DeepLearning Intro - sigmoid and shallow NN
This is a series of Machine Learning summary note. I will combine the deep learning book with the deeplearning open course . Any feedback is welcomed!
First let's go through some basic NN concept using Bernoulli classification problem as an example.
Activation Function
1.Bernoulli Output
1. Definition
When dealing with Binary classification problem, what activavtion function should we use in the output layer?
Basically given \(x \in R^n\), How to get \(P(y=1|x)\) ?
2. Loss function
Let $\hat{y} = P(y=1|x) $, We would expect following output
\[P(y|x) = \begin{cases}
\hat{y} & \quad when & y= 1\\
1-\hat{y} & \quad when & y= 0\\
\end{cases}
\]
Above can be simplified as
\[P(y|x)= \hat{y}^{y}(1-\hat{y})^{1-y}\]
Therefore, the maximum likelihood of m training samples will be
\[\theta_{ML} = argmax\prod^{m}_{i=1}P(y^i|x^i)\]
As ususal we take the log of above function and get following. Actually for gradient descent log has other advantages, which we will discuss later.
\[log(\theta_{ML}) = argmax\sum^{m}_{i=1} ylog(\hat{y})+(1-y)log(1-\hat{y}) \]
And the cost function for optimization is following
\[J(w,b) = \sum ^{m}_{i=1}L(y^i,\hat{y}^i)= -\sum^{m}_{i=1}ylog(\hat{y})+(1-y)log(1-\hat{y})\]
The cost function is the sum of loss from m training samples, which measures the performance of classification algo.
And yes here it is exactly the negative of log likelihood. While Cost function can be different from negative log likelihood, when we apply regularization. But here let's start with simple version.
So here comes our next problem, how can we get 1-dimension $ log(\hat{y})$, given input \(x\), which is n-dimension vector ?
3. Activtion function - Sigmoid
Let \(h\) denotes the output from the previous hidden layer that goes into the final output layer. And a linear transformation is applied to \(h\) before activation function.
Let \(z = w^Th +b\)
The assumption here is
\[log(\hat{y}) = \begin{cases}
z & \quad when & y= 1\\
0 & \quad when & y= 0\\
\end{cases}
\]
Above can be simplified as
\[log(\hat{y}) = yz\quad \to \quad \hat{y} = exp(yz)\]
This is an unnormalized distribution of \(\hat{y}\). Because \(y\) denotes probability, we need to further normalize it to $ [0,1]$.
\[\hat{y} = \frac{exp(yz)} {\sum^1_{y=0}exp(yz)} \\
=\frac{exp(z)}{1+exp(z)}\\
\quad \quad \quad \quad = \frac{1}{1+exp(-z)} = \sigma(z)
\]
Bingo! Here we go - Sigmoid Function: \(\sigma(z) = \frac{1}{1+exp(-z)}\)
\[p(y|x) = \begin{cases}
\sigma(z) & \quad when & y= 1\\
1-\sigma(z) & \quad when & y= 0\\
\end{cases}
\]
Sigmoid function has many pretty cool features like following:
\[ 1- \sigma(x) = \sigma(-x) \\
\frac{d}{dx} \sigma(x) = \sigma(x)(1-\sigma(x)) \\
\quad \quad = \sigma(x)\sigma(-x)
\]
Using the first feature above, we can further simply the bernoulli output into following:
\[p(y|x) = \sigma((2y-1)z)\]
4. gradient descent and back propagation
Now we have target cost fucntion to optimize. How does the NN learn from training data? The answer is -- Back Propagation.
Actually back propagation is not some fancy method that is designed for Neural Network. When training sample is big, we can use back propagation to train linear regerssion too.
Back Propogation is iteratively using the partial derivative of cost function to update the parameter, in order to reach local optimum.
$ \
Looping \quad m \quad samples :\
w= w - \frac{\partial J(w,b)}{\partial w} \
b= b - \frac{\partial J(w,b)}{\partial b}
$
Bascically, for each training sample \((x,y)\), we compare the \(y\) with \(\hat{y}\) from output layer. Get the difference, and compute which part of difference is from which parameter( by partial derivative). And then update the parameter accordingly.
And the derivative of sigmoid function can be calcualted using chaining method:
For each training sample, let \(\hat{y}=a = \sigma(z)\)
\[ \frac{\partial L(a,y)}{\partial w} =
\frac{\partial L(a,y)}{\partial a} \cdot
\frac{\partial a}{\partial z} \cdot
\frac{\partial z}{\partial w}\]
Where
1.$\frac{\partial L(a,y)}{\partial a}
=-\frac{y}{a} + \frac{1-y}{1-a} $
Given loss function is
\(L(a,y) = -(ylog(a) + (1-y)log(1-a))\)
2.\(\frac{\partial a}{\partial z} = \sigma(z)(1-\sigma(z)) = a(1-a)\).
See above for sigmoid features.
3.\(\frac{\partial z}{\partial w} = x\)
Put them together we get :
\[ \frac{\partial L(a,y)}{\partial w} = (a-y)x\]
This is exactly the update we will have from each training sample \((x,y)\) to the parameter \(w\).
5. Entire work flow.
Summarizing everything. A 1-layer binary classification neural network is trained as following:
- Forward propagation: From \(x\), we calculate \(\hat{y}= \sigma(z)\)
- Calculate the cost function \(J(w,b)\)
- Back propagation: update parameter \((w,b)\) using gradient descent.
- keep doing above until the cost function stop improving (improment < certain threshold)
6. what's next?
When NN has more than 1 layer, there will be hidden layers in between. And to get non-linear transformation of x, we also need different types of activation function for hidden layer.
However sigmoid is rarely used as hidden layer activation function for following reasons
- vanishing gradient descent
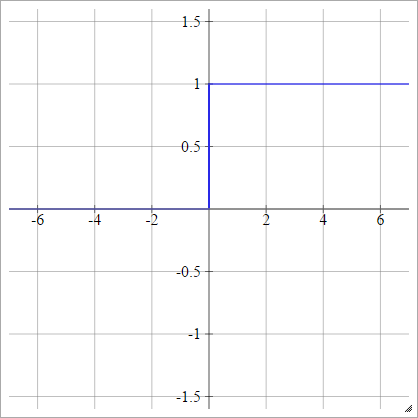
the reason we can't use [left] as activation function is because the gradient is 0 when \(z>1 ,z <0\).
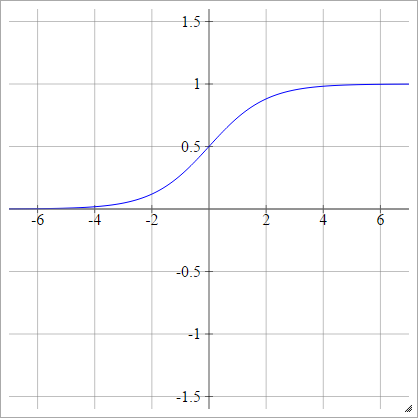
Sigmoid only solves this problem partially. Becuase \(gradient \to 0\), when \(z>1 ,z <0\).
| \(p(y=1\|x)= max\{0,min\{1,z\}\}\) | \(p(y=1\|x)= \sigma(z)\) |
|---|---|
 |
 |
- non-zero centered
To be continued
Reference
- Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, Aaron Conrville, "Deep Learning"
- Deeplearning.ai https://www.deeplearning.ai/
DeepLearning Intro - sigmoid and shallow NN的更多相关文章
- Sigmoid function in NN
X = [ones(m, ) X]; temp = X * Theta1'; t = size(temp, ); temp = [ones(t, ) temp]; h = temp * Theta2' ...
- Deeplearning - Overview of Convolution Neural Network
Finally pass all the Deeplearning.ai courses in March! I highly recommend it! If you already know th ...
- DeepLearning - Regularization
I have finished the first course in the DeepLearnin.ai series. The assignment is relatively easy, bu ...
- DeepLearning - Forard & Backward Propogation
In the previous post I go through basic 1-layer Neural Network with sigmoid activation function, inc ...
- Pytorch_第六篇_深度学习 (DeepLearning) 基础 [2]---神经网络常用的损失函数
深度学习 (DeepLearning) 基础 [2]---神经网络常用的损失函数 Introduce 在上一篇"深度学习 (DeepLearning) 基础 [1]---监督学习和无监督学习 ...
- 0802_转载-nn模块中的网络层介绍
0802_转载-nn 模块中的网络层介绍 目录 一.写在前面 二.卷积运算与卷积层 2.1 1d 2d 3d 卷积示意 2.2 nn.Conv2d 2.3 转置卷积 三.池化层 四.线性层 五.激活函 ...
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Neural Networks and Deep Learning This is the first course of the deep learning specialization at Co ...
- 关于BP算法在DNN中本质问题的几点随笔 [原创 by 白明] 微信号matthew-bai
随着deep learning的火爆,神经网络(NN)被大家广泛研究使用.但是大部分RD对BP在NN中本质不甚清楚,对于为什这么使用以及国外大牛们是什么原因会想到用dropout/sigmoid ...
- Pytorch实现UNet例子学习
参考:https://github.com/milesial/Pytorch-UNet 实现的是二值汽车图像语义分割,包括 dense CRF 后处理. 使用python3,我的环境是python3. ...
随机推荐
- react使用echarts地图实现中国地图大区展示
日常项目中经常会用到百度地图或者echarts图标展示,今天给大家展示的是如何在react开发项目中使用百度echars的地图展示,把中国地图分为东北大区.华东大区.华南大区.华西大区.华中大区以及华 ...
- 一点一点看JDK源码(二)java.util.List
一点一点看JDK源码(二)java.util.List liuyuhang原创,未经允许进制转载 本文举例使用的是JDK8的API 目录:一点一点看JDK源码(〇) 1.综述 List译为表,一览表, ...
- 【2013 ICPC亚洲区域赛成都站 F】Fibonacci Tree(最小生成树+思维)
Problem Description Coach Pang is interested in Fibonacci numbers while Uncle Yang wants him to do s ...
- python初学者日记01(字符串操作方法)
时间:2018/12/16 作者:永远的码农(博客园) 环境: win10,pycharm2018,python3.7.1 1.1 基础操作(交互输入输出) input = input(" ...
- ps命令 百度+加自己的理解
ps故为process status的缩写,即为进程状态的命令, ps命令详解, 1)ps a 显示现行终端机下的所有程序,包括其他用户的程序.2)ps -A 显示所有程序.3)ps c 列出程序时, ...
- Linux常用97条命令
1.ls [选项] [目录名 | 列出相关目录下的所有目录和文件 -a 列出包括.a开头的隐藏文件的所有文件 -A 通-a,但不列出"."和".." -l ...
- DQL数据查询
set hive.fetch.task.conversion=more; -- 避免触发MR job select distinct name from employee_id limit 2; -- ...
- python+selenium webdriver.firefox()方式配置浏览器设置
webdriver.firefox() 爬虫需求: (其实是输入参数可获取.zip/pdf 文件,然后点击下载) ——但是firefox浏览器有Bug,点击下载之后会有弹出窗口,需要你点击确定,这怎 ...
- s3c2440系统时钟详解
一.S3C2440系统时钟体系 S3C2440的时钟控制逻辑可以外接晶振,然后通过内部电路产生时钟源:也可以直接使用内部提供的时钟源,他们通过引脚的设置来选择.时钟逻辑给整个芯片提供了3中时钟:FCL ...
- python三大器之while,if,for循环
一.for循环(遍历循环) 在Python你可能要经常遍历列表的所有元素,对每个元素执行相同的操作;对于包含数字的列表,可能要对每个元素进行相同的计算;在网站中,可能需要显示文章中的每个标题等等.某一 ...
