Paper Reading - Attention Is All You Need ( NIPS 2017 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
Motivation:
- The inherently sequential nature of Recurrent Models precludes parallelization within training examples.
- Attention mechanisms have become an integral part of compelling sequence modeling and transduction models in various tasks, allowing modeling of dependencies without regard to their distance in the input or output sequences. In all but a few cases, however, such attention mechanisms are used in conjunction with a recurrent network.
Innovation:
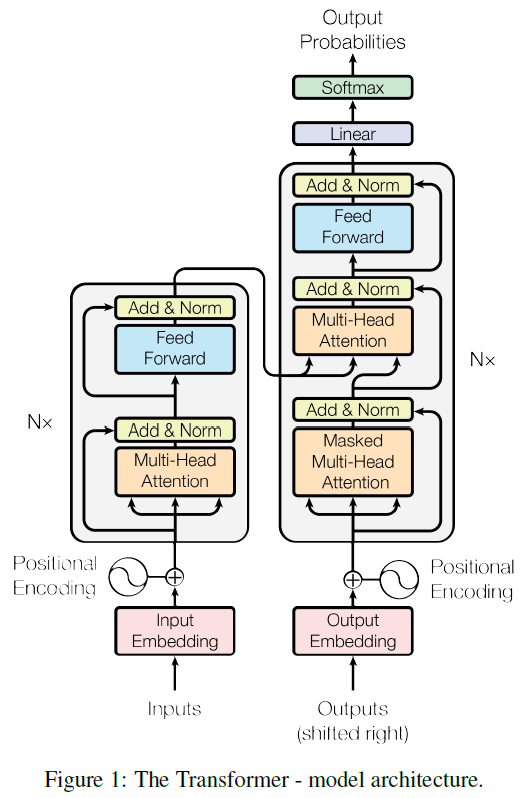
- The first sequence transduction model, the Transformer, relying entirely on self-attention to compute representations of its input and output without using sequence-aligned RNNs or Convolutions. The Transformer follows the overall architecture using stacked self-attention and point-wise, fully connected layers for both the encoder and decoder, shown in the left and right halves of Figure 1, respectively.
- Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position-wise fully connected feed-forward network. The authors employ a residual connection around each of the two sub-layers, followed by layer normalization. That is, the output of each sub-layer is LayerNorm (x + Sublayer(x)), where Sublayer(x) is the function implemented by the sub-layer itself. To facilitate these residual connections, all sub-layers in the model, as well as the embedding layers, produce outputs of dimension dmodel = 512.
- Decoder: The decoder is also composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. In addition to the two sub-layers in each encoder layer, the decoder inserts a third sub-layer, which performs multi-head attention over the output of the encoder stack. Similar to the encoder, they employ residual connections around each of the sub-layers, followed by layer normalization. They also modify the self-attention sub-layer in the decoder stack to prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions. This masking, combined with fact that the output embeddings are offset by one position, ensures that the predictions for position i can depend only on the known outputs at positions less than i.
- Scaled Dot-Product Attention and Multi-Head Attention. The Transformer uses multi-head attention in three different ways:
- In "encoder-decoder attention" layers, the queries come from the previous decoder layer, and the memory keys and values come from the output of the encoder. This allows every position in the decoder to attend over all positions in the input sequence. This mimics the typical encoder-decoder attention mechanisms in sequence-to-sequence models such as [ Google’s neural machine translation system: Bridging the gap between human and machine translation. ].
- The encoder contains self-attention layers. In a self-attention layer all of the keys, values and queries come from the same place, in this case, the output of the previous layer in the encoder. Each position in the encoder can attend to all positions in the previous layer of the encoder. [ More about Attention Definition ]
- Similarly, self-attention layers in the decoder allow each position in the decoder to attend to all positions in the decoder up to and including that position. They need to prevent leftward information flow in the decoder to preserve the auto-regressive property. They implement this inside of scaled dot-product attention by masking out (setting to -∞) all values in the input of the softmax which correspond to illegal connections. See Figure 2.
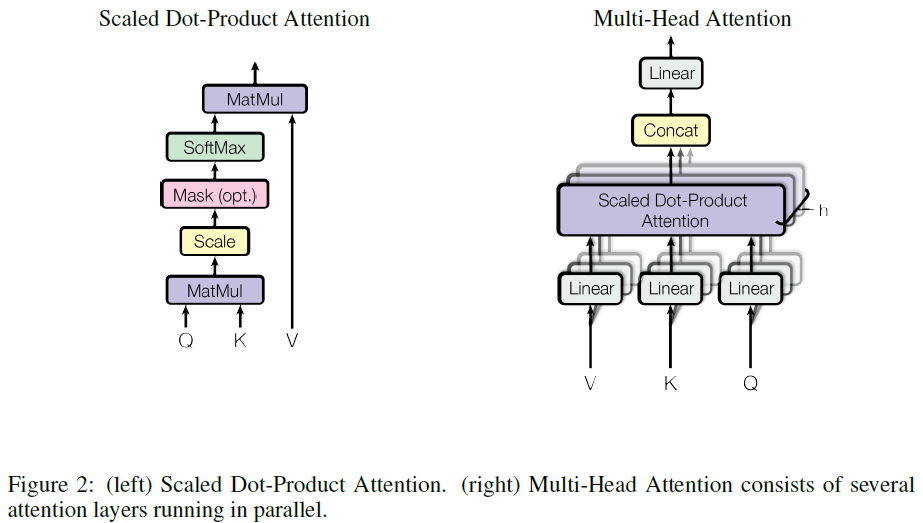
In terms of encoder-decoder, the query Q is usually the hidden state of the decoder. Whereas key K, is the hidden state of the encoder, and the corresponding value V is normalized weight, representing how much attention a key gets. -- The Transformer - Attention is all you need.
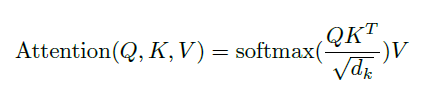

- Positional Encoding: Add "positional encodings" to the input embeddings at the bottoms of the encoder and decoder stacks. In this work, they use sine and cosine functions of different frequencies:
- PE(pos, 2i) = sin ( pos / 100002i/dmodel )
- PE(pos, 2i+1) = cos ( pos / 100002i/dmodel)
Improvement:
- Position-wise Feed-Forward Networks: In addition to attention sub-layers, each of the layers in their encoder and decoder contains a fully connected feed-forward network, which is applied to each position separately and identically. This consists of two linear transformations with a ReLU activation in between. FFN(x) = max(0, xW1 + b1)W2 + b2.
General Points:
- An attention function can be described as mapping a query and a set of key-value pairs to an output, where the query, keys, values, and output are all vectors. The output is computed as a weighted sum of the values, where the weight assigned to each value is computed by a compatibility function of the query with the corresponding key.
- Why Self-Attention:
- One is the total computational complexity per layer. Another is the amount of computation that can be parallelized, as measured by the minimum number of sequential operations required.
- The third is the path length between long-range dependencies in the network.
Paper Reading - Attention Is All You Need ( NIPS 2017 ) ★的更多相关文章
- Paper Reading - Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning ( CoRR 2017 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.03122 Motivation: Compared to recurrent layers, convol ...
- Paper Reading: Stereo DSO
开篇第一篇就写一个paper reading吧,用markdown+vim写东西切换中英文挺麻烦的,有些就偷懒都用英文写了. Stereo DSO: Large-Scale Direct Sparse ...
- Paper Reading - Im2Text: Describing Images Using 1 Million Captioned Photographs ( NIPS 2011 )
Link of the Paper: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4470-im2text-describing-images-using-1-million-captio ...
- Paper Reading - Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention ( ICML 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf Main Points: Encoder-Decoder Framework: Enco ...
- Paper Reading - Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks ( NIPS 2014 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.3215.pdf Main Points: Encoder-Decoder Model: Input seq ...
- [Paper Reading] Show, Attend and Tell: Neural Image Caption Generation with Visual Attention
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf 代码链接:https://github.com/kelvinxu/arctic-captions & htt ...
- Paper Reading - CNN+CNN: Convolutional Decoders for Image Captioning
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.09019 Innovations: The authors propose a CNN + CNN fra ...
- Paper Reading - Learning to Evaluate Image Captioning ( CVPR 2018 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.06422 Innovations: The authors propose a novel learnin ...
- Paper Reading - Convolutional Image Captioning ( CVPR 2018 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09151 Motivation: LSTM units are complex and inherentl ...
随机推荐
- Linux Shell常用技巧(十一)
二十二. 交互式使用Bash Shell: 1. 用set命令设置bash的选项: 下面为set主要选项的列表及其表述: 选项名 开关缩写 描述 allexport -a 打开此开关, ...
- GitHub学生认证示范
打开网址:https://education.github.com/ 点击Get Your Pack 点击I am a Student 填写资料上传学生证照片,等待通过,如果没有GitHub账号就注 ...
- springmvc整合mybatis框架源码 bootstrap html5 mysql oracle maven SSM
A 调用摄像头拍照,自定义裁剪编辑头像 [新录针对本系统的视频教程,手把手教开发一个模块,快速掌握本系统]B 集成代码生成器 [正反双向](单表.主表.明细表.树形表,开发利器)+快速构建表单; 技 ...
- JS判断两个数字的大小
javascript中定义的var类型是弱类型,默认是String类型,在比较两个数字大小的时候默认比较的是两个字符串,比如,在比较10和2时,按数字做比较10是比2大,可是按默认的字符串比较时,第一 ...
- 结对编程总结by黄柏欣李斌
在十一国庆期间(当然,还有国庆之前的几天),我们进行了一个结对编程的项目.对我受益良多,在伙伴面前发现自己的渺小,在知识面前,始终输给这浩瀚的海洋,及时发现了自己的不足,这次项目,对我来说就相当于一个 ...
- micro:bit 软件生态系统介绍
microbit 软件分成在microbit (Target Computer 如下图右边)上执行的及主计算机(Host Computer 如下图左边)上两类 : 一般程序写好后透过USB 转到mic ...
- nRF52832 BLE_DFU空中升级OTA(二)编译下载(SDK14.2.0)
上一篇配置好了开发环境,现在就可以试着跑一下例程了,这里需要两个例程,一个是bootloader的,一个是应用程序的,其路径分别为: bootloader:SDK_14.2.0工程\examples\ ...
- Node.js 引用 gm 包错误 Error: Could not execute GraphicsMagick/ImageMagick
今天在学习前后台图像剪切时,下载了有图片剪切瑞士军刀之称的 GraphicsMagick. 给 gm.exe 配置了环境变量,在 npm 下好了 gm 的模块,但是运行却出现了错误. 错误如图: [E ...
- windows server dump文件
1. mini dump: ***** 需要包含 dbghelp.dll 库 ****mini_dump.h文件: // reference:https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh ...
- IDEA新建Web项目
file->New project->输入项目名(例如这里输入HelloWeb) 选择JDK为合适版本->next ->finish即可 在新建的项目HelloWorld上右击 ...
