tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理
代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-cookbook
数据来源:http://www.cs.cornell.edu/people/pabo/movie-review-data/rt-polaritydata.tar.gz
理解互相关联的单词:king - man + woman = queen
如果已知man和woman语义相关联,那我们可以得出单词man和king的关系就如同woman和queen的关系
创建词向量来表现单词上下文关系
skip-gram:给出目标单词进行上下文相关单词的预测
CBOW(continuous bag of words)连续词袋:从上下文相关单词集合中预测目标单词
skip-gram概念图:
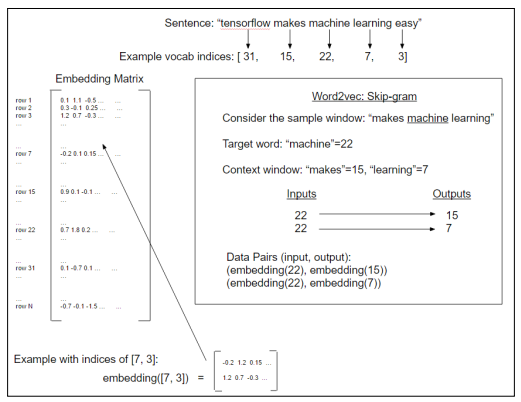
Word2Vec中的skip-gram模型,他是从目标单词中预测上下文窗口大小(上图中两边宽度均为1)内的单词
步骤如下:
- 必要包
- 声明模型参数
- 读取数据集
- 创建单词字典,转换句子列表为单词索引列表
- 生成批量数据
- 构建图
- 训练
step1:必要包
# From this data set we will compute/fit the skipgram model of
# the Word2Vec Algorithm
#
# Skipgram: based on predicting the surrounding words from the
# Ex sentence "the cat in the hat"
# context word: ["hat"]
# target words: ["the", "cat", "in", "the"]
# context-target pairs:
# ("hat", "the"), ("hat", "cat"), ("hat", "in"), ("hat", "the") import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import os
import string
import requests
import collections
import io
import tarfile
import urllib.request
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph() os.chdir(os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) # Start a graph session
sess = tf.Session()
step2:声明一些模型参数
# Declare model parameters
batch_size = 50
embedding_size = 200
vocabulary_size = 10000
generations = 50000
print_loss_every = 500 num_sampled = int(batch_size/2) # Number of negative examples to sample.
window_size = 2 # How many words to consider left and right. # Declare stop words,去停用词
stops = stopwords.words('english') # We pick five test words. We are expecting synonyms to appear
print_valid_every = 2000
valid_words = ['cliche', 'love', 'hate', 'silly', 'sad']
# Later we will have to transform these into indices
参数解释:
batch_size:一次将查找50对词嵌套(批量大小)
embedding_size & vocabulary_size:每个单词的嵌套大小是一个长度为200的向量,并且仅考虑频次最高的前10000的单词(其他单词的分类为“unknown”)
print_loss_every:迭代训练时,每500次打印损失函数
num_sampled:在损失函数中使用,本例中采用噪声对比损失函数(noise-contrastive error,NCE),该参数控制多少个批量转换成随机噪声
window_size:skip_gram模型上下文窗口大小,即查找目标单词两边各两个上下文单词
print_valid_every & valid_words:为了检测词向量的性能,选择一些常用的电影影评单词,每迭代2000次训练打印最近邻域单词
step3:读取数据集
# texts是5331条pos+5331条neg,target是5331个1+5331个0
texts, target = load_movie_data() # 归一化文本
texts = normalize_text(texts, stops) # 影评至少包含3个单词
target = [target[ix] for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if len(x.split()) > 2]
texts = [x for x in texts if len(x.split()) > 2]
step4:创建单词字典,转换句子列表为单词索引列表
# Build our data set and dictionaries
word_dictionary = build_dictionary(texts, vocabulary_size) # 逆序单词字典,可以通过索引找单词
# 当我们想打印出验证单词集中每个单词最近的单词时,可使用它
word_dictionary_rev = dict(zip(word_dictionary.values(), word_dictionary.keys()))
text_data = text_to_numbers(texts, word_dictionary) # Get validation word keys获取待验证单词的索引
valid_examples = [word_dictionary[x] for x in valid_words]
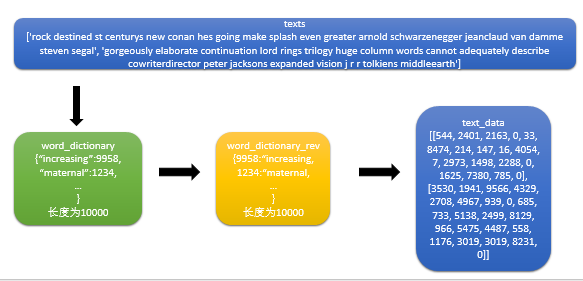
词频不够的单词标记为RARE,他在单词索引列表中的索引值为0
step5:生成批量数据
生成单词对:input:“the cat in the hat”,若in为目标词,窗口大小为2,则output为:(the,in),(cat,in),(the,in),(hat,in)
看一下单步执行的中间结果,利于更好理解处理过程:
#随机选择一个文本
>>> rand_sentence = np.random.choice(text_data)
>>> rand_sentence
[2520, 1421, 146, 1215, 5, 468] #窗口中的单词
>>> window_sequences = [rand_sentence[max((ix-window_size),0):(ix+window_size+1)] for ix, x in enumerate(rand_sentence)]
>>> window_sequences
[[2520, 1421, 146], [2520, 1421, 146, 1215], [2520, 1421, 146, 1215, 5], [1421, 146, 1215, 5, 468], [146, 1215, 5, 468], [1215, 5, 468]] #记录窗口中目标词的索引位置
>>> label_indices = [ix if ix<window_size else window_size for ix,x in enumerate(window_sequences)]
>>> label_indices
[0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2] #目标词和输出上下文的词做对应
>>> batch_and_labels = [(x[y], x[:y] + x[(y+1):]) for x,y in zip(window_sequences, label_indices)]
>>> batch_and_labels
[(2520, [1421, 146]), (1421, [2520, 146, 1215]), (146, [2520, 1421, 1215, 5]), (1215, [1421, 146, 5, 468]), (5, [146, 1215, 468]), (468, [1215, 5])] >>> tuple_data = [(x, y_) for x,y in batch_and_labels for y_ in y]
>>> tuple_data
[(2520, 1421), (2520, 146), (1421, 2520), (1421, 146), (1421, 1215), (146, 2520), (146, 1421), (146, 1215), (146, 5), (1215, 1421), (1215, 146), (1215, 5), (1215, 468), (5, 146), (5, 1215), (5, 468), (5, 1815), (468, 1215), (468, 5)] #提取batch和labels
>>> batch, labels = [list(x) for x in zip(*tuple_data)]
>>> batch
[2520, 2520, 1421, 1421, 1421, 146, 146, 146, 146, 1215, 1215, 1215, 1215, 5, 5, 5, 468, 468]
>>> labels
[1421, 146, 2520, 146, 1215, 2520, 1421, 1215, 5, 1421, 146, 5, 468, 146, 1215, 468, 1215, 5]
step6:构建图
# Define Embeddings初始化待拟合嵌套矩阵:
embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0)) # NCE loss parameters
nce_weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([vocabulary_size, embedding_size],
stddev=1.0 / np.sqrt(embedding_size)))
nce_biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([vocabulary_size])) # Create data/target placeholders
x_inputs = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size])
y_target = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=[batch_size, 1])
valid_dataset = tf.constant(valid_examples, dtype=tf.int32) # Lookup the word embedding:
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, x_inputs) # Get loss from prediction
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.nce_loss(nce_weights, nce_biases, embed, y_target,num_sampled, vocabulary_size)) # Create optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=1.0).minimize(loss) # Cosine similarity between words先把嵌入矩阵的词向量标准化,再计算验证单词集和所有词向量之间的余弦相似度
norm = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(embeddings), 1, keep_dims=True))
normalized_embeddings = embeddings / norm
valid_embeddings = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(normalized_embeddings, valid_dataset)
similarity = tf.matmul(valid_embeddings, normalized_embeddings, transpose_b=True)
损失函数的选择:softmax损失函数是用来实现多类分类问题常见的损失函数,上一节中其计算预测错误单词分类的损失。本例中目标是10000个分类,所以会导致稀疏性非常高。稀疏性会导致算法模型拟合或者收敛问题。为解决该问题,本例中将使用噪声对比损失函数(noise-contrastive error,NCE)。NCE损失函数将问题转换成一个二值预测,预测单词分类和随机噪声。num_sampled参数控制多少个批量转化成随机噪声。
step7:训练
#Add variable initializer.
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init) # Run the skip gram model.
loss_vec = []
loss_x_vec = []
for i in range(generations):
batch_inputs, batch_labels = generate_batch_data(text_data, batch_size, window_size)
feed_dict = {x_inputs : batch_inputs, y_target : batch_labels} # Run the train step
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict=feed_dict) # Return the loss
if (i+1) % print_loss_every == 0:
loss_val = sess.run(loss, feed_dict=feed_dict)
loss_vec.append(loss_val)
loss_x_vec.append(i+1)
print("Loss at step {} : {}".format(i+1, loss_val)) # Validation: Print some random words and top 5 related words
if (i+1) % print_valid_every == 0:
sim = sess.run(similarity, feed_dict=feed_dict)
for j in range(len(valid_words)):
valid_word = word_dictionary_rev[valid_examples[j]]
top_k = 5 # number of nearest neighbors
nearest = (-sim[j, :]).argsort()[1:top_k+1]
log_str = "Nearest to {}:".format(valid_word)
for k in range(top_k):
close_word = word_dictionary_rev[nearest[k]]
log_str = "%s %s," % (log_str, close_word)
print(log_str)

工作原理:在电影影评文本集上通过skip-gram方法训练完Word2Vec模型。下载数据集,把单词转换为单词字典,并使用索引数字作为嵌套查找。最后训练预测每个单词最接近的单词。
延伸学习:期望的最近单词是同义词。但一个句子的每个单词周围很少会出现同义词。我们得到的是数据集中每个单词的同义词的预测。为了使用单词嵌套,必须将其保持和重用。
tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram模型的更多相关文章
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Doc2Vec情感分析
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——CBOW词嵌入模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Word2Vec预测
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——TF-IDF算法
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——词袋
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- TensorFlow Object Detection API中的Faster R-CNN /SSD模型参数调整
关于TensorFlow Object Detection API配置,可以参考之前的文章https://becominghuman.ai/tensorflow-object-detection-ap ...
- 三分钟快速上手TensorFlow 2.0 (中)——常用模块和模型的部署
本文学习笔记参照来源:https://tf.wiki/zh/basic/basic.html 前文:三分钟快速上手TensorFlow 2.0 (上)——前置基础.模型建立与可视化 tf.train. ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——辅助函数
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram & CBOW原理总结
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7160330.html 先看下列三篇,再理解此篇会更容易些(个人意见) skip-gram,CBOW,Word2Vec 词向量基 ...
随机推荐
- Codeforces 404B
毫无疑问这题不是难题,但是这种题目最让人纠结 打心里对这种题目就比较害怕,果然,各种WE 这里贴上代码,用Python写的,比较偷懒: def cur_pos(a, d): if 0 <= d ...
- eclipse忽略js文件报错
eclipse中js文件报错的情况,或许大家早已习以为常了,那么有什么好的方法可以将其忽略掉呢?如果你也在寻找此问题,那么本文或许可以帮助到你忽略某个js文件报错的方法: Project Proper ...
- DAY1-作业
Python-day1-------> 本节内容: Python介绍 发展史 Python 2 or 3? 安装 Hello World程序 变量 用户输入 模块初识 .pyc是个什么鬼? 数据 ...
- PyChram创建虚拟环境
目录 1. python创建虚拟环境 2. pycharm中添加python虚拟环境 1. python创建虚拟环境 首先要安装virtualenv模块.打开命令行,输入pip install vir ...
- More Effective C++: 05技术(30-31)
30:Proxy classes 代理类 在C++中使用变量作为数组大小是违法的,也不允许在堆上分配多维数组: int data[dim1][dim2]; int *data = new int[di ...
- 网络流24题 搭配飞行员(DCOJ8000)
题目描述 飞行大队有若干个来自各地的驾驶员,专门驾驶一种型号的飞机,这种飞机每架有两个驾驶员,需一个正驾驶员和一个副驾驶员.由于种种原因,例如相互配合的问题,有些驾驶员不能在同一架飞机上飞行,问如何搭 ...
- initwithcoder和 initwithframe 区别?
每个ios开发者对loadView和viewDidLoad肯定都很熟悉,虽然这两个函数使用上真的是非常简单,但是和类似的initWithNibName/awakeFromNib/initWithCod ...
- hdu1532&&poj1273 最大流
Dinic算法: 层次图:根据源点到该点的距离建图,这里设相邻的都差1. (下面部分转) 在这幅图中我们首先要增广1->2->4->6,这时可以获得一个容量为2的流,但是如果不建立4 ...
- python 不定长参数**kwargs
- [HLSL]HLSL 入门参考 (dx11龙书附录B译文)
原文:[HLSL]HLSL 入门参考 (dx11龙书附录B译文) HLSL 高级着色语言 参考文档 龙书DirectX12现已推出中文版,其附录B的高级着色器语言参考的翻译质量比本文更高,有条件的读者 ...
