leetcode#42 Trapping rain water的五种解法详解
leetcode#42 Trapping rain water
这道题十分有意思,可以用很多方法做出来,每种方法的思想都值得让人细细体会。
42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
For example,
Given [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1], return 6.

Solution 1:
通过分别计算每一坐标i上有多少水,进而将其相加得到答案。
问题是我们如何知道每一坐标i上有多少水呢?仔细思考,其实只有出现“两高夹一矮”才可能会存到水,如下图所示。

进而,我们可以想到:每一坐标i上存多少水是由 1.其自身高度 2.它左边的最高高度left_most 3.它右边的最高高度right_most三种因素决定的。
当 min{ left_most, right_most} 小于或等于其自身高度时,它能存的水就是0,比如array[1]=1,其left_most= array[0]=0, 其right_most=array[7]=3, min{left_most, right_most}=left_most=0< height= array[1]=1,这也就是说坐标1 存不了水。
当min{ left_most,right_most} 大于其自身高度时,这时这三者间出现了“两高夹一矮”的情况,故其能存水,而且其存水数= min{left_most,right_most} - height。
我们分别来对一些坐标进行验证:
坐标1,存水数=0.//正确
坐标2,leff_most=1,right_most=3,存水数=left_most-height=1-0=1.//正确
坐标3,left_most=1,right_most=3,min{left_most,right_most}=1=height,存水数=0.//正确
读者可以对每个坐标进行验证,会发现以上结论皆是正确的。所以,现在我们的solution就出来了,我们只需要求出每个坐标对应的left_most和right_most,再把存水数相加,就是总的存水数了。
所以,很朴素自然的一个想法就是,遍历一遍数组,对每个数组元素遍历左边一次求出left_most,遍历右边一次求出right_most。
代码如下,
//29ms 6.36%
//complexity: O(N^2)
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
int ans = 0;
int size = height.size();
for (int i = 1; i < size - 1; i++) {
int max_left = 0, max_right = 0;
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) { //Search the left part for max bar size
max_left = max(max_left, height[j]);
}
for (int j = i; j < size; j++) { //Search the right part for max bar size
max_right = max(max_right, height[j]);
}
ans += min(max_left, max_right) - height[i];
}
return ans;
}
Solution 2:
在solution 1里,我们已经知道只要求出left_most和right_most,就可以求出答案,那能不能优化一下求这两个数的过程呢?当然是可以的,我们只需要左遍历一次数组,右遍历一次数组,即可得到left_most和right_most。
/*Solution2: 上一种方法其实有优化的空间
通过两次for循环可分别求得left_most和right_most,第三次for循环即可求得sum,
complexity: O(n)
*/
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
if(height == null)
return ;
int ans = ;
int size = height.size();
vector<int> left_max(size), right_max(size);
left_max[] = height[];
for (int i = ; i < size; i++) {
left_max[i] = max(height[i], left_max[i - ]);
}
right_max[size - ] = height[size - ];
for (int i = size - ; i >= ; i--) {
right_max[i] = max(height[i], right_max[i + ]);
}
for (int i = ; i < size - ; i++) {
ans += min(left_max[i], right_max[i]) - height[i];
}
return ans;
}
Solution 3:
这里再介绍一种优化方法,双指针法,在数组首尾分别创建一个指针,两指针相见时结束循环。
int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
int left = , right = height.size() - ;
int ans = ;
int left_max = , right_max = ;
while (left < right) {
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
height[left] >= left_max ? (left_max = height[left]) : ans += (left_max - height[left]);
++left;
}
else {
height[right] >= right_max ? (right_max = height[right]) : ans += (right_max - height[right]);
--right;
}
}
return ans;
}
Solution 4:
既然可以纵向的求存水数,那我们能不能一层一层的求存水数呢?

这是第一层,当我们遇到一个空的,且不在边界,存水数+1,所以第一层我们在i=2,i=5 时分别+1.

第二层,存水数+4,依次类推,最终可以求出答案。
代码笔者就不给了,读者有兴趣的可以自己写来试试。
Soluton 5:
这是在leetcode中solution给出的一种很新颖的解法,利用了栈的结构,通过维护一个非递增栈来得到答案。
本质思想还是利用了要存水必须是“两高夹一矮”这个特点,只不过这里是用非递增栈来实现。
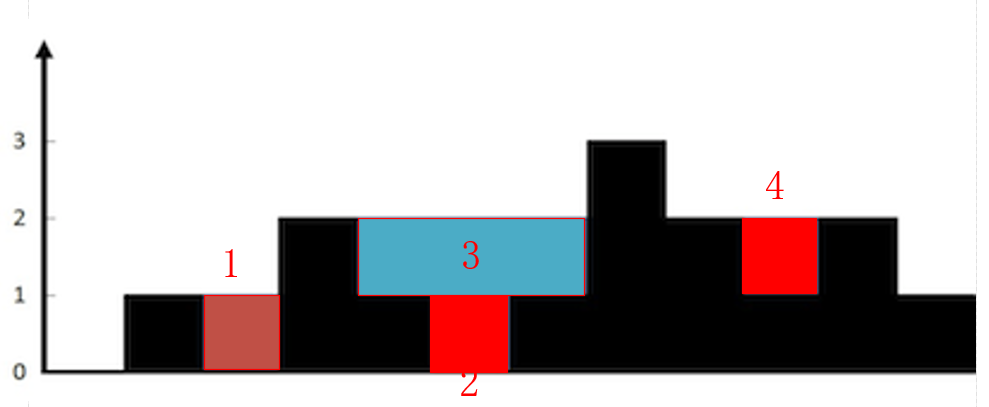
下面定义一些符号以便理解:
stack[-1] 栈顶元素
stack[-2] 栈顶的下面一个元素(即倒数第二个元素)
solution4的整个算法是这么实现的:遍历数组,遇到一个元素时,将其与栈顶元素比较,如果其小于等于栈顶元素,直接压栈,将其放入栈中(为维护非递增栈的结构,不能将比栈顶元素大的元素压栈),
若是其大于栈顶元素,此时一定形成了一个“两高夹一矮”局面,因为栈是非递增栈,所以 stack[-1]<stack[-2],又 current>stack[-1],所以是一个“两高夹一矮”局面,此时算完存水数后栈顶元素出栈,继续判断,
递归处理即可。
在上例中整个过程是这样的。
step0: 0不入栈
step1: 1>0 array[1] 入栈 栈:[1]
step2: 0<stack[-1]=1 入栈 栈:[1,0]
step3: 2>stack[-1]=0 存水数+1,0出栈,2>stack[-1]=1, 此时stack内元素不足2,不足以形成“两高夹一矮”局面, 1出栈,2入栈 栈:[2]
step4: 1<stack[-1]=2 1入栈 栈:[2,1]
step5: 0<stack[-1]=1 0入栈 栈:[2,1,0]
step6: 1>stack[-1]=0 存水数+1,0出栈 1=stack[-1] 1入栈 栈:[2,1,1]
step7: 3>stack[-1]=1 存水数+0,1出栈 3>stack[-1]=1 存水数+3,1出栈 3>stack[-1]=2 存水数+0 2出栈 3入栈 栈:[3]
step8: 2<stack[-1] 2入栈 栈:[3,2]
step9: 1<stack[-1] 1入栈 栈:[3,2,1]
step10: 2>stack[-1] 存水数+1 1出栈 2入栈 栈:[3,2,2]
step 11:1<stack[-1] 入栈 栈:[3,2,2,1]
done
/*Solution4
Stack solution
这个solution利用了栈结构,通过维护一个非递增栈,一步一步算出ans
*/ int trap(vector<int>& height)
{
int ans = , current = ;
stack<int> st;
while (current < height.size()) {
while (!st.empty() && height[current] > height[st.top()]) {
int top = st.top();
st.pop();
if (st.empty())
break;
int distance = current - st.top() - ;
int bounded_height = min(height[current], height[st.top()]) - height[top];
ans += distance * bounded_height;
}
st.push(current++);
}
return ans;
}
leetcode#42 Trapping rain water的五种解法详解的更多相关文章
- LeetCode 42. Trapping Rain Water 【两种解法】(python排序遍历,C++ STL map存索引,时间复杂度O(nlogn))
LeetCode 42. Trapping Rain Water Python解法 解题思路: 本思路需找到最高点左右遍历,时间复杂度O(nlogn),以下为向左遍历的过程. 将每一个点的高度和索引存 ...
- [array] leetcode - 42. Trapping Rain Water - Hard
leetcode - 42. Trapping Rain Water - Hard descrition Given n non-negative integers representing an e ...
- LeetCode - 42. Trapping Rain Water
42. Trapping Rain Water Problem's Link ------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- [LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water 收集雨水
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, comput ...
- leetCode 42.Trapping Rain Water(凹槽的雨水) 解题思路和方法
Trapping Rain Water Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of e ...
- [LeetCode] 42. Trapping Rain Water 解题思路
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, comput ...
- [leetcode]42. Trapping Rain Water雨水积水问题
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, comput ...
- LeetCode 42 Trapping Rain Water(积水体积)
题目链接: https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/?tab=Description Problem: 根据所给数组的值,按照上图的示意 ...
- Java [Leetcode 42]Trapping Rain Water
题目描述: Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, ...
随机推荐
- NOIP2015运输计划(树上前缀和+LCA+二分)
Description 公元 2044 年,人类进入了宇宙纪元. L 国有 n 个星球,还有 n−1 条双向航道,每条航道建立在两个星球之间,这 n−1 条航道连通了 L 国的所有星球. 小 P 掌管 ...
- linux 下gcc生成intel汇编
留作备忘: gcc -S -masm=intel xxxx.c 生成elf可执行文件: gcc -o xxx xxxx.s 反汇编 objdump xxx 补充: 在使用gcc 对C语言程序进行编译时 ...
- 个人怎么申请微信小程序
1.打开微信公众平台(mp.weixin.qq.com).拉到中间的"账号分类",鼠标悬浮于"小程序"框中并点击"查看详情". 2.进入微信 ...
- Tomcat 笔记-配置虚拟目录
,默认情况下,只有webapps下的目录才能被Tomcat自动管理成一个web站点,把web站点的目录分散到其他磁盘管理就需要配置虚拟目录.把web应用所在目录交给web服务器管理,这个过程称之为虚拟 ...
- 为什么String类是不可变的?
为什么String类是不可变的? String类 什么是不可变对象 当满足以下条件时,对象才是不可变的: 对象创建以后其状态就不能修改. 对象的所有域都是final类型的. 对象是正确创建的(在对象的 ...
- Java的继承、封装与多态
Java的继承.封装与多态 基本概念 面向对象OO(Object Oriented):把数据及对数据的操作方法放在一起,作为一个相互依存的整体,即对象. 对同类对象抽象出共性,即类. 比如人就是一个类 ...
- 有序链表--Java实现
/*有序链表--使用的是单链表实现 *在插入的时候保持按照值顺序排列 *对于删除最小值的节点效率最高--适合频繁的删除最小的节点 * */ public class MySortedLinkList ...
- C++内联函数(03)
在C++中我们通常定义以下函数来求两个整数的最大值: 代码如下: int max(int a, int b){ return a > b ? a : b;} 为这么一个小的操作定义一个函数的好处 ...
- 使用Hibernate Tools从数据库逆向生成Hibernate实体类
自动生成model.java.*.hbm.xml 甚至是dao.java.*.ddl.*.html等等.一般也就如下三种方式1. MyEclipse 自带插件2. jboss的 hibernate-t ...
- vi 编辑器笔记
摘要: vi从安装到使用 vi从菜鸟到高手 0. vim - Vi IMproved, a programmers text editor 分为 VI和VIM,现在流行的发行版里面VI=VIM 是一个 ...
