《DSP using MATLAB》示例 Example 10.1
坚持到第10章了,继续努力!
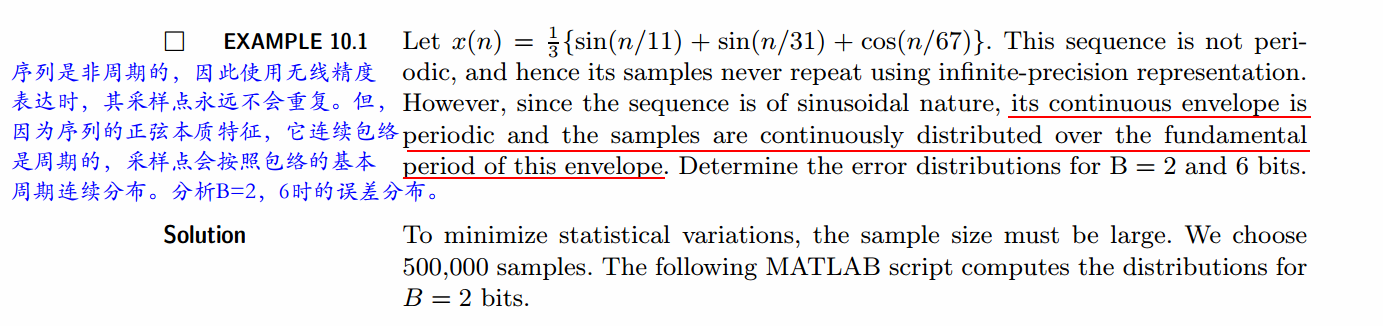
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Exameple 10.1 \n\n'); time_stamp = datestr(now, 31);
[wkd1, wkd2] = weekday(today, 'long');
fprintf(' Now is %20s, and it is %7s \n\n', time_stamp, wkd2);
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ clear; close all; % Example parameters
B = 2; N = 500000; n = [1:N];
xn = (1/3)*(sin(n/11) + sin(n/31) + cos(n/67)); clear n; % Quantization error analysis
[H1, H2, Q, estat] = StatModelR(xn, B, N); % Compute histograms
H1max = max(H1); H1min = min(H1); % Max and Min of H1
H2max = max(H2); H2min = min(H2); % Max and Min of H2 Hf1 = figure('units', 'inches', 'position', [1, 1, 8, 6], ...
'paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 4], ...
'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 10.1a');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
TF = 10;
title('Normalized error e1 and e2');
subplot(2, 1, 1);
bar(Q, H1); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on; xlabel('Normalized error e1'); ylabel('Distribution of e1 ', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, [1:1:4]/128] );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(1)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %f', estat(2))) ; subplot(2, 1, 2);
bar(Q, H2); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
%title('Normalized error e2');
xlabel('Normalized error e2'); ylabel('Distribution of e2', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(3)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %f', estat(4))) ; %% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
%% B = 6
%% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
% Example parameters
B = 6; N = 500000; n = [1:N];
xn = (1/3)*(sin(n/11) + sin(n/31) + cos(n/67)); clear n; % Quantization error analysis
[H1, H2, Q, estat] = StatModelR(xn, B, N); % Compute histograms
H1max = max(H1); H1min = min(H1); % Max and Min of H1
H2max = max(H2); H2min = min(H2); % Max and Min of H2 Hf2 = figure('units', 'inches', 'position', [1, 1, 8, 6], ...
'paperunits', 'inches', 'paperposition', [0, 0, 6, 4], ...
'NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Exameple 10.1b');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
TF = 10; subplot(2, 1, 1);
bar(Q, H1); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
title('Normalized error e1'); ylabel('Distribution of e1 ', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(1)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H1max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %.7f', estat(2))) ; subplot(2, 1, 2);
bar(Q, H2); axis([-0.5, 0.5, -0.001, 4/128]); grid on;
title('Normalized error e2'); ylabel('Distribution of e2', 'vertical', 'baseline');
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 1:1:4]/128 );
text(-0.45, 0.030, sprintf('SAMPLE SIZE N = %d', N));
text(-0.45, 0.025, sprintf(' ROUNDED TO B = %d BITS', B));
text(-0.45, 0.020, sprintf(' MEAN = %.4e', estat(3)));
text(0.10, 0.030, sprintf('MIN PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2min)) ;
text(0.10, 0.025, sprintf('MAX PROB BAR HEIGHT = %f', H2max)) ;
text(0.10, 0.020, sprintf(' SIGMA = %.7f', estat(4))) ;
运行结果:
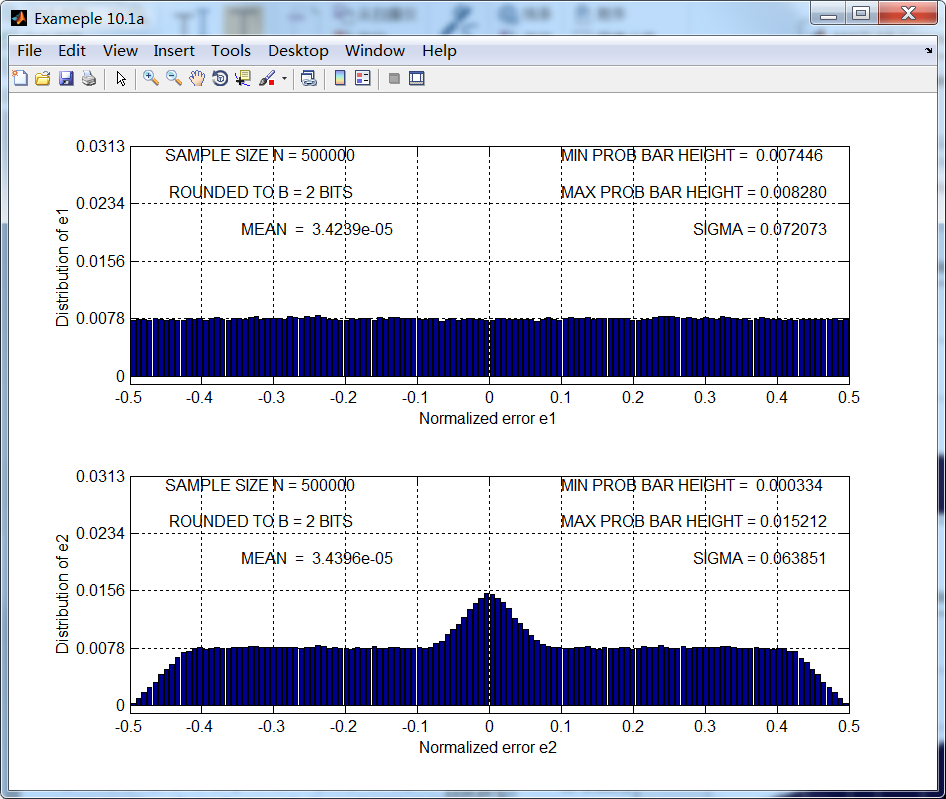
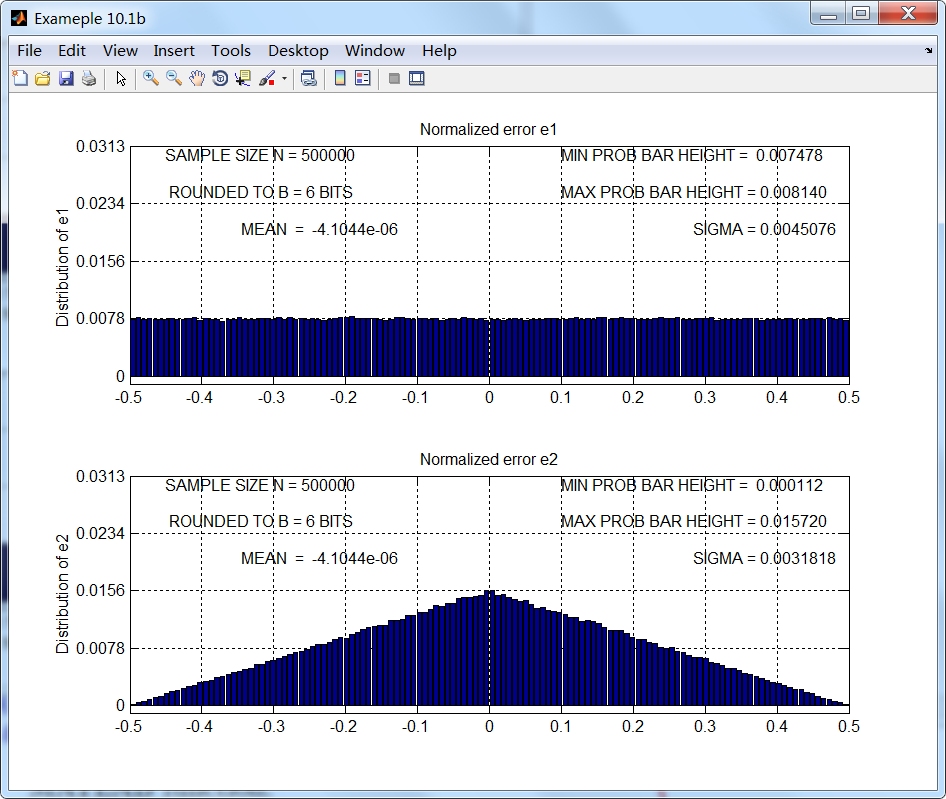
B=2的结果如第1张图所示,很明显,即使误差看起来均匀分布,但误差采样序列不是独立的。对应B=6的
结果如第2张图所示,当B≥6时,结果满足误差模型假设条件。
《DSP using MATLAB》示例 Example 10.1的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)) + j * rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % ...
- DSP using MATlAB 示例Example2.10
上代码 % noise sequence 1 x = [3, 11, 7, 0, -1, 4, 2]; nx = [-3:3]; % given signal x(n) [y,ny] = sigshi ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.13
上代码: w = [0:1:500]*pi/500; % freqency between 0 and +pi, [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. H = ex ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
用到的性质 代码: n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.8
代码: x = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [0,pi] axis divided into 501 points. X = ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.7
上代码: x1 = rand(1,11); x2 = rand(1,11); n = 0:10; alpha = 2; beta = 3; k = 0:500; w = (pi/500)*k; % [ ...
随机推荐
- uva11090 Bellman-Ford 运用
给定一一个n个点m条边的加权有向图, 平均值最小的回路. 二分答案,对于每个二分的mid 做一次Bellman-Fprd , 假设有k条边组成的回路. 回路上各条边的权值为 w1 , w2 ..wk ...
- 工具推荐. 在线unix, 在线python/perl脚本测试环境
在线python, perl, javascript, Lisp, Ruby等 http://melpon.org/wandbox/ 正则表达式在线测试工具 http://tools.jb51.ne ...
- mybatis的namespace
Mybatis的namespace是用来绑定Dao接口的,使用了namespace之后就可以不用写接口实现类,dao接口的方法对应mapper.xml中的sql语句. 详情见:https://blog ...
- OpenCV中Denoising相关函数的简单介绍
参考:http://wenhuix.github.io/research/denoise.html一.基本情况 (一)基本方法 Fast Non-Local Me ...
- 20145314郑凯杰《网络对抗技术》可选实验 shellcode注入与Return-to-libc攻击实验
20145314郑凯杰<网络对抗技术>可选实验 shellcode注入与Return-to-libc攻击实验 1.0 实践内容 Return-to-libc攻击是一种特殊的缓冲区溢出攻击, ...
- 20145319 《网络渗透》Adobe阅读器渗透攻击
20145319 <网络渗透>Adobe阅读器渗透攻击 一 实验内容 初步掌握平台matesploit的使用 有了初步完成渗透操作的思路 本次攻击对象:windows xp sp3 Ad ...
- postman中如何使用OAuth
https://learning.getpostman.com/docs/postman/sending_api_requests/authorization/ Authorization The a ...
- python应用-随机漫步
对python应用的一个巩固,以及熟悉matplotlib的用法 效果如下: # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Fri Sep ...
- POJ 1122 FDNY to the Rescue!(最短路+路径输出)
http://poj.org/problem?id=1122 题意:给出地图并且给出终点和多个起点,输出从各个起点到终点的路径和时间. 思路: 因为有多个起点,所以这里反向建图,这样就相当于把终点变成 ...
- 简单购物车的实现,session的使用
购物车浏览商品界面代码<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http:// ...
