【python实现卷积神经网络】优化器的实现(SGD、Nesterov、Adagrad、Adadelta、RMSprop、Adam)
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch
卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride、padding)的具体实现:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/12706576.html
激活函数的实现(sigmoid、softmax、tanh、relu、leakyrelu、elu、selu、softplus):https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/12713081.html
损失函数定义(均方误差、交叉熵损失):https://www.cnblogs.com/xiximayou/p/12713198.html
先看下优化器实现的代码:
import numpy as np
from mlfromscratch.utils import make_diagonal, normalize # Optimizers for models that use gradient based methods for finding the
# weights that minimizes the loss.
# A great resource for understanding these methods:
# http://sebastianruder.com/optimizing-gradient-descent/index.html class StochasticGradientDescent():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.momentum = momentum
self.w_updt = None def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.w_updt is None:
self.w_updt = np.zeros(np.shape(w))
# Use momentum if set
self.w_updt = self.momentum * self.w_updt + (1 - self.momentum) * grad_wrt_w
# Move against the gradient to minimize loss
return w - self.learning_rate * self.w_updt class NesterovAcceleratedGradient():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.001, momentum=0.4):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.momentum = momentum
self.w_updt = np.array([]) def update(self, w, grad_func):
# Calculate the gradient of the loss a bit further down the slope from w
approx_future_grad = np.clip(grad_func(w - self.momentum * self.w_updt), -1, 1)
# Initialize on first update
if not self.w_updt.any():
self.w_updt = np.zeros(np.shape(w)) self.w_updt = self.momentum * self.w_updt + self.learning_rate * approx_future_grad
# Move against the gradient to minimize loss
return w - self.w_updt class Adagrad():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.G = None # Sum of squares of the gradients
self.eps = 1e-8 def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.G is None:
self.G = np.zeros(np.shape(w))
# Add the square of the gradient of the loss function at w
self.G += np.power(grad_wrt_w, 2)
# Adaptive gradient with higher learning rate for sparse data
return w - self.learning_rate * grad_wrt_w / np.sqrt(self.G + self.eps) class Adadelta():
def __init__(self, rho=0.95, eps=1e-6):
self.E_w_updt = None # Running average of squared parameter updates
self.E_grad = None # Running average of the squared gradient of w
self.w_updt = None # Parameter update
self.eps = eps
self.rho = rho def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.w_updt is None:
self.w_updt = np.zeros(np.shape(w))
self.E_w_updt = np.zeros(np.shape(w))
self.E_grad = np.zeros(np.shape(grad_wrt_w)) # Update average of gradients at w
self.E_grad = self.rho * self.E_grad + (1 - self.rho) * np.power(grad_wrt_w, 2) RMS_delta_w = np.sqrt(self.E_w_updt + self.eps)
RMS_grad = np.sqrt(self.E_grad + self.eps) # Adaptive learning rate
adaptive_lr = RMS_delta_w / RMS_grad # Calculate the update
self.w_updt = adaptive_lr * grad_wrt_w # Update the running average of w updates
self.E_w_updt = self.rho * self.E_w_updt + (1 - self.rho) * np.power(self.w_updt, 2) return w - self.w_updt class RMSprop():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, rho=0.9):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.Eg = None # Running average of the square gradients at w
self.eps = 1e-8
self.rho = rho def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.Eg is None:
self.Eg = np.zeros(np.shape(grad_wrt_w)) self.Eg = self.rho * self.Eg + (1 - self.rho) * np.power(grad_wrt_w, 2) # Divide the learning rate for a weight by a running average of the magnitudes of recent
# gradients for that weight
return w - self.learning_rate * grad_wrt_w / np.sqrt(self.Eg + self.eps) class Adam():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.001, b1=0.9, b2=0.999):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.eps = 1e-8
self.m = None
self.v = None
# Decay rates
self.b1 = b1
self.b2 = b2 def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.m is None:
self.m = np.zeros(np.shape(grad_wrt_w))
self.v = np.zeros(np.shape(grad_wrt_w)) self.m = self.b1 * self.m + (1 - self.b1) * grad_wrt_w
self.v = self.b2 * self.v + (1 - self.b2) * np.power(grad_wrt_w, 2) m_hat = self.m / (1 - self.b1)
v_hat = self.v / (1 - self.b2) self.w_updt = self.learning_rate * m_hat / (np.sqrt(v_hat) + self.eps) return w - self.w_updt
这里导入了了mlfromscratch.utils中的make_diagonal, normalize函数,它们在data_manipulation.py中。但是好像没有用到,还是去看一下这两个函数:
def make_diagonal(x):
""" Converts a vector into an diagonal matrix """
m = np.zeros((len(x), len(x)))
for i in range(len(m[0])):
m[i, i] = x[i]
return m
def normalize(X, axis=-1, order=2):
""" Normalize the dataset X """
l2 = np.atleast_1d(np.linalg.norm(X, order, axis))
l2[l2 == 0] = 1
return X / np.expand_dims(l2, axis)
make_diagonal()的作用是将x中的元素变成对角元素。
normalize()函数的作用是正则化。
补充:
- np.linalg.norm(x, ord=None, axis=None, keepdims=False):需要注意ord的值表示的是范数的类型。
- np.atleast_1d():改变维度,将输入直接视为1维,比如np.atleast_1d([1])的输出就是[1]
- np.expand_dims():用于扩展数组的维度,要深入了解还是得去查一下。
然后再看看优化器的实现,以最常用的随机梯度下降为例:
class StochasticGradientDescent():
def __init__(self, learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0):
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.momentum = momentum
self.w_updt = None def update(self, w, grad_wrt_w):
# If not initialized
if self.w_updt is None:
self.w_updt = np.zeros(np.shape(w))
# Use momentum if set
self.w_updt = self.momentum * self.w_updt + (1 - self.momentum) * grad_wrt_w
# Move against the gradient to minimize loss
return w - self.learning_rate * self.w_updt
直接看带动量的随机梯度下降公式:

这里的β就是动量momentum的值,一般取值是0.9。正好是对应上面的公式,最后更新W和b就是:
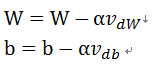
其中 α就表示学习率learning_rate。
至于不同优化器之间的优缺点就不在本文的考虑追之中了,可以自行去查下。
【python实现卷积神经网络】优化器的实现(SGD、Nesterov、Adagrad、Adadelta、RMSprop、Adam)的更多相关文章
- 各种优化器对比--BGD/SGD/MBGD/MSGD/NAG/Adagrad/Adam
指数加权平均 (exponentially weighted averges) 先说一下指数加权平均, 公式如下: \[v_{t}=\beta v_{t-1}+(1-\beta) \theta_{t} ...
- 各种优化方法总结比较(sgd/momentum/Nesterov/adagrad/adadelta)
前言 这里讨论的优化问题指的是,给定目标函数f(x),我们需要找到一组参数x,使得f(x)的值最小. 本文以下内容假设读者已经了解机器学习基本知识,和梯度下降的原理. Batch gradient d ...
- 基于Python的卷积神经网络和特征提取
基于Python的卷积神经网络和特征提取 用户1737318发表于人工智能头条订阅 224 在这篇文章中: Lasagne 和 nolearn 加载MNIST数据集 ConvNet体系结构与训练 预测 ...
- 深度学习笔记:优化方法总结(BGD,SGD,Momentum,AdaGrad,RMSProp,Adam)
深度学习笔记:优化方法总结(BGD,SGD,Momentum,AdaGrad,RMSProp,Adam) 深度学习笔记(一):logistic分类 深度学习笔记(二):简单神经网络,后向传播算法及实现 ...
- 【python实现卷积神经网络】开始训练
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch 卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride.padding)的具体实现:https ...
- 【python实现卷积神经网络】卷积层Conv2D反向传播过程
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch 卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride.padding)的具体实现:https ...
- 【python实现卷积神经网络】全连接层实现
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch 卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride.padding)的具体实现:https ...
- 【python实现卷积神经网络】批量归一化层实现
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch 卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride.padding)的具体实现:https ...
- 【python实现卷积神经网络】池化层实现
代码来源:https://github.com/eriklindernoren/ML-From-Scratch 卷积神经网络中卷积层Conv2D(带stride.padding)的具体实现:https ...
随机推荐
- MVC设计模式简介
刚刚学习了MVC相关知识,在这里进行一下总结MVC设计模式提高了Java开发中的代码可读性,提高了开发效率,实乃开发利器 1在MVC中由客户端发送一个带参数的请求,经过servlet处理后做出相应的处 ...
- git提交更改都是一个作者
为什么提交到github的commit都是一个作者 参考链接 重要知识点讲解 问题如下所示 git是分布式去中心化的管理系统 ssh秘钥对生成.并把id_rsa.pub加入github.com中(这个 ...
- 三万字、91道MySQL面试题。 附PDF
文末领取面试题 高清PDF 数据库基础知识 1. 为什么要使用数据库 数据保存在内存 优点:存取速度快 缺点:数据不能永久保存 数据保存在文件 优点:数据永久保存 缺点:1)速度比内存操作慢,频繁的I ...
- 「建议心心」要就来15道多线程面试题一次爽到底(1.1w字用心整理)
. 本文是给**「建议收藏」200MB大厂面试文档,整理总结2020年最强面试题库「CoreJava篇」**写的答案,所有相关文章已经收录在码云仓库:https://gitee.com/bingqil ...
- 爬虫如何使用phantomjs无头浏览器解决网页源代码经过渲染的问题(以scrapy框架为例)
一.浏览器的构成 许多开发商提供了商用的浏览器来解释和显示Web文档,而所有这些浏览器几乎都使用相同的体系架构.每一种浏览器(browser)通常由三部分构成:一个控制程序,客户协议和一些解释程序.控 ...
- wpf xaml CS0426 错误原因
wpf 程序集中 类命名空间名称和类名不能相同,否则在 xaml生成 i.g.cs时,会导致 自动生成代码无法推到处是类型还是命名空间的问题. 触发这个错误的条件是类命名空间 与 类名相同 并 ...
- HTTPS加密传输过程
HTTPS加密传输过程 HTTPS全称Hyper Text Transfer Protocol over SecureSocket Layer,是以安全为目标的HTTP通道,在HTTP的基础上通过传输 ...
- SpringBoot启动的时候出现log4j警告(配置文件找不到)
SpringBoot启动的时候报如下的警告 在启动SpringBoot项目的时候,idea出现如下警告信息,也就是log4j 配置文件找不到的问题 log4j:WARN No appenders co ...
- [AI开发]一个例子说明机器学习和深度学习的关系
深度学习现在这么火热,大部分人都会有‘那么它与机器学习有什么关系?’这样的疑问,网上比较它们的文章也比较多,如果有机器学习相关经验,或者做过类似数据分析.挖掘之类的人看完那些文章可能很容易理解,无非就 ...
- Ali_Cloud++:阿里云Centos配置iptables防火墙教程
虽说阿里云推出了云盾服务,但是自己再加一层防火墙总归是更安全些,下面是我在阿里云vps上配置防火墙的过程,目前只配置INPUT.OUTPUT和FORWORD都是ACCEPT的规则 1):检查iptab ...
