ML: 聚类算法R包-对比
测试验证环境
数据: 7w+ 条,数据结构如下图:
> head(car.train)
DV DC RV RC SOC HV LV HT LT Type TypeName
1 379 85.09 0.00 0.0 62.99 3.99 0.00 12 0 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
2 379 85.09 370.89 59.9 63.99 4.01 0.00 12 0 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
3 379 85.09 0.00 0.0 64.99 4.01 0.00 12 0 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
4 379 85.09 0.00 0.0 66.00 4.03 1.55 12 11 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
5 379 85.09 0.00 0.0 67.00 4.03 0.00 12 0 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
6 379 85.09 0.00 0.0 68.00 4.05 0.00 13 0 10f689e8-e6cc-47a3-be5a-dbc3833428ef EV200
机器配置:

R version:
> version
_
platform x86_64-w64-mingw32
arch x86_64
os mingw32
system x86_64, mingw32
status
major 3
minor 2.5
year 2016
month 04
day 14
svn rev 70478
language R
version.string R version 3.2.5 (2016-04-14)
nickname Very, Very Secure Dishes
R包性能对比
全局函数及参数设置
##----------------------全局设置-------------------------------
remove(list=ls())
space_path <- c("E:\\RScore\\kmeans\\")
setwd(space_path)
Sys.setlocale(category = "LC_ALL",local="chinese") ##table 行列转换函数
tblView <- function (tbl)
{
##install.packages("tidyr")
library(tidyr)
df <- as.data.frame(tbl)
df <- spread(data = df, key = Var2, value = Freq)
datatable(df)
} ## 公共函数:数据读写及计算
source("core.R",encoding="utf-8")
teld.ml.init() ##训练样本
car.train <- teld.ml.rQuery("D_Cluster")
newdata <- car.train[1:8]
stats::kmeans
source code:
> ################################################stats::kmeans######################################
> startTime <- Sys.time();
>
> library(stats)
> kc <- kmeans(x=newdata, centers = 13)
> #plot(newdata[,c("DV","DC")],col=kc$cluster)
> tbl <- table(car.train$TypeName,kc$cluster)
> tblView(tbl)
>
> ##耗时间
> endTime <- Sys.time()
> difTime <- difftime(endTime,startTime,units = "secs")
> print(paste0("stats::kmeans total time:", difTime))
[1] "stats::kmeans total time:0.195545196533203"
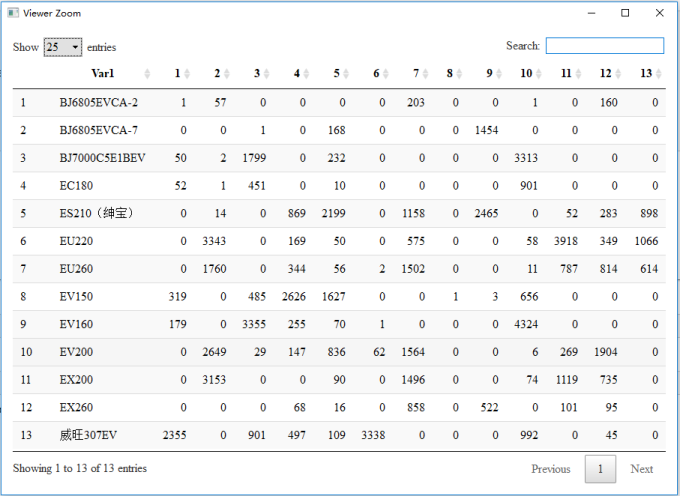
stats::kmeans total time:0.195545196533203, result view:
fpc::kmeansruns
source code:
> ################################################fpc::kmeansruns######################################
> startTime <- Sys.time();
>
> library(fpc)
> kc1 <- kmeansruns(data = newdata,krange = 1:15,critout = TRUE)
2 clusters 9394.437
3 clusters 185919.7
4 clusters 482630.4
5 clusters 414875.3
6 clusters 376338
7 clusters 334493.6
8 clusters 303976.7
9 clusters 279036.3
10 clusters 432009.9
11 clusters 363074.8
12 clusters 405784.7
13 clusters 397422.8
14 clusters 371842.5
15 clusters 408561.7
Warning messages:
1: Quick-TRANSfer stage steps exceeded maximum (= 3507150)
2: Quick-TRANSfer stage steps exceeded maximum (= 3507150)
3: Quick-TRANSfer stage steps exceeded maximum (= 3507150)
> tbl<- table(car.train$TypeName,kc1$cluster)
> tblView(tbl)
>
> ##耗时间
> endTime <- Sys.time()
> difTime <- difftime(endTime,startTime,units = "secs")
> print(paste0("fpc::kmeansruns total time:", difTime))
[1] "fpc::kmeansruns total time:107.454074859619"
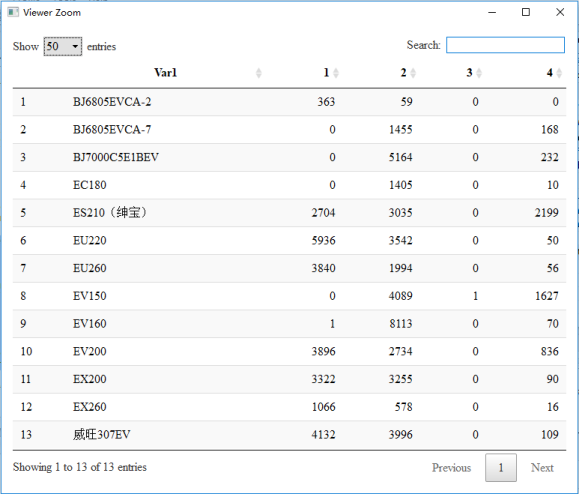
[1] "fpc::kmeansruns total time:107.454074859619" result view:
cluster::pam
source code
> ################################################cluster::pam######################################
>
> library(cluster)
> cPam <- pam(x=newdata,k=13)
Error in pam(x = newdata, k = 13) :
have 70143 observations, but not more than 65536 are allowed
Error: 待确认
fpc::pamk
source code
> ################################################fpc::pamk######################################
>
> library(fpc)
> fPamk <- pamk(newdata,krang=1:15)
Error in pam(sdata, k, diss = diss, ...) :
have 70143 observations, but not more than 65536 are allowed
Error: 待确认
stats::hclust
source code:
################################################fpc::pamk######################################
>
> library(fpc)
> fPamk <- pamk(newdata,krang=1:15)
Error in pam(sdata, k, diss = diss, ...) :
have 70143 observations, but not more than 65536 are allowe
Error: 待确认
mclust::Mclust
source code:
> ################################################mclust::Mclust######################################
> library(mclust)
> EM<-Mclust(newdata)
Error in hcVVV(data = c(379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, :
NAs in foreign function call (arg 13)
In addition: Warning message:
In hcVVV(data = c(379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, 379, :
NAs introduced by coercion to integer range
Error: 待确认
cluster::fanny
source code:
> ################################################cluster::fanny######################################
> library(cluster)
> fannyz=fanny(newdata,13,metric="SqEuclidean")
Error in fanny(newdata, 13, metric = "SqEuclidean") :
long vectors (argument 5) are not supported in .Fortran
Error: 待确认
e1071::cmeans
source code:
> ################################################e1071::cmeans######################################
> startTime <- Sys.time();
>
> library("e1071")
> eCm<-cmeans(newdata,15)
> tbl <- table(car.train$TypeName,eCm$cluster)
> tblView(tbl)
>
> ##耗时间
> endTime <- Sys.time()
> difTime <- difftime(endTime,startTime,units = "secs")
> print(paste0("stats::kmeans total time:", difTime))
[1] "stats::kmeans total time:8.7237401008606"
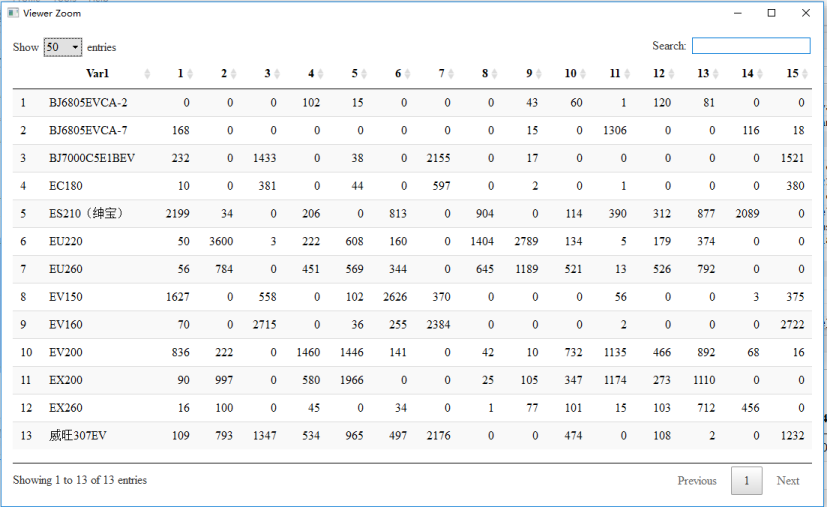
[1] "stats::kmeans total time:8.7237401008606" result view:
待验证
ML: 聚类算法R包-对比的更多相关文章
- ML: 聚类算法R包 - 模型聚类
模型聚类 mclust::Mclust RWeka::Cobweb mclust::Mclust EM算法也称为期望最大化算法,在是使用该算法聚类时,将数据集看作一个有隐形变量的概率模型,并实现模型最 ...
- ML: 聚类算法R包-层次聚类
层次聚类 stats::hclust stats::dist R使用dist()函数来计算距离,Usage: dist(x, method = "euclidean", di ...
- ML: 聚类算法R包-模糊聚类
1965年美国加州大学柏克莱分校的扎德教授第一次提出了'集合'的概念.经过十多年的发展,模糊集合理论渐渐被应用到各个实际应用方面.为克服非此即彼的分类缺点,出现了以模糊集合论为数学基础的聚类分析.用模 ...
- ML: 聚类算法R包-网格聚类
网格聚类算法 optpart::clique optpart::clique CLIQUE(Clustering In QUEst)是一种简单的基于网格的聚类方法,用于发现子空间中基于密度的簇.CLI ...
- ML: 聚类算法R包-K中心点聚类
K-medodis与K-means比较相似,但是K-medoids和K-means是有区别的,不一样的地方在于中心点的选取,在K-means中,我们将中心点取为当前cluster中所有数据点的平均值, ...
- ML: 聚类算法R包 - 密度聚类
密度聚类 fpc::dbscan fpc::dbscan DBSCAN核心思想:如果一个点,在距它Eps的范围内有不少于MinPts个点,则该点就是核心点.核心和它Eps范围内的邻居形成一个簇.在一个 ...
- ML: 聚类算法-K均值聚类
基于划分方法聚类算法R包: K-均值聚类(K-means) stats::kmeans().fpc::kmeansruns() K-中心点聚类(K-Medoids) ...
- ML: 聚类算法-概论
聚类分析是一种重要的人类行为,早在孩提时代,一个人就通过不断改进下意识中的聚类模式来学会如何区分猫狗.动物植物.目前在许多领域都得到了广泛的研究和成功的应用,如用于模式识别.数据分析.图像处理.市场研 ...
- 【转】利用python的KMeans和PCA包实现聚类算法
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/yjd_hycf_space/p/7094005.html 题目: 通过给出的驾驶员行为数据(trip.csv),对驾驶员不同时段的驾驶类型进行聚 ...
随机推荐
- 调整Windows XP 输入法顺序
執行 Regedit.exe 至 HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Keyboard Layout\Preload 調整輸入法順序,右邊欄中名稱為 1 的鍵值就是內定的輸入法,其值一般為 00000 ...
- 最长可重区间集 spfa费用流
给定实直线L上的n个开区间,和一个正整数k 选取若干个区间,在保证实直线L上的任意一个点最多被选出区间覆盖k次的情况下,使得这些区间的长度和最大 先把区间按照左端点排序, 考虑到重复其实就代表着相交, ...
- 对Functional Language的认识
What: A functional language is a programming language built over and around logical functions or pro ...
- Oracle导入导出表
使用PL SQL Developer进行操作 一.导出 工具<<导出表<<sql插入<<选择用户和要导出的表,勾选创建表,选择输出文件(格式最好为.sql),点击导 ...
- js学习:return arguments
return函数 arguments
- iostat iotop 查看硬盘的读写、 free 查看内存的命令 、netstat 命令查看网络、tcpdump 命令
iostat 命令 查看硬盘的使用情况: iostat iostat -x iotop 命令: 若没安装先安装: yum install iotop -y free 命令,用于查看内存的使用量: fr ...
- 为移动端而设计的bootstrap的使用
一.下载 --bs ---css ----bootstrap.css ----bootstrap.min.css ---fonts ---js ----bootstrap.js ----jquery. ...
- springboot+kotlin+springcloud+java+grade+maven混编?
springboot + maven + java vs springboot + gradle + kotlin 快速搭建:https://start.spring.io/ springclould ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.4
结论: 正常直接II型流图和转换直接I型非常相似:正常直接I型流图和转换直接II型非常相似.
- linux——git安装使用
系统环境centos7 安装git命令 yum install git -y 安装好之后使用命令查看git版本 git –version [root@bogon ~]# git --version g ...
