吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression():
'''
加载用于回归问题的数据集
'''
#使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
# 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4
return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor()
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("Training score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Testing score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test)) # 获取分类数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
# 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor
test_GradientBoostingRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 n_estimators 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
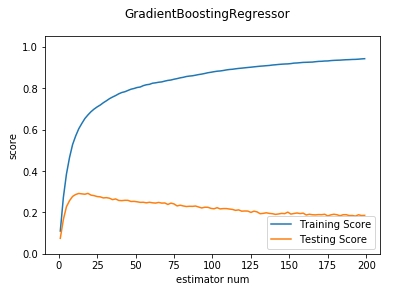
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_depth 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
maxdepths=np.arange(1,20)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for maxdepth in maxdepths:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_depth=maxdepth,max_leaf_nodes=None)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_maxdepth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)

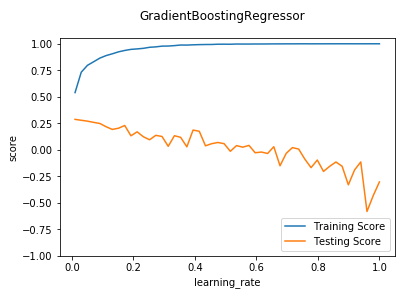
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 learning_rate 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
learnings=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for learning in learnings:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(learning_rate=learning)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(learnings,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(learnings,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("learning_rate")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_learning(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
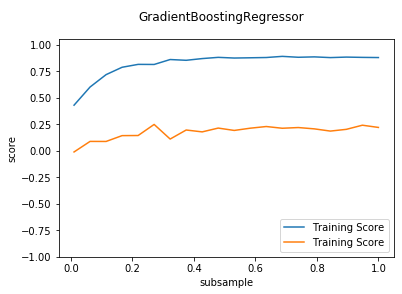
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 subsample 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
subsamples=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,num=20)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for subsample in subsamples:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(subsample=subsample)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(subsamples,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(subsamples,testing_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.set_xlabel("subsample")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_subsample(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
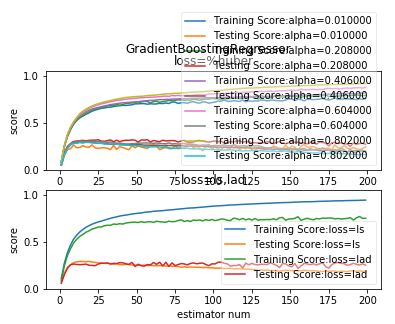
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随不同的损失函数和 alpha 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
nums=np.arange(1,200,step=2)
########## 绘制 huber ######
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,1)
alphas=np.linspace(0.01,1.0,endpoint=False,num=5)
for alpha in alphas:
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss='huber',alpha=alpha)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:alpha=%f"%alpha)
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:alpha=%f"%alpha)
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4)
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.set_title("loss=%huber")
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
#### 绘制 ls 和 lad
ax=fig.add_subplot(2,1,2)
for loss in ['ls','lad']:
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(n_estimators=num,loss=loss)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score:loss=%s"%loss)
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score:loss=%s"%loss)
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right",framealpha=0.4)
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
ax.set_title("loss=ls,lad")
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_loss(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
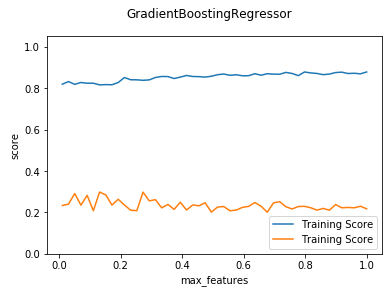
def test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(*data):
'''
测试 GradientBoostingRegressor 的预测性能随 max_features 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
max_features=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for features in max_features:
regr=ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor(max_features=features)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_features")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("GradientBoostingRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features
test_GradientBoostingRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestClassifier分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理字典学习模型
from sklearn.decomposition import DictionaryLearning #数据预处理字典学习DictionaryLearning模型 def test_Diction ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络感知机学习算法的应用
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn import neighbors, datasets from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——人工神经网络与原始感知机模型
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D from ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——分类决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——回归决策树模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.model_s ...
随机推荐
- Bootstrap框架中radio设置值
Bootstrap中的radio设置值不能像我们平常给普通radio赋值那样,因为无效. 我们用Bootstrap框架里的radio组件,代码: <div class="radio-l ...
- 开发过程中遇到的代理Proxy配置问题
proxy代理问题 在公司不能访问外网的时候,使用IDEA开发.. 需要配置IDEA Proxy Maven Git IDEA开发工具Proxy配置,使用Spring Boot快读构建工具 Maven ...
- windows ltsc版本没有Microsoft Store怎么解决
[背景]以前一直都是使用windows的企业版,后来发现ltsc版本更好,这个好处在这里就不多说,懂的人自然会懂.但是发现很多应用都没有,包括Microsoft Store商店都没有.下面就是解决 ...
- unittest框架下的HTMLTestRunner报告模块使用及优化
引言 在做接口自动化测试的时候,使用python单元测试框架unittest下HTMLTestRunner报告模板,可以很好的展示我们测试结果的数据. 官方的标准版模板地址:http://tungwa ...
- 【Unity|C#】番外篇(1)——6个重要概念:栈与堆,值类型与引用类型,装箱与拆箱
传送门:https://www.cnblogs.com/arthurliu/archive/2011/04/13/2015120.html
- 10.pandas的替换和部分替换(replace)
在处理数据的时候,很多时候会遇到批量替换的情况,如果一个一个去修改效率过低,也容易出错.replace()是很好的方法. 源数据 1.替换全部或者某一行 replace的基本结构是:df.repl ...
- VS 2017 mscorlib.dll 加载元数据时发生严重错误,需要终止调试
VS 2017 mscorlib.dll 加载元数据时发生严重错误,需要终止调试 C:\Windows\Microsoft.Net\assembly\GAC_64\mscorlib\v4.0_4.0. ...
- linux异常
常见报错语句 Command not found; - 找不到命令(敲入的命令有误或者该命令还没安装) No Such file or directory; - 找不到输入的文件或者目录
- Spring Boot的27个注解【核心】
导读[约定大于配置] Spring Boot方式的项目开发已经逐步成为Java应用开发领域的主流框架,它不仅可以方便地创建生产级的Spring应用程序,还能轻松地通过一些注解配置与目前比较火热的微服务 ...
- python3练习100题——016
今天的题目比较容易了,旨在让人掌握datetime模块下的一些用法. 链接:http://www.runoob.com/python/python-exercise-example16.html 题目 ...
