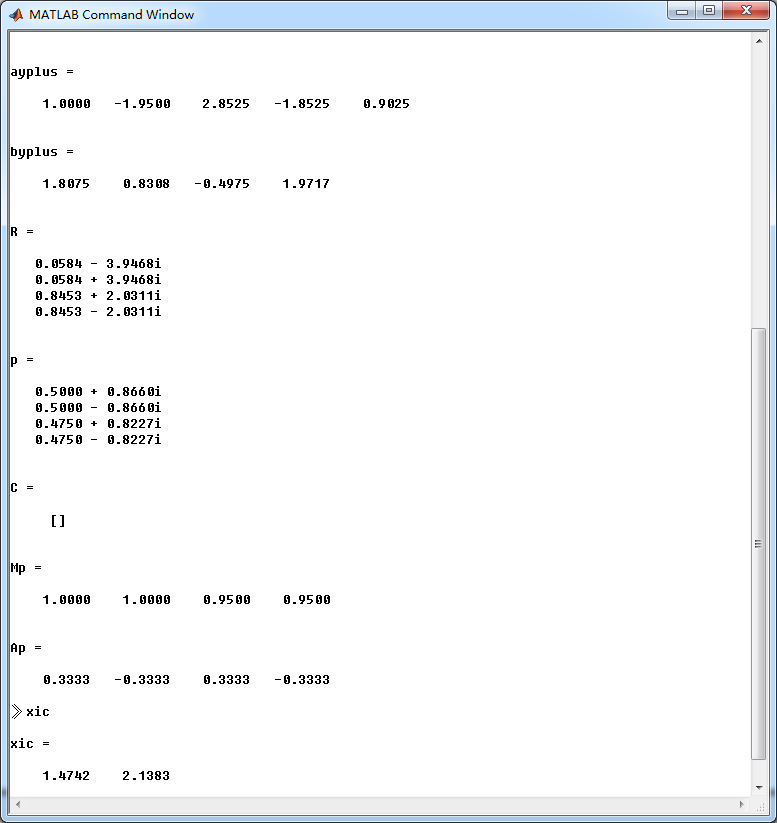
ayplus = conv(a, axplus) % Denominator of Yplus(z)
byplus = conv(b,bxplus) + conv(xic,axplus) % Numerator of Yplus(z) [R, p, C] = residuez(byplus, ayplus)
Mp = (abs(p))' , Ap = (angle(p))'/pi % polar form %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 1st form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
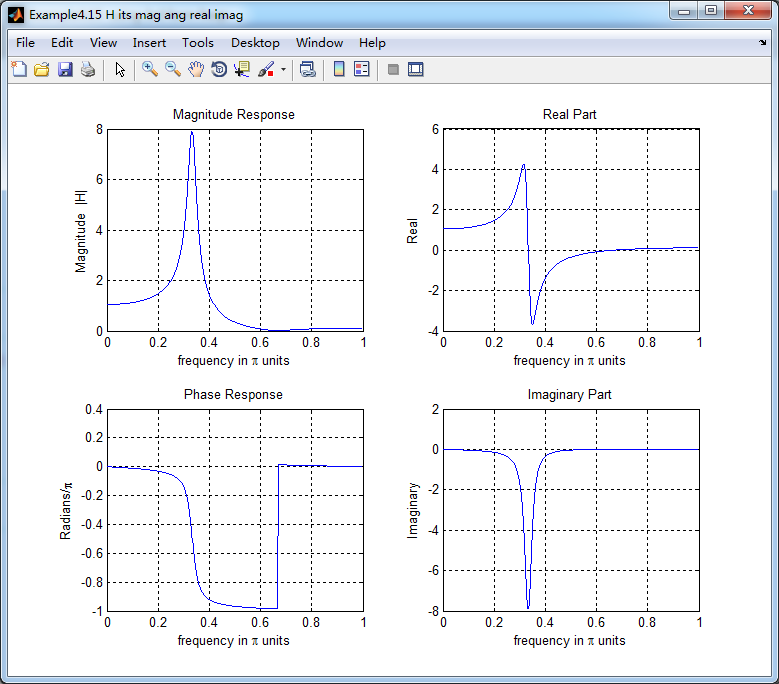
[H,w] = freqz(b,a,500); % 1st form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.15 H its mag ang real imag');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START b |H| <H
%% 3rd form of freqz
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
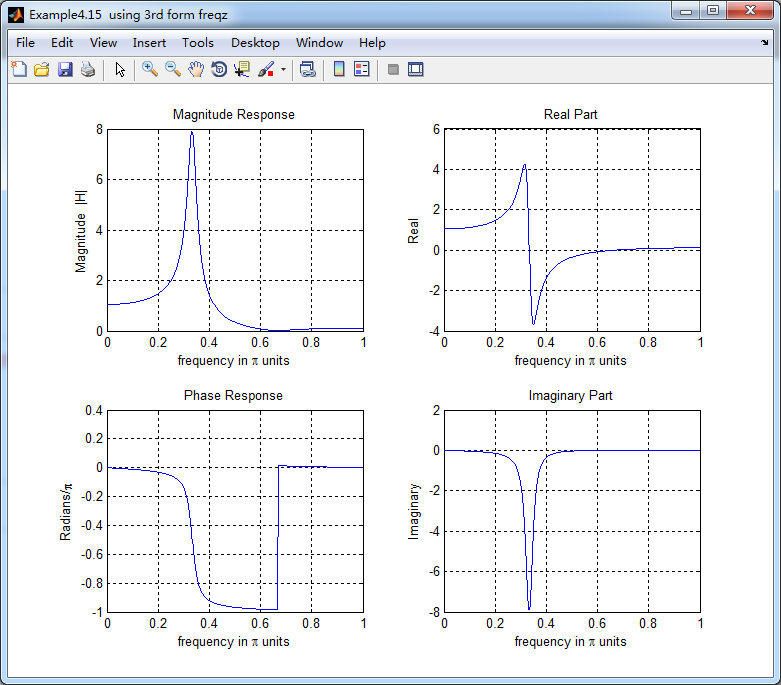
w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; H = freqz(b,a,w);
%[H,w] = freqz(b,a,200,'whole'); % 3rd form of freqz magH = abs(H); angH = angle(H); realH = real(H); imagH = imag(H); %% ================================================
%% START H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Example4.15 using 3rd form freqz ');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magH); grid on; %axis([0,1,0,1.5]);
title('Magnitude Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |H|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angH/pi); grid on; % axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Phase Response');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realH); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagH); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% ==================================================
%% END H's mag ang real imag
%% ================================================== %% ---------------------------------------------------------------
%% END b |H| <H
%% --------------------------------------------------------------- %% START Check
n = [0:7]; x = cos(pi*n/3); y_ori = filter(b,a,x,xic) %% MATLAB verification
A = real(2*R(1)); B = imag(2*R(1)); C = real(2*R(3)); D = imag(2*R(4));
y_check = A*cos(pi*n/3) + B *sin(pi*n/3) + ((0.95).^n) .* (C*cos(pi*n/3) + D*sin(pi*n/3))
结果:
《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example4.15的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.15
上代码: subplot(1,1,1); b = 1; a = [1, -0.8]; n = [0:100]; x = cos(0.05*pi*n); y = filter(b,a,x); figur ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.9
用到的性质 上代码: n = 0:100; x = cos(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8
代码: x = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. X = ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.7
上代码: x1 = rand(1,11); x2 = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; alpha = 2; beta = 3; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [ ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.6
代码: n = [-5:5]; x = (-0.9).^n; % x(n) = k = -200:200; w = (pi/100)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 101 ...
随机推荐
- VB中字符串操作函数
Len Len(string|varname) 返回字符串内字符的数目,或是存储一变量所需的字节数. Trim Trim(string) 将字符串前后的空格去掉 Ltrim Ltrim(string) ...
- 将file转变成contenthash
一.将MultipartFile转file CommonsMultipartFile cf= (CommonsMultipartFile)file; DiskFileItem fi = (DiskFi ...
- 【leetcode】 Unique Binary Search Trees II (middle)☆
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n. For e ...
- 【leetcode】 search Insert Position(middle)
Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the ...
- MAC系统下,删除.svn文件
MAC系统下,.svn文件是隐藏的. 如果项目是非export导出的,那么项目中会有很多的.svn文件. 如果项目的体积非常庞大,我们如何快速的批量删除.svn文件呢?下面是操作方法: 打开终端,cd ...
- Centos以rpm方式进行安装MySql
安装过很多次mysql了,却没好好总结过,每次安装完了都忘,下次还要重新Google,这次总结下,自己以后也有的查. 1.安装采用的的rpm包的方式,安装前要先看系统内是否安装了旧版本的MySql和m ...
- XMPP框架下微信项目总结(3)获取点子名片信息(个人资料)更新电子名片
思路:1 调用方法,添加点子名片模块(名片信息含电话,头像,单位个人信息)等 开启ps:APP发送请求到服务器openfire,服务器返回个人信息,app存储到数据库,app界面需要数据通过数据库获取 ...
- MyString(重写String)
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/d7ac113243323968011c925b.html 已知类String的原型为: class String { public: ...
- NYOJ之XX和OO
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAskAAAI0CAIAAABgWyN9AAAgAElEQVR4nO3dPW7jyt4n4NmEcy/EaW
- 利用drozer进行Android渗透测试
一.安装与启动 1. 安装 第一步:从 http://mwr.to/drozer 下载Drozer (Windows Installer) 第二步:在 Android 设备中安装 agent.apk ...
