[转]WPF中Binding的技巧
在WPF应用的开发过程中Binding是一个非常重要的部分。
在实际开发过程中Binding的不同种写法达到的效果相同但事实是存在很大区别的。
这里将实际中碰到过的问题做下汇总记录和理解。
1. source = {binding} 和source = {binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource self},Path=DataContext}效果相同
理解:{binding} 不设定明确的绑定的source,这样binding就去从本控件类为开始根据可视树的层次结构自下而上查找不为空的Datacontext属性的值。
{binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource self},Path=DataContext}中RelativeSource self的含义为绑定的source为控件自身,这样binding 就绑定了自身控件的Datacontext。
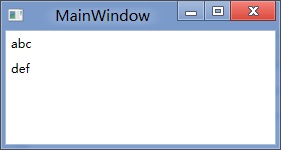
效果:
<StackPanel DataContext="abc">
<Label Content="{Binding}"></Label>
<Label Content="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self},Path=DataContext}"></Label>
</StackPanel>

<StackPanel DataContext="abc">
<Label Content="{Binding}"></Label>
<Label DataContext="def" Content="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self},Path=DataContext}"></Label>
</StackPanel>
2.在Template的Trigger中改变Template中某个样式控件的属性
<Style TargetType="{x:Type Button}">
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type Button}">
<Border>
<Label x:Name="PART_Label" Content="{TemplateBinding ContentA}" />
</Border>
<ControlTemplate.Triggers>
<Trigger Property="IsChecked" Value="True">
注: <Setter TargetName="PART_Label" Property="Content" Value="{Binding Path=ContentB, RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}}" />
</Trigger>
</ControlTemplate.Triggers>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
当然把注:的这句改成<Setter TargetName="PART_Label" Property="Content" Value="{Binding Path=ContentB, RelativeSource={RelativeSource AncestorType={x:TypeButton}}}">效果一样。
先写到这,下篇继续关注Binding中ElementName,RelativeSource,Source的相同点和区别。
转载时,请注明本文来源:www.cnblogs.com/tmywu
接上篇,
我们来看一看Elementname,Source,RelativeSource 三种绑定的方式
1.ElementName顾名思义就是根据Ui元素的Name来进行绑定:
例子:
<Window x:Name="MainWindow">
<Grid>
<Button Background=”{Binding ElementName=MainWindow, Path=Background}”/>
</Grid>
</Window>
效果等同于
<Window>
<Grid>
<Button Background=”{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource Mode=FindAncestor, AncestorType={x:Type Window},Path=Background}”/>
</Grid>
</Window>
区别:
ElementName属性用于引用一个UI对象的名称,其的作用域在同一XAML文件内,不能引用另一XAML文件的某个Ui元素名。
2.Source属性用于指定对象绑定路径的引用。 其特点是:Source属性通常用于绑定设置的对象时,是已知的。
<Window x:Name="MainWindow">
<Grid>
<Button Background=”{Binding Source={StaticResource ButtonStyle}}”/>
</Grid>
</Window>
3.RelativeSource
在不确定绑定的Source时,但知道与绑定对象两者相对关系时就需要使用RelativeSource,这也是RelativeSource 与ElementName和Source的最大区别。
RelativeSource 的三种典型用法:
/1.UI元素的一个属性绑定在自身的另一个属性上
<Label Background = {Binding Path=Forgroud, RelativeSource={RelativeSource Self}} />
/2.UI元素的一个属性绑定在某个父元素的属性上
<Grid>
<Label Background = {Binding Path=Background, RelativeSource={RelativeSource AncestorType={x:Type Grid}}}/>
</Grid>
/3.Template中的元素的属性绑定在Template使用者元素的属性上
{Binding Path=PathToProperty, RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}}
例子:
<Style TargetType="{x:Type local:NumericUpDown}">
<Setter Property="HorizontalAlignment" Value="Center"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalAlignment" Value="Center"/>
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type local:NumericUpDown}">
<Grid Margin="3">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition/>
<RowDefinition/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition/>
<ColumnDefinition/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Border BorderThickness="1" BorderBrush="Gray"
Margin="2" Grid.RowSpan="2"
VerticalAlignment="Center" HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"><TextBlock Text="{Binding RelativeSource={RelativeSource TemplatedParent}, Path=Value}"
Width="60" TextAlignment="Right" Padding="5"/>
</Border>
</Grid>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
</Style>
利用TemplateBinding 绑定模板与原对象之间的属性
{TemplateBinding Path=PathToProperty}
例子:
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type Button}" x:Key="buttonTemp">
<Border BorderThickness="3" Background="{TemplateBinding Foreground}">
<TextBlock Foreground="{TemplateBinding Background}"/>
</Border>
</ControlTemplate>
转载时,请注明本文来源:www.cnblogs.com/tmywu
[转]WPF中Binding的技巧的更多相关文章
- 【转】WPF中Binding的技巧(一)
WPF中Binding的技巧(一) 在WPF应用的开发过程中Binding是一个非常重要的部分. 在实际开发过程中Binding的不同种写法达到的效果相同但事实是存在很大区别的. 这里将实际中碰到 ...
- WPF中Binding使用StringFormat格式化字符串方法
原文:WPF中Binding使用StringFormat格式化字符串方法 货币格式 <TextBlock Text="{Binding Price, StringFormat={}{0 ...
- 整理:WPF中Binding的几种写法
原文:整理:WPF中Binding的几种写法 目的:整理WPF中Bind的写法 <!--绑定到DataContext--> <Button Content="{Bindin ...
- WPF之Binding深入探讨
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/fwj380891124/article/details/8107646 1,Data Binding在WPF中的地位 程序的本质是数据+算法.数据会在 ...
- WPF的Binding功能解析
1,Data Binding在WPF中的地位 程序的本质是数据+算法.数据会在存储.逻辑和界面三层之间流通,所以站在数据的角度上来看,这三层都很重要.但算法在3层中的分布是不均匀的,对于一个3层结构的 ...
- WPF之Binding的使用
引出: 在WPF中Binding可以比作数据的桥梁,桥梁的两端分别是Binding的源(Source)和目标(Target).一般情况下,Binding源是逻辑层对象,Binding目标是UI层的控件 ...
- WPF之Binding深入探讨--Darren
1,Data Binding在WPF中的地位 程序的本质是数据+算法.数据会在存储.逻辑和界面三层之间流通,所以站在数据的角度上来看,这三层都很重要.但算法在3层中的分布是不均匀的,对于一个3层结构的 ...
- 深入浅出WPF之Binding的使用(一)
在WPF中Binding可以比作数据的桥梁,桥梁的两端分别是Binding的源(Source)和目标(Target).一般情况下,Binding源是逻辑层对象,Binding目标是UI层的控件对象:这 ...
- WPF之Binding【转】
WPF之Binding[转] 看到WPF如此之炫,也想用用,可是一点也不会呀. 从需求谈起吧: 首先可能要做一个很炫的界面.见MaterialDesignInXAMLToolKit. 那,最主要的呢, ...
随机推荐
- 【JZOJ6294】动态数点
description analysis 这题出的失败在只卡正解不卡暴力 比较好想的方法是枚举约数,向两边二分,但是这个不满足二分性 首先用\(ST\)表维护区间的\(\gcd\),不用线段树,这样查 ...
- 携程的 Dubbo 之路
本篇文章整理自董艺荃在 Dubbo 社区开发者日上海站的演讲. 缘起 携程当初为什么要引入 Dubbo 呢?实际上从 2013 年底起,携程内主要使用的就是基于 HTTP 协议的 SOA 微服务框架. ...
- nginx的配置:目的是使用nginx反向代理后,应用程序获取用户真实ip
一.了解nginx Nginx是lgor Sysoev为俄罗斯访问量第二的rambler.ru站点设计开发的.从2004年发布至今,凭借开源的力量,已经接近成熟与完善. Nginx功能丰富,可作为HT ...
- ros-slam的链接
http://wiki.ros.org/navigation/Tutorials/RobotSetup 稍后整理
- 自定义Collection View布局
转自answer-huang的博客 原文出自:Custom Collection View Layouts UICollectionView在iOS6中第一次被介绍,也是UIKit视图类中的一颗 ...
- VS2010-MFC(图形图像:GDI对象之画笔CPen)
转自:http://www.jizhuomi.com/software/246.html 上一节讲了CDC类及其屏幕绘图函数,本节的主要内容是GDI对象之画笔CPen. GDI对象 在MFC中,CGd ...
- ul列表元素在float:right后li元素倒转
发现对li元素进行float:right后,虽然成功右浮动,但是的元素是倒转的 解决方案: 对ul进行右浮动,然后对li左浮动 结果
- Spring有关面试问题
问题清单: 什么是Spring框架?Spring框架有哪些主要模块? 使用Spring框架有什么好处? 什么是控制反转(IOC)?什么是依赖注入? 请解释下Spring中的IOC? BeanFacto ...
- Oracle一条数据多表连插
insert all into T_TRAIN_MARSHALLING <trim prefix="(GKEY," suffix=")" suffixOv ...
- day 57 Django基础五之django模型层之关联管理器
Django基础五之django模型层之关联管理器 class RelatedManager "关联管理器"是在一对多或者多对多的关联上下文中使用的管理器.它存在于下面两种情况 ...
