Service Locator Pattern 服务定位
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/service-locator-pattern/

Service Locator Pattern
Last Updated: 06-03-2018
The service locator pattern is a design pattern used in software development to encapsulate the processes involved in obtaining a service with a strong abstraction layer. This pattern uses a central registry known as the “service locator” which on request returns the information necessary to perform a certain task.
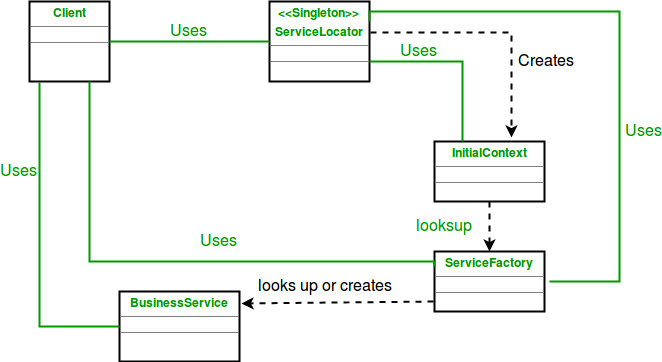
The ServiceLocator is responsible for returning instances of services when they are requested for by the service consumers or the service clients.
- Service Locator : The Service Locator abstracts the API lookup services, vendor dependencies, lookup complexities, and business object creation, and provides a simple interface to clients. This reduces the client’s complexity. In addition, the same client or other clients can reuse the Service Locator.
- InitialContext : The InitialContext object is the start point in the lookup and creation process. Service providers provide the context object, which varies depending on the type of business object provided by the Service Locator’s lookup and creation service.
- ServiceFactory : The ServiceFactory object represents an object that provides life cycle management for the BusinessService objects. The ServiceFactory object for enterprise beans is an EJBHome object.
- BusinessService : The BusinessService is a role that is fulfilled by the service the client is seeking to access. The BusinessService object is created or looked up or removed by the ServiceFactory. The BusinessService object in the context of an EJB application is an enterprise bean.
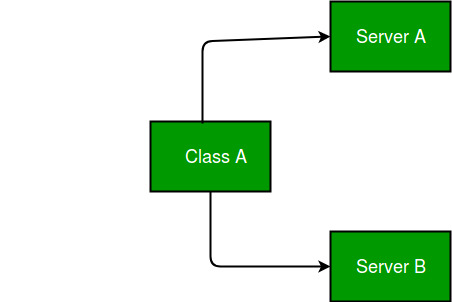
Suppose classes with dependencies on services whose concrete types are specified at compile time.
In the above diagram, ClassA has compile time dependencies on ServiceA and ServiceB.But this situation has drawbacks.
- If we want to replace or update the dependencies we must change the classes source code and recompile the solution.
- The concrete implementation of the dependencies must be available at compile time.
By using the Service Locator pattern :
In simple words, Service Locator pattern does not describe how to instantiate the services. It describes a way to register services and locate them.
Let’s see an example of Service Locator Pattern.
edit
play_arrow
brightness_4
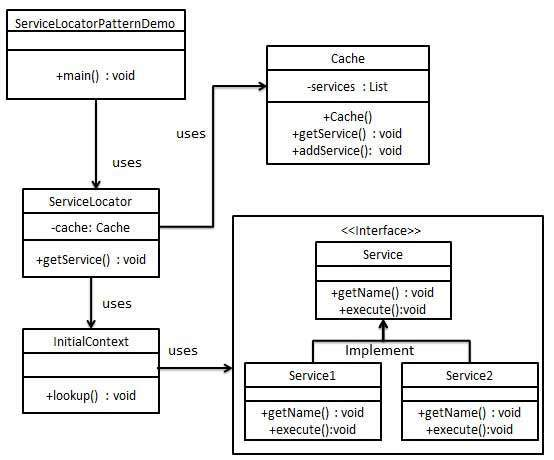
// Java program to // illustrate Service Design Service // Locator Pattern import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // Service interface // for getting name and // Executing it. interface Service { public String getName(); public void execute(); } // Service one implementing Locator class ServiceOne implements Service { public void execute() { System.out.println("Executing ServiceOne"); } @Override public String getName() { return "ServiceOne"; } } // Service two implementing Locator class ServiceTwo implements Service { public void execute() { System.out.println("Executing ServiceTwo"); } @Override public String getName() { return "ServiceTwo"; } } // Checking the context // for ServiceOne and ServiceTwo class InitialContext { public Object lookup(String name) { if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("ServiceOne")) { System.out.println("Creating a new ServiceOne object"); return new ServiceOne(); } else if (name.equalsIgnoreCase("ServiceTwo")) { System.out.println("Creating a new ServiceTwo object"); return new ServiceTwo(); } return null; } } class Cache { private List<Service> services; public Cache() { services = new ArrayList<Service>(); } public Service getService(String serviceName) { for (Service service : services) { if (service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(serviceName)) { System.out.println("Returning cached " + serviceName + " object"); return service; } } return null; } public void addService(Service newService) { boolean exists = false; for (Service service : services) { if (service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(newService.getName())) { exists = true; } } if (!exists) { services.add(newService); } } } // Locator class class ServiceLocator { private static Cache cache; static { cache = new Cache(); } public static Service getService(String name) { Service service = cache.getService(name); if (service != null) { return service; } InitialContext context = new InitialContext(); Service ServiceOne = (Service)context.lookup(name); cache.addService(ServiceOne); return ServiceOne; } } // Driver class class ServiceLocatorPatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Service service = ServiceLocator.getService("ServiceOne"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("ServiceTwo"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("ServiceOne"); service.execute(); service = ServiceLocator.getService("ServiceTwo"); service.execute(); } } |
Output:
Creating a new ServiceOne object
Executing ServiceOne
Creating a new ServiceTwo object
Executing ServiceTwo
Returning cached ServiceOne object
Executing ServiceOne
Returning cached ServiceTwo object
Executing ServiceTwo
Advantages :
- Applications can optimize themselves at run-time by selectively adding and removing items from the service locator.
- Large sections of a library or application can be completely separated. The only link between them becomes the registry.
Disadvantages :
- The registry makes the code more difficult to maintain (opposed to using Dependency injection), because it becomes unclear when you would be introducing a breaking change.
- The registry hides the class dependencies causing run-time errors instead of compile-time errors when dependencies are missing.
Strategies
The following strategies are used to implement service Locator Pattern :
- EJB Service Locator Strategy : This strategy uses EJBHome object for enterprise bean components and this EJBHome is cached in the ServiceLocator for future use when the client needs the home object again.
- JMS Queue Service Locator Strategy : This strategy is applicable to point to point messaging requirements. The following the strategies under JMS Queue Service Locator Strategy.
- JMS Queue Service Locator Strategy
- JMS Topic Service Locator Strategy
- Type Checked Service Locator Strategy : This strategy has trade-offs. It reduces the flexibility of lookup, which is in the Services Property Locator strategy, but add the type checking of passing in a constant to the ServiceLocator.getHome() method.
Design Pattern - Service Locator Pattern - Tutorialspoint https://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/service_locator_pattern.htm
Service Locator Pattern 服务定位的更多相关文章
- .NET 服务器定位模式(Service Locator Pattern)——Common Service Locator
本文内容 场景 目标 解决方案 实现细节 思考 相关模式 更多信息 参考资料 Common Service Locator 代码很简单,它一般不会单独使用,而是作为一个单件模式,与像 .net Uni ...
- [Design Pattern] Service Locator Pattern 简单案例
Service Locator Pattern,即服务定位模式,用于定位不同的服务.考虑到 InitialContext::lookup 的成本比较高,提供了 Cache 类缓存以定位到的服务. 代码 ...
- 《Prism 5.0源码走读》Service Locator Pattern
在Prism Bootstrapper里面取实例的时候使用 ServiceLocator模式,使用的是CommonServiceLocator库 (http://commonservicelocato ...
- 服务定位器(Service Locator)
服务定位器(Service Locator) 跟DI容器类似,引入Service Locator目的也在于解耦.有许多成熟的设计模式也可用于解耦,但在Web应用上, Service Locator绝对 ...
- Design Pattern - Service Locator Pattern--转载
原文地址:http://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/service_locator_pattern.htm The service locator de ...
- Service Locator 模式
什么是Service Locator 模式? 服务定位模式(Service Locator Pattern)是一种软件开发中的设计模式,通过应用强大的抽象层,可对涉及尝试获取一个服务的过程进行封装.该 ...
- Atitit。如何实现dip, di ,ioc ,Service Locator的区别于联系
Atitit.如何实现dip, di ,ioc ,Service Locator的区别于联系 1. Dip原则又来自于松耦合思想方向1 2. 要实现dip原则,有以下俩个模式1 3. Ioc和di的 ...
- 【转】Understanding Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection and Service Locator Print
原文:https://www.dotnettricks.com/learn/dependencyinjection/understanding-inversion-of-control-depende ...
- PHP中应用Service Locator服务定位及单例模式
单例模式将一个对象实例化后,放在静态变量中,供程序调用. 服务定位(ServiceLocator)就是对象工场Factory,调用者对象直接调用Service Locator,与被调用对象减轻了依赖关 ...
随机推荐
- sql 中 foreach 中传入多个不同的参数问题
<!--查找某用户绑定的药物不良反应报告列表--> <select id="selectSurveyListByUserProId" resultType=&qu ...
- Flowable 简介
一.Flowable 入门介绍 官网地址:https://www.flowable.org/ Flowable6.3中文教程:https://tkjohn.github.io/flowable-use ...
- 【C++】C++之类型转换
作者:李春港 出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/lcgbk/p/14209848.html 目录 一.前言 二.static_cast 2.1 使用场景 2.2 实例 三.dyna ...
- Vue从零开发SPA项目
所谓SPA(single page web application),就是单页面项目的意思. vue的亮点就是我们只需要关注数据的变化,下面演示一下从零开始创建一个独立项目,并且能自定义路由,提交表单 ...
- WebSocket入门及使用指南
最近在一个项目中,需要使用到websocket,于是就花了一点时间来熟悉websocket并总结写篇blog. 为何使用websocket 在浏览器与服务器通信间,传统的 HTTP 请求在某些场景下并 ...
- 远程控制卡 使用ipmitools设置ipmi
远程控制卡 使用ipmitools设置ipmi 使用DELL的远程控制卡可以方便的管理服务器 在CentOS中可以使用ipmitools管理 IPMI( Intelligent Platform Ma ...
- Rejecting mapping update to [xxx] as the final mapping would have more than 1 type: [xxx, xx]
说明: 1.elasticsearch 版本 6.3.1 2.在同一个index下创建两个type时报错,信息如下: 在创建第二个type:solr时,先前已经在相同索引下创建了一个type:es [ ...
- 上班从换一张桌面壁纸开始——开源小工具Bing每日壁纸
发布一个自用的开源小软件,Bing每日壁纸,使用c# winform开发.该小软件可以自动获取Bing的精美图片设置为壁纸,并且支持随机切换历史壁纸,查看壁纸故事. 功能特性 自动获取Bing最新图片 ...
- 【JavaWeb】Servlet 程序
Servlet 程序 Servlet Servlet 是在 Web 服务器中运行的小型 Java 程序.Servlet 通常通过 HTTP(超文本传输协议)接收和响应来自 Web 客户端的请求. ...
- 2020周阳SpringCloud完整版笔记--一
微服务架构入门 微服务 的概念最早产生于Martin Fowler在2014年的一篇论文中. 微服务架构是一种架构模式,他提倡将单一应用程序划分成一组小的服务,服务与服务之间互相协调.相互配合,为用户 ...
