《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.31
参照Example7.27,因为0.1π=2πf1 f1=0.05,0.9π=2πf2 f2=0.45
所以0.1π≤ω≤0.9π,0.05≤|H|≤0.45
代码:
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 7.31 \n\n'); banner();
%% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ f = [0 0.1 0.9 1]; % in w/pi units
m = [0 0.05 0.45 0]; % Magnitude values M = 25; % length of filter
N = M - 1; % Nth-order
h = firpm(N, f, m, 'differentiator');
%h
[db, mag, pha, grd, w] = freqz_m(h, [1]); [Hr, ww, c, L] = Hr_Type3(h);
%[Hr,omega,P,L] = ampl_res(h); l = 0:M-1;
%% -------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% -------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi, db); grid on; axis([0 2 -90 10]);
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-60,-40,-20,0])
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['60';'40';'20';' 0']);
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[0,0.1,0.9,1,1.1,1.9,2]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB'); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, mag); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Absolute'); title('Magnitude Response in absolute');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',[0,0.1,0.9,1,1.1,1.9,2]);
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[0,1.0,2.0]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi, pha); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Phase Response in Radians');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi, grd*pi/180); grid on; %axis([0 1 -100 10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Rad'); title('Group Delay'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31')
set(gcf,'Color','white'); subplot(2,2,1); stem(l, h); axis([-1, M, -0.6, 0.5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response, M=25');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0,12,25]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-0.6:0.2:0.6]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, db); axis([0, 1, -80, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude Response in dB ');
set(gca,'XTickMode','manual','XTick',f)
set(gca,'YTickMode','manual','YTick',[-60,-40,-20,0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['60';'40';'20';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, Hr); axis([0, 1, -0.2, 1.5]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('Hr(w)'); title('Amplitude Response'); n = [0:1:100];
x = 3*sin(0.25*pi*n);
y = filter(h,1,x);
y_chk = 0.75*cos(0.25*pi*n); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31 x(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem([0:M-1], h); axis([0 M-1 -0.5 0.5]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('h(n)'); title('Actual Impulse Response, M=25'); subplot(2,1,2); stem(n, x); axis([0 100 0 3]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); title('Input sequence'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31 y(n) and y_chk(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
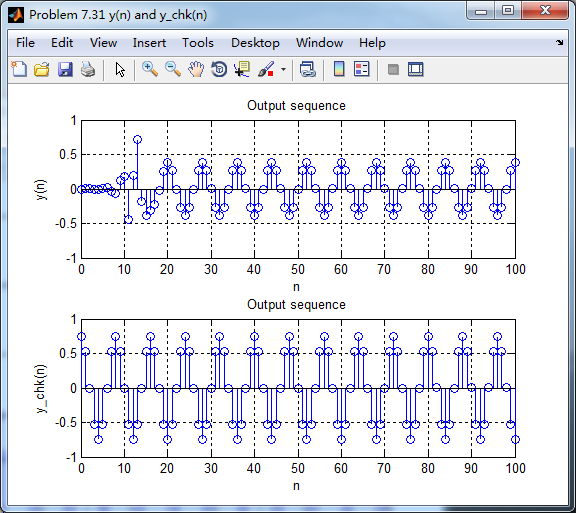
subplot(2,1,1); stem(n, y); axis([0 100 -1 1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('y(n)'); title('Output sequence'); subplot(2,1,2); stem(n, y_chk); axis([0 100 -1 1]); grid on;
xlabel('n'); ylabel('y\_chk(n)'); title('Output sequence'); % ---------------------------
% DTFT of x
% ---------------------------
MM = 500;
[X, w1] = dtft1(x, n, MM);
[Y, w1] = dtft1(y, n, MM); magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X);
magY = abs(Y); angY = angle(Y); realY = real(Y); imagY = imag(Y); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31 DTFT of x(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w1/pi, angX/pi); grid on; axis([0,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w1/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w1/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31 DTFT of y(n)')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magY); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Y|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w1/pi, angY/pi); grid on; axis([0,2,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w1/pi, realY); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w1/pi, imagY); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 7.31 Magnitude Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(1,2,1); plot(w1/pi,magX); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part of Input');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(1,2,2); plot(w1/pi,magY); grid on; %axis([0,2,0,15]);
title('Magnitude Part of Output');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |Y|');
运行结果:
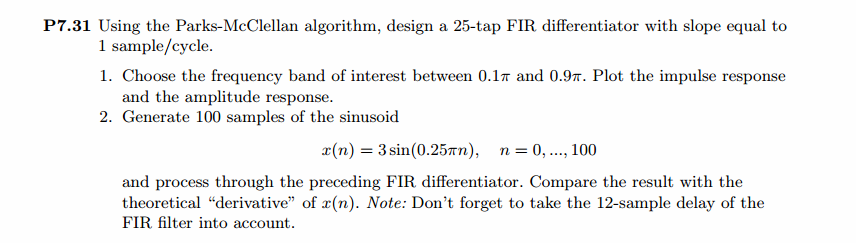
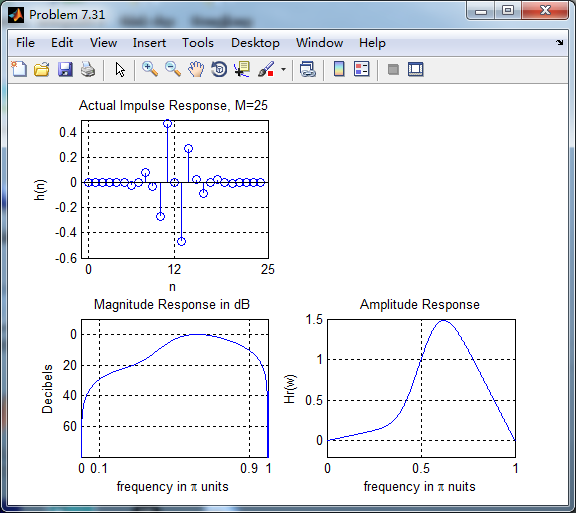
根据线性相位FIR性质,differentiator为第3类线性相位FIR,下图为脉冲响应、幅度谱和振幅谱。
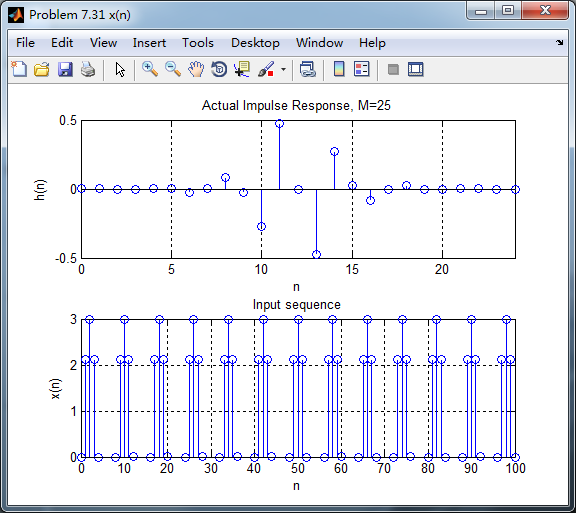
脉冲响应和输入序列
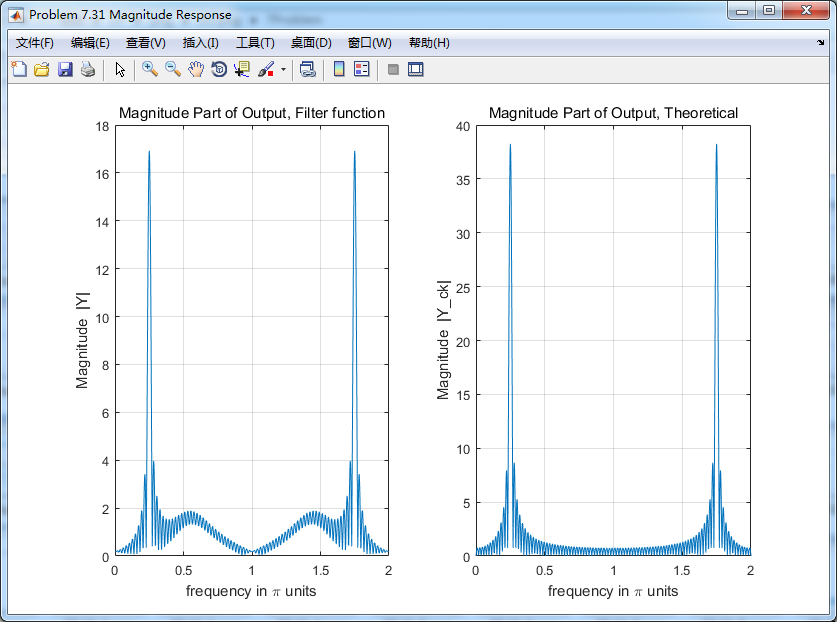
下图分别用卷积法和数学求导数方法得到的输出,
各自求其离散时间傅氏变换DTFT,得
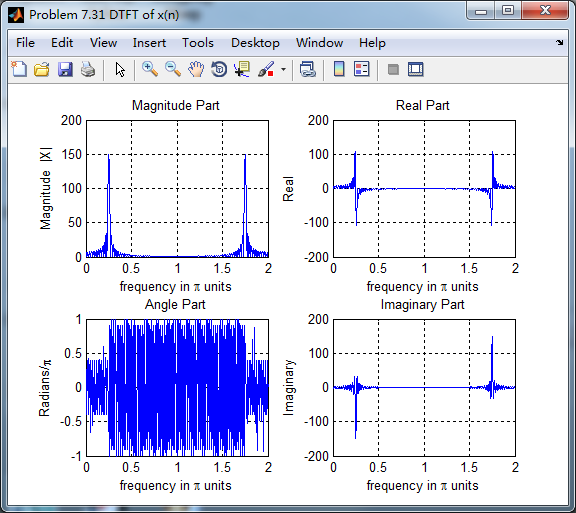
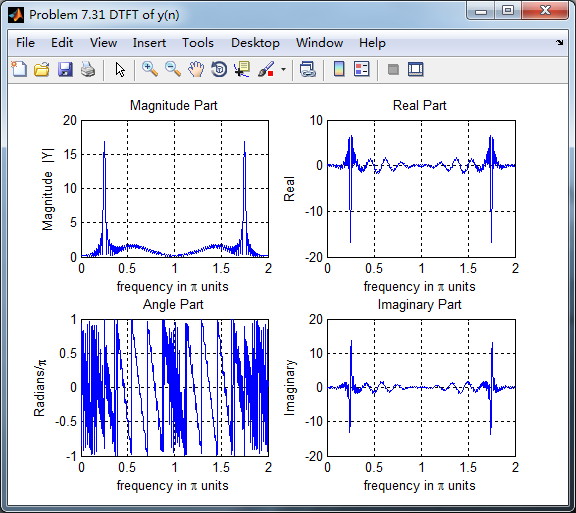
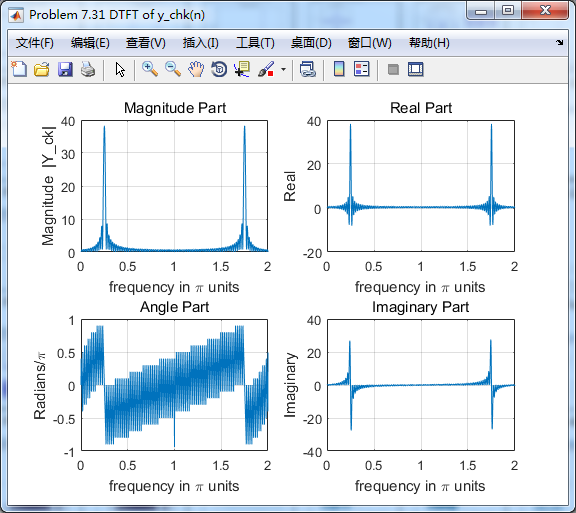
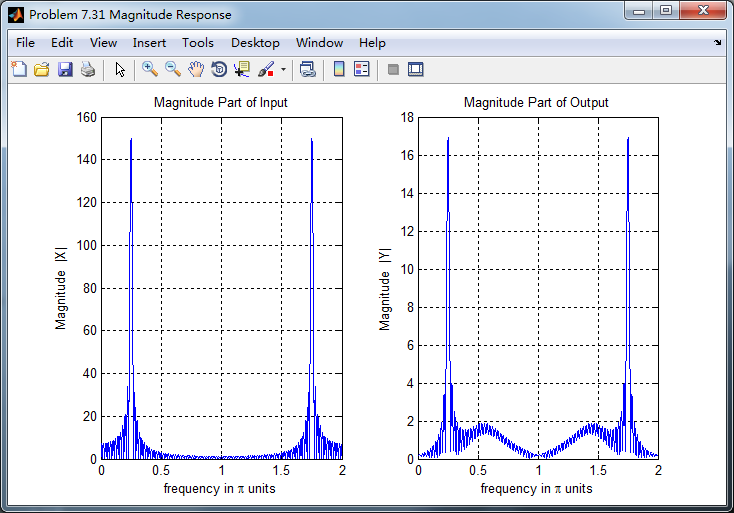
两种求微分结果幅度谱对比,可以看出:
1、设计滤波器卷积输入,输出的0.5π频率附近出现能量,数学求法没有;
2、设计滤波器卷积输入,幅度较数学求法小(能量有损失?);
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.31的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.31
第3小题: 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Out ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.31
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.26
注意:高通的线性相位FIR滤波器,不能是第2类,所以其长度必须为奇数.这里取M=31,过渡带里采样值抄书上的. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.24
又到清明时节,…… 注意:带阻滤波器不能用第2类线性相位滤波器实现,我们采用第1类,长度为基数,选M=61 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.12
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.10
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.7
1.代码: function [xe,xo,m] = evenodd_cv(x,n) % % Complex signal decomposition into even and odd parts ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.6
1.代码 %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info abou ...
随机推荐
- 驱动层hook系统函数的时,如何屏蔽掉只读属性?
对于Intel 80486或以上的CPU,CR0的位16是写保护(Write Proctect)标志.当设置该标志时,处理器会禁止超级用户程序(例如特权级0的程序)向只读页面执行写操作:当该位复位时则 ...
- Python sort()函数和sorted()
1.原址排序 1)列表有自己的sort方法,其对列表进行原址排序,既然是原址排序,那显然元组不可能拥有这种方法,因为元组是不可修改的. truple无组报错: 2.副本排序 1)[:]分片方法 注意: ...
- 17.splash_case03
# python执行lua脚本 import requests from urllib.parse import quote lua = ''' function main(splash) retur ...
- ORM下实现继承的三种方式(TPH TPC TPT)
TPH(Table Per Hierarchy):所有的数据都放在同一个表格内,但是使用辨别标志(Discriminator)的方式来区分 TPC(Table Per Concrete-Type):由 ...
- [转载]Emmet (ZenCoding) 缩写语法
Emmet 使用类似于 CSS 选择器的语法描述元素在生成的文档树中的位置及其属性. 元素 可以使用元素名(如 div 或者 p)来生成 HTML 标签.Emmet 没有预定义的有效元素名的集合,可以 ...
- 前缀后缀——cf1167E
想了很久没弄明白,对于边界的情况还是有问题 等题解出了再看看 然后枚举每个后缀r,找到比它小,并且在其左边的前缀l,那么删<=l,r-1的都可以 最后的二分很迷:要多考虑特殊情况:前缀跑到后缀后 ...
- Python更新后ros用不了的bug
一.原因 我同时安装了python2.7 和3.5,而且将python默认配置为python3.5,所以ros并不支持,所以提示找不到. 2.解决方式 通过修改不同版本的python的优先级,将pyt ...
- 第十三章 Odoo 12开发之创建网站前端功能
Odoo 起初是一个后台系统,但很快就有了前端界面的需求.早期基于后台界面的门户界面不够灵活并且对移动端不友好.为解决这一问题,Odoo 引入了新的网站功能,为系统添加了 CMS(Content Ma ...
- centos 6.5 yum安装rabbitMQ
1.查看系统版本, 升级系统基本lib库 [root@test ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 6.5 (Final) [root@test ~] ...
- 当EntityFramework爱上AutoMapper
有时候相识即是一种缘分,相爱也不需要太多的理由,一个眼神足矣,当EntityFramework遇上AutoMapper,就是如此,恋爱虽易,相处不易. 在DDD(领域驱动设计)中,使用AutoMapp ...
