Web从入门到放弃<8>
Ref:
Cameron D. - HTML5, JavaScript and jQuery (Programmer to Programmer) - 2015
http://www.runoob.com/svg/svg-path.html
MacLees N. - jQuery for Designers Beginner’s Guide - 2012
jQuery for Designers 2014
<1> CSS Responsive box

关键字:display:inline-block;
html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.box {
height:200px;
width:200px;
display:inline-block;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="background:red"></div>
<div id="middleBox" class="box" style="background:green"></div>
<div id="thirdBox" class="box" style="background:blue"></div>
<div id="lastBox" class="box" style="background:yellow"></div> </body>
</html>
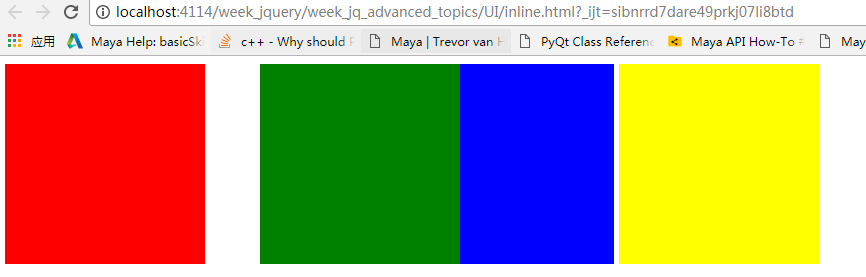
如果要把绿色的立方体移动50px,把蓝色向右推动50px,在这种静态布局是不可能的.先试试position:relative.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.box {
height:200px;
width:200px;
display:inline-block;
}
#middleBox{
position: relative;
left:50px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="background:red"></div>
<div id="middleBox" class="box" style="background:green"></div>
<div id="thirdBox" class="box" style="background:blue"></div>
<div id="lastBox" class="box" style="background:yellow"></div> </body>
</html>
position设置为relative,意思就在现在的位置作为基础,然后再做移动。
position设置为absolute:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
.box {
height:200px;
width:200px;
display:inline-block;
}
#middleBox{
position: absolute;
left:150px;
top:150px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="background:red"></div>
<div id="middleBox" class="box" style="background:green"></div>
<div id="thirdBox" class="box" style="background:blue"></div>
<div id="fourthBox" class="box" style="background:yellow"></div>
<div id="lastBox" class="box" style="background:black"></div>
</body>
</html>

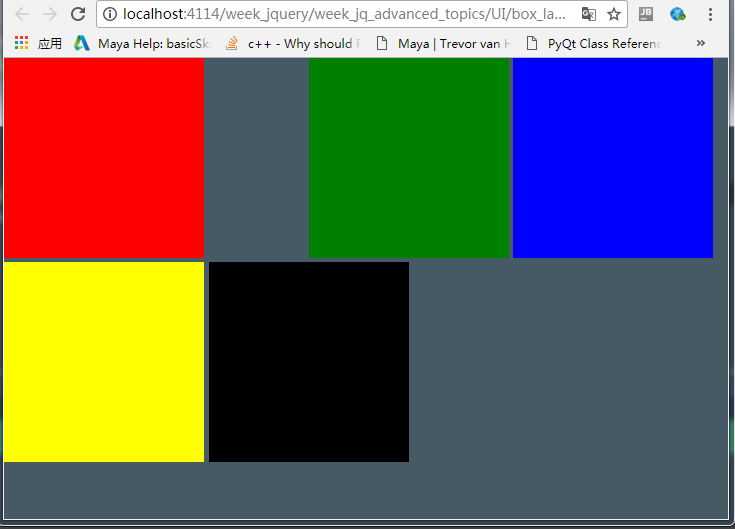
要把绿色放入下面写:z-index:-1;
margin-left:100px;
left:100px;区别就是,margin-left是会把下一个节点往右边推动.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
body{
margin: 0;
background-color: #455a64;
}
.box {
height:200px;
width:200px;
display:inline-block;
}
#middleBox{
position: relative;
margin-left: 100px;
} </style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box" style="background:red"></div>
<div id="middleBox" class="box" style="background:green"></div>
<div id="thirdBox" class="box" style="background:blue"></div>
<div id="fourthBox" class="box" style="background:yellow"></div>
<div id="lastBox" class="box" style="background:black"></div>
</body>
</html>
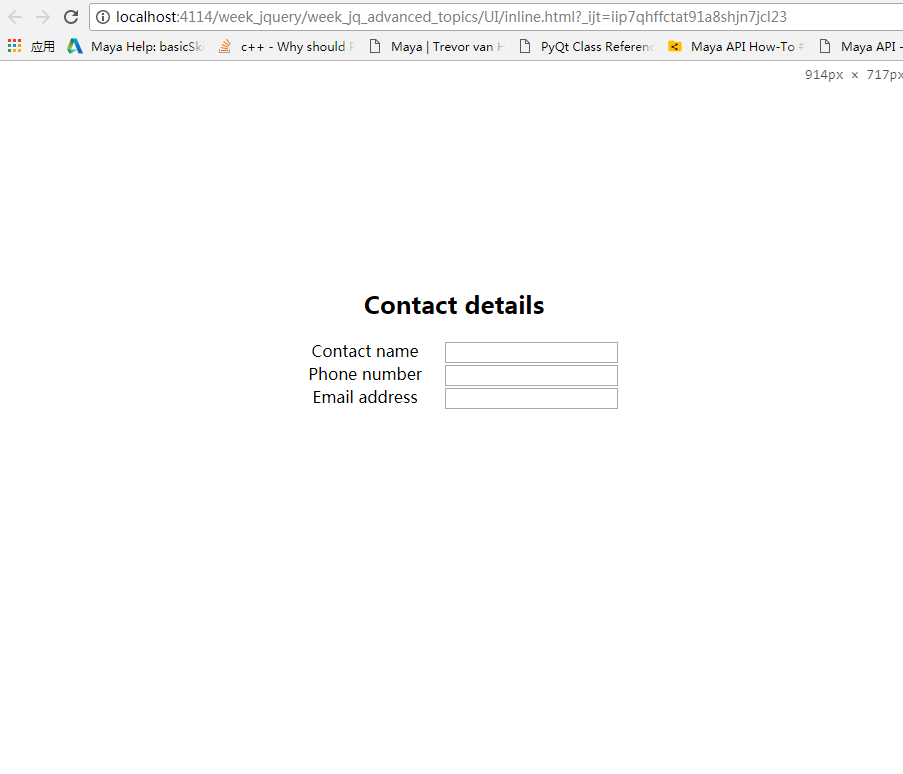
<2>居中
复杂的整个元素居中方案:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<style>
label {
width:150px;
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: top;
}
#contactDetails{
position:absolute;
width: 400px;
height: 200px;
text-align: center;
top:50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -150px;
margin-left: -200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body> <div id="contactDetails"><h2>Contact details</h2>
<form method="post">
<div class="formRow">
<label for="contactName">Contact name</label>
<input name="contactName" id="contactName" type="text"/>
</div> <div class="formRow">
<label for="phoneNumber">Phone number</label>
<input name="phoneNumber" id="phoneNumber" type="text"/>
</div>
<div class="formRow">
<label for="emailAddress">Email address</label>
<input name="emailAddress" id="emailAddress" type="text"/>
</div>
</form>
</div> </body>
</html>
水平居中是最简单的:
.box{
margin: 0 auto;
width:300px;
height:200px;
}
<3>UI/CSS
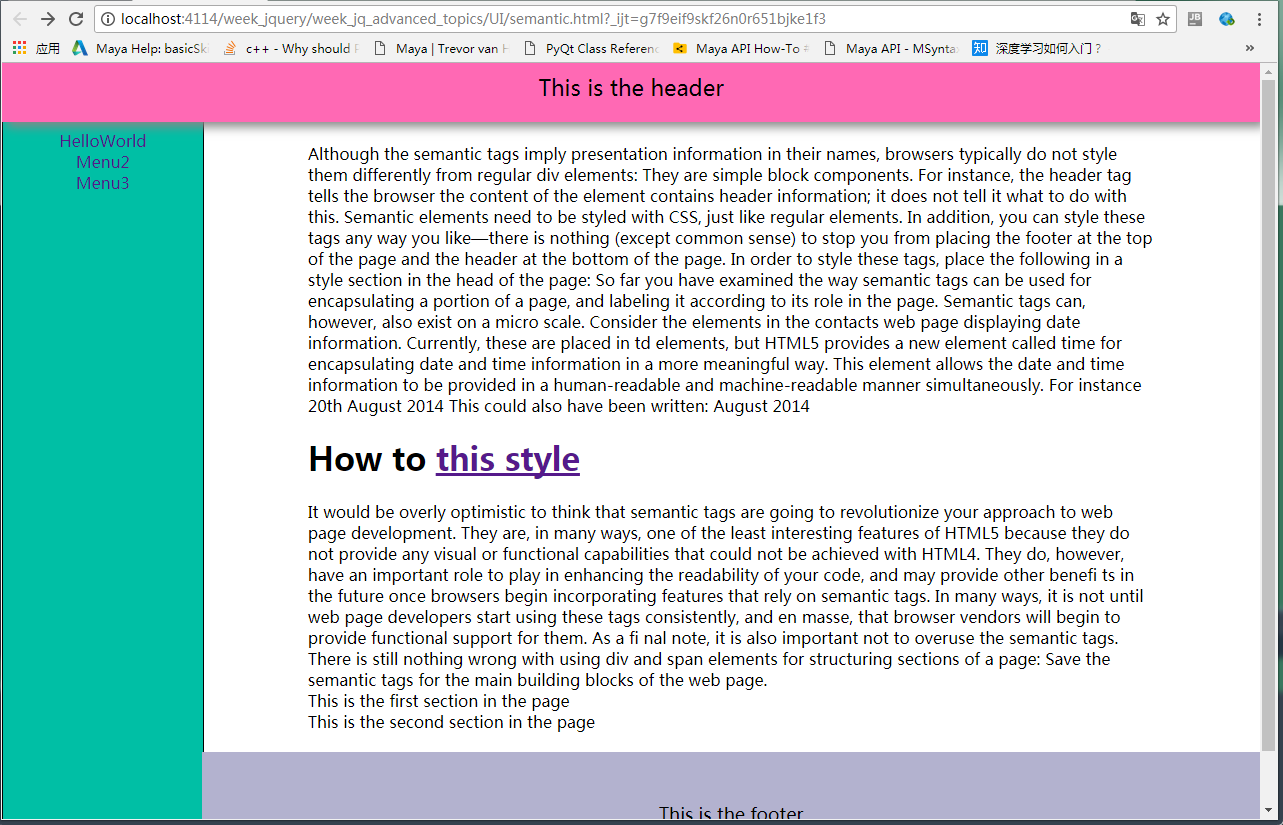
一个网页的简单构造v1:
<1>顶部为固定的:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
body{
min-height:100%;
margin:0;
padding:0;
position:relative;
}
header {
padding-top: 20px;
padding-bottom: 20px;
width:100%;
background:hotpink;
text-align:center;
top:-10px;
left: 0px;
position: fixed;
box-shadow: 5px 5px 15px #888888;
}
footer{
width:100%;
background:#B3B2CF;
text-align:center;
}
header {
font-size:22px;
}
aside {
position:fixed;
float:left;
width:200px;
height:100%;
border: 1px solid black;
padding-top: 40px;
left: 0; !important;
z-index: -1;
background-color: #00bfa5;
}
footer {
clear: both;
margin-top: 100px;
font-size:18px;
z-index: -1;
padding-top: 50px;
padding-bottom: 50px;
}
main{
position: absolute;
left: 200px;
}
.container{
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto; /* make container objects to center*/
top:80px;
position: relative;
z-index: -1;
} .sidebar-nav{
padding-top: 10px;
}
.sidebar-nav-ul{
list-style: none;
display:block;
padding: 0;
text-align: center;
}
.sidebar-nav-ul li a{
text-decoration:none
} </style>
</head>
<body> <header>This is the header</header>
<aside>
<div class="sidebar-nav">
<ul class="sidebar-nav-ul">
<li><a href="">HelloWorld</a></li>
<li><a href="">Menu2</a></li>
<li><a href="">Menu3</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</aside> <main>
<div class="container">
<div class="TextArea">
Although the semantic tags imply presentation information in their names, browsers typically
do not style them differently from regular div elements: They are simple block components. For
instance, the header tag tells the browser the content of the element contains header information; it
does not tell it what to do with this.
Semantic elements need to be styled with CSS, just like regular elements. In addition, you can style
these tags any way you like—there is nothing (except common sense) to stop you from placing the
footer at the top of the page and the header at the bottom of the page.
In order to style these tags, place the following in a style section in the head of the page: So far you have examined the way semantic tags can be used for encapsulating a portion of a
page, and labeling it according to its role in the page. Semantic tags can, however, also exist on a
micro scale.
Consider the elements in the contacts web page displaying date information. Currently, these are
placed in td elements, but HTML5 provides a new element called time for encapsulating date and
time information in a more meaningful way. This element allows the date and time information to
be provided in a human-readable and machine-readable manner simultaneously. For instance
<time datetime="2014-08-20">20th August 2014</time>
This could also have been written:
<time datetime="2014-08-20">August 2014</time>
</div> <div>
<h1>
How to <a href="https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000006896298?_ea=1171298">this style</a>
</h1>
It would be overly optimistic to think that semantic tags are going to revolutionize your approach to
web page development. They are, in many ways, one of the least interesting features of HTML5 because
they do not provide any visual or functional capabilities that could not be achieved with HTML4.
They do, however, have an important role to play in enhancing the readability of your code, and
may provide other benefi ts in the future once browsers begin incorporating features that rely on
semantic tags. In many ways, it is not until web page developers start using these tags consistently,
and en masse, that browser vendors will begin to provide functional support for them.
As a fi nal note, it is also important not to overuse the semantic tags. There is still nothing wrong
with using div and span elements for structuring sections of a page: Save the semantic tags for the
main building blocks of the web page.
</div> <section>This is the first section in the page</section>
<section>This is the second section in the page</section> </div>
<footer>
This is the footer
</footer> </main> </body>
</html>
<2>Responsive imgs:
html:
<ul class="thumbs">
<li><img src="imgs/1.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/2.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/3.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/4.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/5.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/6.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/6.png"></li>
</ul>
css:
.thumbs li{
width: 25%;
height: 140px;
display: inline;
padding: 10px;
}
.thumbs li img{
width: 150px;
height: 101px;
padding: 3px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
background-color: #fff;
position: relative;
}

<3>: dropdown with fix header:
css:
@import url("../../../normalize.css");
body{
background-color: gray;
}
.nav-bar{
background-color: #333;
border-bottom: 2px solid #cccccc;
width: 100%;
height: 40px;
position: fixed;
box-shadow: 3px 3px 5px #555555;
}
.nav-list{
list-style: none;
padding-left:;
margin: 0 auto; /*hide top margin*/
width: 900px; /* if set to 80%, will responsive */
}
.nav-list > li {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 120px;
height: 40px;
display: inline-block;
}
.nav-list > li > a{
text-decoration: none;
color:white;
position: absolute;
width: inherit;
height: inherit;
text-align: center;
/* very import */
padding-top: 12px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.nav-list >li >a:hover{
background-color: #555;
}
.dropdown{
display: none;
position: absolute;
top:40px;
padding-left:;
width: 150px;
list-style: none;
z-index:;
}
.dropdown li{
background-color: #555;
position: relative;
width: 150px;
height: 35px;
}
.dropdown li a{
color:#ddd;
text-decoration: none;
position: absolute;
width: 150px;
height: 35px;
padding: 10px 0 0 10px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.dropdown li a:hover{
background-color: #777;
}
.container{
padding-top: 40px;
width: 80%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* thumbnails*/
.thumbs{
list-style: none;
padding-left:;
}
.thumbs li{
width: 25%;
height: 25%;
display: inline;
}
.thumbs li img{
width: 25%;
height: 25%;
}
js:
$(document).ready(function () {
$('li').has('.dropdown').hover(
function () {
$(this).find('.dropdown').slideDown(150);
},
function () {
$(this).find('.dropdown').slideUp(150);
});
$('.thumbs > li > img').hover(
function () {
$(this).animate({
width:"160px",
height:"110px"
},500)
},
function () {
$(this).animate({
width:"150",
height:"101px"
},500)
}
)
});
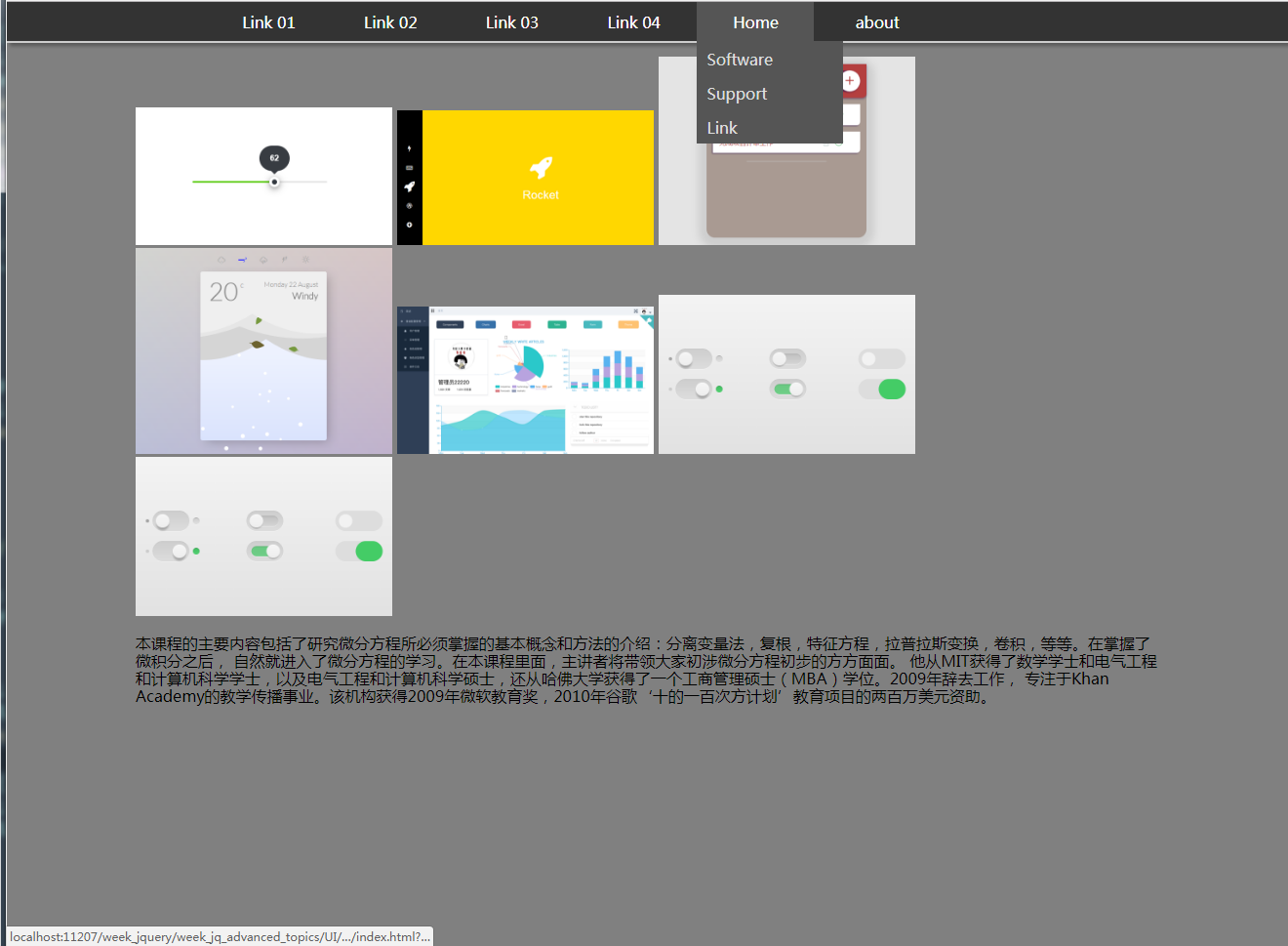
html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../../../normalize.css">
<script src="../../../jquery/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="index.js"></script> </head>
<body> <nav class="nav-bar">
<ul class="nav-list">
<li><a href="#">Link 01</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link 02</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link 03</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Link 04</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Home</a>
<ul class="dropdown">
<li><a>Software</a></li>
<li><a>Support</a></li>
<li><a>Link</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li><a href="#!">about</a></li>
</ul>
</nav> <div class="container">
<ul class="thumbs">
<li><img src="imgs/1.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/2.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/3.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/4.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/5.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/6.png"></li>
<li><img src="imgs/6.png"></li>
</ul> <p>
本课程的主要内容包括了研究微分方程所必须掌握的基本概念和方法的介绍:分离变量法,复根,特征方程,拉普拉斯变换,卷积,等等。在掌握了微积分之后,
自然就进入了微分方程的学习。在本课程里面,主讲者将带领大家初涉微分方程初步的方方面面。
他从MIT获得了数学学士和电气工程和计算机科学学士,以及电气工程和计算机科学硕士,还从哈佛大学获得了一个工商管理硕士(MBA)学位。2009年辞去工作,
专注于Khan Academy的教学传播事业。该机构获得2009年微软教育奖,2010年谷歌‘十的一百次方计划’教育项目的两百万美元资助。
</p>
</div> </body>
</html>
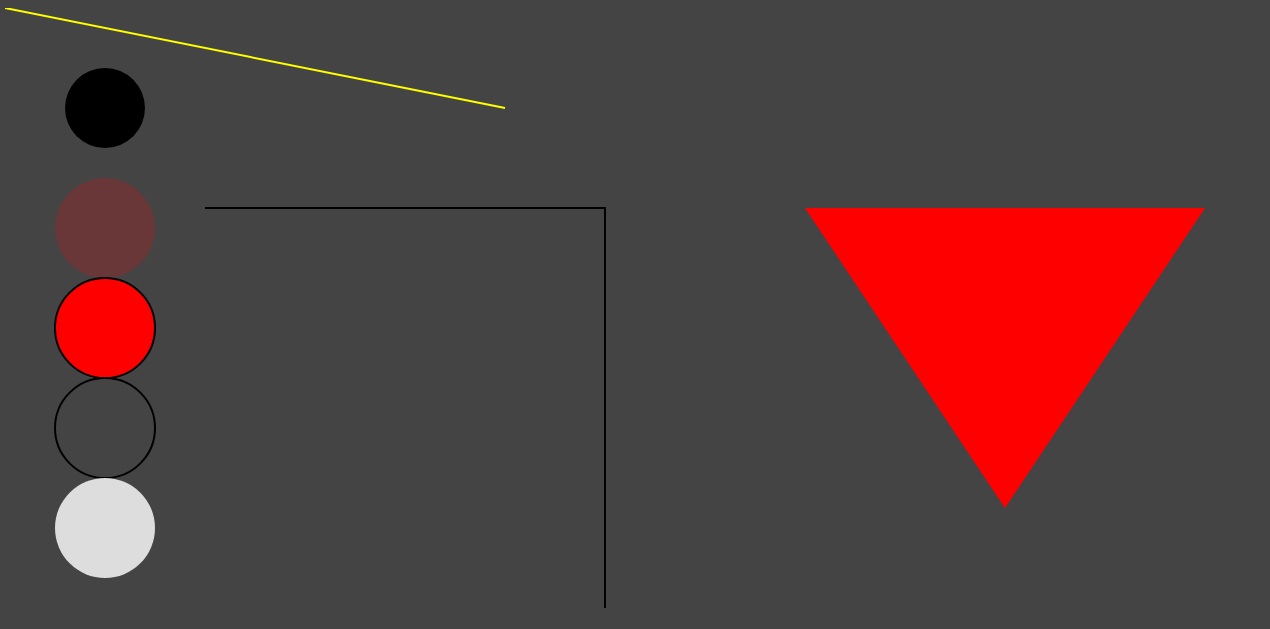
<4> SVG
<1>基本图形1:
html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #444444;"> <svg width="100%" height="800">
<circle r="40" cx="100" cy="100" stroke-width="1" ></circle>
<circle r="50" cx="100" cy="220" fill="red" fill-opacity="0.2"></circle>
<circle r="50" cx="100" cy="320" fill="red" stroke-width="2" stroke="black"></circle>
<circle r="50" cx="100" cy="420" fill-opacity="0" stroke-width="2" stroke="black"></circle>
<circle r="50" cx="100" cy="520" style="fill: #dddddd;cursor: all-scroll;"></circle> <line x1="0" y1="0" x2="500" y2="100" style="stroke-width: 2; stroke: yellow;"> </line>
<polygon points="800,200 1200,200 1000,500" style="fill: red;"></polygon> <polyline points="200,200 600,200 600,600 " style="stroke:black;stroke-width: 2; fill:none;"></polyline>
</svg> <p>hello ssfdsfdss </p> </body>
</html>
Web从入门到放弃<8>的更多相关文章
- Web从入门到放弃<7>
从这章开始读<javascript高级程序设计> <1>typeof 返回字符串 / 类型 未定义:undefined 布尔:boolean 字符串:string 数值:num ...
- Web从入门到放弃<5>
<1> CSS_DOM 1,structural layer 2,presentation layer 3,behavior layer style也是一个属性 <!DOCTYPE ...
- Web从入门到放弃<1>
HTML大法: <01> <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta char ...
- Web从入门到放弃<6>
<1> Canvas. 1,灰度图: js: function showAsGray() { var imgNode = document.getElementById('img'); ...
- Web从入门到放弃<4>
1,插入 如下html: <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset=&q ...
- Web从入门到放弃<3>
UI简单的美化全部来源于Bootstrap 知识来自<javascript dom编程艺术第二版> <1> 点击列表 页面不跳转图片刷新: 主要点: href如何点击完如何不 ...
- Web从入门到放弃<2>
<添加debug-toolbar> django现在1.11是必须这么做: pip install django-debug-toolbar 设置1: INSTALLED_APPS = [ ...
- 后端API入门到放弃指北
后端API入门学习指北 了解一下一下概念. RESTful API标准] 所有的API都遵循[RESTful API标准]. 建议大家都简单了解一下HTTP协议和RESTful API相关资料. 阮一 ...
- OpenStack从入门到放弃
OpenStack从入门到放弃 目录: 为何选择云计算/云计算之前遇到的问题 什么是云计算 云服务模式 云应用形式 传统应用与云感知应用 openstack及其相关组件介绍 flat/vlan/gre ...
随机推荐
- UUID简记
一.概述 wiki上的解释: A universally unique identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit number used to identify informati ...
- java面试准备之面向对象
面向对象 下面列出了面向对象软件开发的优点: (1) 代码开发模块化,更易维护和修改. (2) 代码复用. (3) 增强代码的可靠性和灵活性. (4) 增加代码的可理解性. 面向对象编程有很多重要的特 ...
- UIImagePickerDelegate - 官方文档说明
- (void)imagePickerController:(UIImagePickerController *)picker didFinishPickingMediaWithInfo:(NSDic ...
- IPv6绝不仅仅是对IPv4地址长度的增加
众所周知,IPv6 IP地址长度是IPv4 IP地址长度的四倍,是解决IPv4公共网址资源枯竭的最佳技术.的确,IETF在制定IPv6标准时也是基于这一因素考虑的.当时正是90年代初,Web开始出现, ...
- hMailServer配置图文详细教程
https://www.hmailserver.org/viewtopic.php?f=4&t=6
- Linux scp sudo
command line - scp to remote server with sudo - Super Userhttps://superuser.com/questions/138893/scp ...
- 题解 P1601 【A+B Problem(高精)】
P1601 A+B Problem(高精) 题目描述 高精度加法,x相当于a+b problem,b不用考虑负数. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 分两行输入a,b<=10^500 输出格式: 输出只 ...
- js字符串轉數組,數組轉字符串
字符串轉數組:split(',') 數組轉字符串:join(‘,’) https://www.cnblogs.com/woodk/p/5714329.html
- python基础3 字符串常用方法
一. 基础数据类型 总览 int:用于计算,计数,运算等. 1,2,3,100...... str:'这些内容[]' 用户少量数据的存储,便于操作. bool: True, False,两种状态 ...
- 位运算之——按位与(&)操作——(快速取模算法)
学习redis 字典结构,hash找槽位 求槽位的索引值时,用到了 hash值 & sizemask操作, 其后的scan操作涉及扫描顺序逻辑,对同模的槽位 按一定规则扫描! 其中涉及位运算 ...
