吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(3)
import os
import sys
import random
import math
import re
import time
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from config import Config
import utils
import model as modellib
import visualize
from model import log %matplotlib inline # Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.getcwd() # Directory to save logs and trained model
MODEL_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs") # Local path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
# Download COCO trained weights from Releases if needed
if not os.path.exists(COCO_MODEL_PATH):
utils.download_trained_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH)
class ShapesConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on the toy shapes dataset.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the toy shapes dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "shapes" # Train on 1 GPU and 8 images per GPU. We can put multiple images on each
# GPU because the images are small. Batch size is 8 (GPUs * images/GPU).
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 8 # Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 3 # background + 3 shapes # Use small images for faster training. Set the limits of the small side
# the large side, and that determines the image shape.
IMAGE_MIN_DIM = 128
IMAGE_MAX_DIM = 128 # Use smaller anchors because our image and objects are small
RPN_ANCHOR_SCALES = (8, 16, 32, 64, 128) # anchor side in pixels # Reduce training ROIs per image because the images are small and have
# few objects. Aim to allow ROI sampling to pick 33% positive ROIs.
TRAIN_ROIS_PER_IMAGE = 32 # Use a small epoch since the data is simple
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = 100 # use small validation steps since the epoch is small
VALIDATION_STEPS = 5 config = ShapesConfig()
config.display()

def get_ax(rows=1, cols=1, size=8):
"""Return a Matplotlib Axes array to be used in
all visualizations in the notebook. Provide a
central point to control graph sizes. Change the default size attribute to control the size
of rendered images
"""
_, ax = plt.subplots(rows, cols, figsize=(size*cols, size*rows))
return ax
class ShapesDataset(utils.Dataset):
"""Generates the shapes synthetic dataset. The dataset consists of simple
shapes (triangles, squares, circles) placed randomly on a blank surface.
The images are generated on the fly. No file access required.
""" def load_shapes(self, count, height, width):
"""Generate the requested number of synthetic images.
count: number of images to generate.
height, width: the size of the generated images.
"""
# Add classes
self.add_class("shapes", 1, "square")
self.add_class("shapes", 2, "circle")
self.add_class("shapes", 3, "triangle") # Add images
# Generate random specifications of images (i.e. color and
# list of shapes sizes and locations). This is more compact than
# actual images. Images are generated on the fly in load_image().
for i in range(count):
bg_color, shapes = self.random_image(height, width)
self.add_image("shapes", image_id=i, path=None,
width=width, height=height,
bg_color=bg_color, shapes=shapes) def load_image(self, image_id):
"""Generate an image from the specs of the given image ID.
Typically this function loads the image from a file, but
in this case it generates the image on the fly from the
specs in image_info.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
bg_color = np.array(info['bg_color']).reshape([1, 1, 3])
image = np.ones([info['height'], info['width'], 3], dtype=np.uint8)
image = image * bg_color.astype(np.uint8)
for shape, color, dims in info['shapes']:
image = self.draw_shape(image, shape, dims, color)
return image def image_reference(self, image_id):
"""Return the shapes data of the image."""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
if info["source"] == "shapes":
return info["shapes"]
else:
super(self.__class__).image_reference(self, image_id) def load_mask(self, image_id):
"""Generate instance masks for shapes of the given image ID.
"""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
shapes = info['shapes']
count = len(shapes)
mask = np.zeros([info['height'], info['width'], count], dtype=np.uint8)
for i, (shape, _, dims) in enumerate(info['shapes']):
mask[:, :, i:i+1] = self.draw_shape(mask[:, :, i:i+1].copy(),
shape, dims, 1)
# Handle occlusions
occlusion = np.logical_not(mask[:, :, -1]).astype(np.uint8)
for i in range(count-2, -1, -1):
mask[:, :, i] = mask[:, :, i] * occlusion
occlusion = np.logical_and(occlusion, np.logical_not(mask[:, :, i]))
# Map class names to class IDs.
class_ids = np.array([self.class_names.index(s[0]) for s in shapes])
return mask, class_ids.astype(np.int32) def draw_shape(self, image, shape, dims, color):
"""Draws a shape from the given specs."""
# Get the center x, y and the size s
x, y, s = dims
if shape == 'square':
cv2.rectangle(image, (x-s, y-s), (x+s, y+s), color, -1)
elif shape == "circle":
cv2.circle(image, (x, y), s, color, -1)
elif shape == "triangle":
points = np.array([[(x, y-s),
(x-s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
(x+s/math.sin(math.radians(60)), y+s),
]], dtype=np.int32)
cv2.fillPoly(image, points, color)
return image def random_shape(self, height, width):
"""Generates specifications of a random shape that lies within
the given height and width boundaries.
Returns a tuple of three valus:
* The shape name (square, circle, ...)
* Shape color: a tuple of 3 values, RGB.
* Shape dimensions: A tuple of values that define the shape size
and location. Differs per shape type.
"""
# Shape
shape = random.choice(["square", "circle", "triangle"])
# Color
color = tuple([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Center x, y
buffer = 20
y = random.randint(buffer, height - buffer - 1)
x = random.randint(buffer, width - buffer - 1)
# Size
s = random.randint(buffer, height//4)
return shape, color, (x, y, s) def random_image(self, height, width):
"""Creates random specifications of an image with multiple shapes.
Returns the background color of the image and a list of shape
specifications that can be used to draw the image.
"""
# Pick random background color
bg_color = np.array([random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)])
# Generate a few random shapes and record their
# bounding boxes
shapes = []
boxes = []
N = random.randint(1, 4)
for _ in range(N):
shape, color, dims = self.random_shape(height, width)
shapes.append((shape, color, dims))
x, y, s = dims
boxes.append([y-s, x-s, y+s, x+s])
# Apply non-max suppression wit 0.3 threshold to avoid
# shapes covering each other
keep_ixs = utils.non_max_suppression(np.array(boxes), np.arange(N), 0.3)
shapes = [s for i, s in enumerate(shapes) if i in keep_ixs]
return bg_color, shapes
# Training dataset
dataset_train = ShapesDataset()
dataset_train.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
dataset_train.prepare() # Validation dataset
dataset_val = ShapesDataset()
dataset_val.load_shapes(50, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
dataset_val.prepare()
# Load and display random samples
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_train.image_ids, 4)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset_train.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset_train.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset_train.class_names)
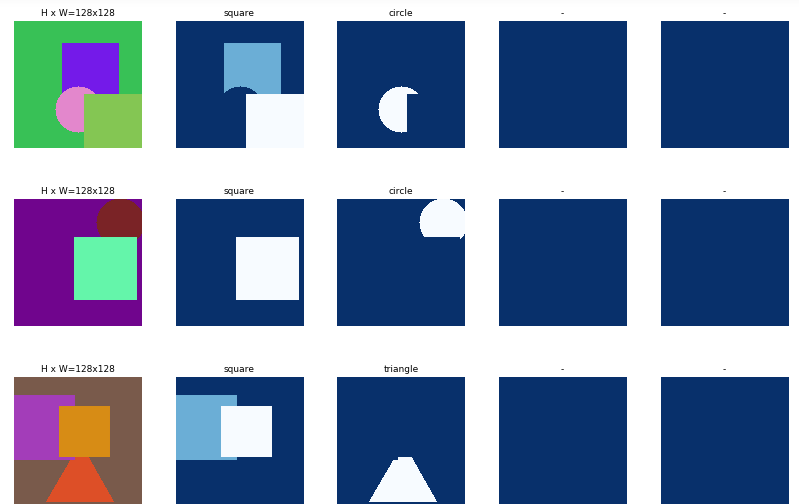
# Create model in training mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR)
# Which weights to start with?
init_with = "coco" # imagenet, coco, or last if init_with == "imagenet":
model.load_weights(model.get_imagenet_weights(), by_name=True)
elif init_with == "coco":
# Load weights trained on MS COCO, but skip layers that
# are different due to the different number of classes
# See README for instructions to download the COCO weights
model.load_weights(COCO_MODEL_PATH, by_name=True,
exclude=["mrcnn_class_logits", "mrcnn_bbox_fc",
"mrcnn_bbox", "mrcnn_mask"])
elif init_with == "last":
# Load the last model you trained and continue training
model.load_weights(model.find_last()[1], by_name=True)
# Train the head branches
# Passing layers="heads" freezes all layers except the head
# layers. You can also pass a regular expression to select
# which layers to train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=1,
layers='heads')

# Fine tune all layers
# Passing layers="all" trains all layers. You can also
# pass a regular expression to select which layers to
# train by name pattern.
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10,
epochs=2,
layers="all")

# Save weights
# Typically not needed because callbacks save after every epoch
# Uncomment to save manually
# model_path = os.path.join(MODEL_DIR, "mask_rcnn_shapes.h5")
# model.keras_model.save_weights(model_path)
class InferenceConfig(ShapesConfig):
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1 inference_config = InferenceConfig() # Recreate the model in inference mode
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference",
config=inference_config,
model_dir=MODEL_DIR) # Get path to saved weights
# Either set a specific path or find last trained weights
# model_path = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, ".h5 file name here")
model_path = model.find_last()[1] # Load trained weights (fill in path to trained weights here)
assert model_path != "", "Provide path to trained weights"
print("Loading weights from ", model_path)
model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True)
# Test on a random image
image_id = random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids)
original_image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\
modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config,
image_id, use_mini_mask=False) log("original_image", original_image)
log("image_meta", image_meta)
log("gt_class_id", gt_class_id)
log("gt_bbox", gt_bbox)
log("gt_mask", gt_mask) visualize.display_instances(original_image, gt_bbox, gt_mask, gt_class_id,
dataset_train.class_names, figsize=(8, 8))
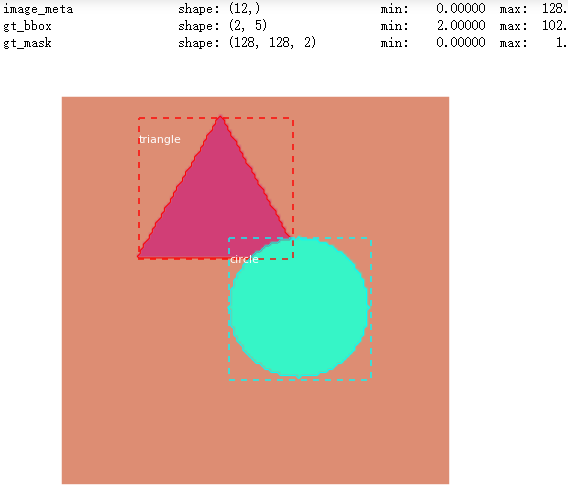
results = model.detect([original_image], verbose=1) r = results[0]
visualize.display_instances(original_image, r['rois'], r['masks'], r['class_ids'],
dataset_val.class_names, r['scores'], ax=get_ax())

# Compute VOC-Style mAP @ IoU=0.5
# Running on 10 images. Increase for better accuracy.
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset_val.image_ids, 10)
APs = []
for image_id in image_ids:
# Load image and ground truth data
image, image_meta, gt_class_id, gt_bbox, gt_mask =\
modellib.load_image_gt(dataset_val, inference_config,
image_id, use_mini_mask=False)
molded_images = np.expand_dims(modellib.mold_image(image, inference_config), 0)
# Run object detection
results = model.detect([image], verbose=0)
r = results[0]
# Compute AP
AP, precisions, recalls, overlaps =\
utils.compute_ap(gt_bbox, gt_class_id, gt_mask,
r["rois"], r["class_ids"], r["scores"], r['masks'])
APs.append(AP) print("mAP: ", np.mean(APs))
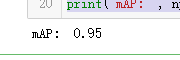
吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(3)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——基于MASK_RCNN目标检测(5)
import os import sys import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib import matplotlib. ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——基于MASK_RCNN目标检测(4)
import os import sys import random import math import re import time import numpy as np import tenso ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(2)
import os import sys import itertools import math import logging import json import re import random ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于Mask_RCNN目标检测(1)
import os import sys import random import math import numpy as np import skimage.io import matplotli ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——基于神经网络算法在智能医疗诊断中的应用探索代码简要展示
#K-NN分类 import os import sys import time import operator import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import ...
- 吴裕雄 PYTHON 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台智能分诊模块及系统健康养生公告简约版代码展示
#coding:utf-8 import sys import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tensorflow a ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台用户复诊模块简约版代码展示
#复诊 import sys import os import time import operator import cx_Oracle import numpy as np import pand ...
- 吴裕雄 python 人工智能——智能医疗系统后台用户注册、登录和初诊简约版代码展示
#用户注册.登录模块 #数据库脚本 CREATE TABLE usertable( userid number(8) primary key not null , username varchar(5 ...
- TF项目实战(基于SSD目标检测)——人脸检测1
SSD实战——人脸检测 Tensorflow 一 .人脸检测的困难: 1. 姿态问题 2.不同种族人, 3.光照 遮挡 带眼睛 4.视角不同 5. 不同尺度 二. 数据集介绍以及转化VOC: 1. F ...
随机推荐
- Paper: A Novel Time Series Forecasting Method Based on Fuzzy Visibility Graph
Problem define a fuzzy visibility graph (undirected weighted graph), then give a new similarity meas ...
- C++-标准模板库
C++较之C语言强大的功能之一是,C++编译器自带了大量的可复用代码库,我们称为标准模板库(standard template library),STL.标准模板库是一套常用的数据结构的集合,包括链表 ...
- 中国城市区号脚本-mysql
中国城市区号 300个. SET NAMES utf8mb4; ; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `citycode`; CREATE TABLE `citycode` ( `codeId ...
- 集成Log4Net到自己的Unity工程
需要使用的插件库说明: Loxodon Framework Log4NetVersion: 1.0.0© 2016, Clark Yang=============================== ...
- 【译】用 `Wasmer` 进行插件开发 1
[译]用 Wasmer 进行插件开发 1 Using Wasmer for Plugins Part 1 译文 原文链接 https://wiredforge.com/blog/wasmer-plug ...
- k8s集群问题记录
k8s集群问题记录 k8s学习方案 问题解决思路 主要学习路径: rancher(k8s)->rke->helm->kubectl->k8s(k8s中文api) 常见问题总结: ...
- Dreamoon and WiFi
Dreamoon is standing at the position 0 on a number line. Drazil is sending a list of commands throug ...
- sqlserver表中导入大批量数据
背景: 想要往sqlserver数据库中导入大批量数据,使得数据库的备份文件大于几个G. 注意: 导入的数据不能太规范,数据表最好不一致,否则会自动压缩. 解决办法: 1)通过excel导入,可以参考 ...
- [AGC027C]ABland Yard
Description AGC027C 给定一张图,点有标号A或B,计算是否对于任意的一个由AB构成的字符串都在图中有对应的路径. Solution 观察可以发现,如果有个环(不一定是简单环)是AAB ...
- Oracle常用函数记录
Oracle函数 --schema:hcf --不带任何参数 http://www.cnblogs.com/wuyisky/archive/2010/05/11/oracle_function.htm ...
