Android(java)学习笔记89:Bundle和Intent类使用和交互
1. Bundle 和 Intent:
Bundle只是一个信息的载体 将内部的内容以键值对组织 ,Intent负责Activity之间的交互自己是带有一个Bundle的。Intent.putExtras(Bundle bundle)直接将Intent的内部Bundle设置为参数里的bundle,Intent.getExtras()直接可以获取Intent带有的Bundle.
Intent携带了Bundle数据,Bundle是一种数据包裹(打包数据),利用Intent机制通过Bundle数据进行不同Activity通信。
两个activity之间的通讯可以通过bundle类来实现,做法就是:
(1)新建一个bundle类
Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();
(2)bundle类中加入数据(key -value的形式,另一个activity里面取数据的时候,就要用到key,找出对应的value)
mBundle.putString("Data", "data from TestBundle");
(3)新建一个intent对象,并将该bundle加入这个intent对象
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(TestBundle.this, Target.class);
intent.putExtras(mBundle);
完整代码如下:
AndroidManifest.xml如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tencent.test"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".TestBundle"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity android:name=".Target"></activity>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
</manifest>
两个类如下:intent从TestBundle类发起,到Target类。
类1:TestBundle类:
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button; public class TestBundle extends Activity { private Button button1;
private OnClickListener cl;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main); button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
cl = new OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(TestBundle.this, Target.class);
Bundle mBundle = new Bundle();
mBundle.putString("Data", "data from TestBundle");//压入数据
intent.putExtras(mBundle);
startActivity(intent);
}
};
button1.setOnClickListener(cl);
}
}
类2: Target
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle; public class Target extends Activity{ public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.target);
<span style="color:#ff6600;">Bundle bundle = getIntent().getExtras(); </span> //得到传过来的bundle
String data = bundle.getString("Data");//读出数据
setTitle(data); }
}
布局文件main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/button"
android:id = "@+id/button1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
target.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/target"
/>
</LinearLayout>
String.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
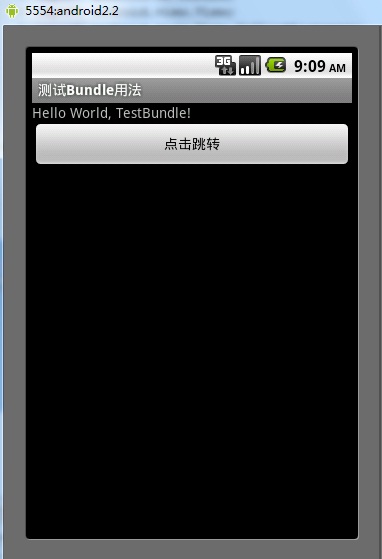
<string name="hello">Hello World, TestBundle!</string>
<string name="app_name">测试Bundle用法</string>
<string name="button">点击跳转</string>
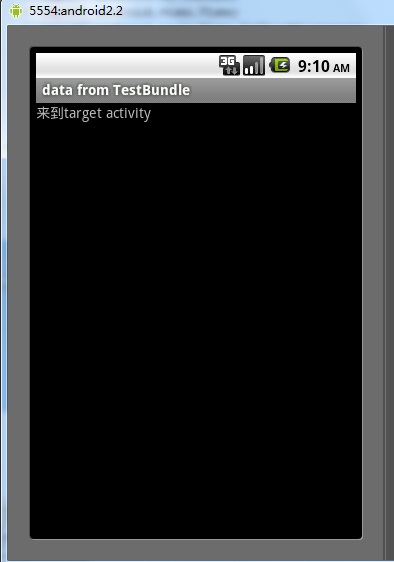
<string name="target">来到target activity</string>
</resources>
结果:
跳转结果:
Android(java)学习笔记89:Bundle和Intent类使用和交互的更多相关文章
- Android(java)学习笔记146:Bundle和Intent类使用和交互
Bundle只是一个信息的载体 将内部的内容以键值对组织 ,Intent负责Activity之间的交互自己是带有一个Bundle的.Intent.putExtras(Bundle bu ...
- 疯狂java学习笔记之面向对象(一) - 定义类、方法、构造器
Java面向对象 1.定义类 2.创建对象.调用方法 类和对象: 某一类对象的概念定义. 比如:人类 - 抽象出来的概念(不特指某个人) 对象 - 在类的概念下产生的一个实例,它就是一个对象了. ja ...
- java学习笔记(三):类和对象
创建对象 构造器 每一个类都有一个构造器. 如果我们不单独为一个类编写构造器那么 Java 的编译器将会给这个类建立一个默认的构造器. 每当一个新的对象被创建,至少一个构造器将会被调用. 构造器的一 ...
- Java学习笔记(七)——获取类中方法的信息,java的LinkedList
[前面的话] 在实际项目中学习知识总是最快和最有效的,既能够较好的掌握知识,又能够做出点东西,还是简单的知识总结,最近一直在总结笔记,写的东西还是比较水,希望慢慢可以写出一些干货. 学习过程中的小知识 ...
- java学习笔记37(sql工具类:JDBCUtils)
在之前的内容中,我们发现,当我们执行一条语句时,每新建一个方法,就要重新连接一次数据库,代码重复率很高,那么能不能把这些重复代码封装成一个类呢,我们学习方法时,就学习到方法就是为了提高代码的利用率,所 ...
- java学习笔记(五):公共类
什么是公共类,公共类就是和源文件名同名的类,举例来说:类的名称是 public class aaa{},那么源文件就应该是 aaa.java. 每个源文件中只能有一个公共类. 每个源文件可以有很多非公 ...
- Java学习笔记49(DBUtils工具类二)
上一篇文章是我们自己模拟的DBUtils工具类,其实有开发好的工具类 这里使用commons-dbutils-1.6.jar 事务的简单介绍: 在数据库中应用事务处理案例:转账案例 张三和李四都有有自 ...
- Java学习笔记48(DBUtils工具类一)
上一篇的例子可以明显看出,在增删改查的时候,很多的代码都是重复的, 那么,是否可以将增删改查封装成一个类,方便使用者 package demo; /* * 实现JDBC的工具类 * 定义方法,直接返回 ...
- Java学习笔记_22_Set接口的实现类
22.Set接口的实现类: Set接口存放的元素是无序的且不包括反复元素. 1>实现类HashSet: HashSet类依据元素的哈希码进行存放,取出时也能够依据哈希码高速找到.HashSet不 ...
随机推荐
- MATLAB实现插值和拟合
插值问题在应用领域中,由有限个已知数据点,构造一个解析表达式,由此计算数据点之间的函数值,称之为插值.实例:海底探测问题某公司用声纳对海底进行测试,在5×5海里的坐标点上测得海底深度的值,希望通过这些 ...
- App裂变活动多种玩法解析
移动互联网时代,流量为王.在App获取流量的过程中,有资金的砸广告,没资金的铺渠道,但是不管你有钱没钱,社交平台都是必须重点争夺的流量阵地. 毕竟,截至2018年底,微信及WeChat的合并月活跃账户 ...
- python web开发之flask框架学习(1) 创建flask项目
python 开发越来越火,作为菜鸟,也应该学习一下,感觉还可以,记录下来,方便学习参考. 不管做什么开发首先肯定是安装环境,这里我用的是pycharm,python3.如果不清楚怎么安装环境可以去网 ...
- 帝都Day6——图论
//P2O5呢? 一.图的存储: 邻接矩阵:邻接表. 邻接矩阵:n*n的[][],[i][j]节点有边记1没边0 缺点 空间复杂度O(n^2) 占用内存较大(我为什么要把这些东西写到这里呢???) 邻 ...
- 41.QT-多线程与界面之间交互总结
1. 线程与界面组件需要注意的地方 在QThread线程中不能直接创建QWidget之类的界面组件. 因为在QT中,所有界面组件相关的操作都必须在主线程中(也就是GUI thread) 所以, QTh ...
- Webpack, 现在最流行的模块打包工具.压缩打包
压缩bundle.js 1.把我们项目的代码从es6 -> es5 [babel] 参考:http://babeljs.io/docs/setup/#installation 1.1.安装包 b ...
- 牛客练习赛41D(思维转化)
AC通道 要点 思路:题解中将所求进行转化\[max\{相似度\} = max\{M-不相似度\} = M-min\{不相似度\}\]因此转化为求某01串T与所给众S串的最小不相似度,而最终答案是选取 ...
- OpenCV3的配置(VS2015)
1:首先下载和解压到给定的目录 2:设置环境变量...\build\x64\vc14\bin 3:打开VS,新建一个项目,再添加一个代码,刚开始当然是报错的 #include<opencv2\o ...
- Django---登录(含随机生成图片验证码)、注册示例讲解
登录(验证码).注册功能具体代码 # urls.py from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path from app01 ...
- FileTest
package com.yd.wmsc.util; import java.io.File; public class FileTest { public static void main(Strin ...
