tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Word2Vec预测
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理
代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-cookbook
数据:http://www.cs.cornell.edu/people/pabo/movie-review-data/rt-polaritydata.tar.gz
问题:加载和使用预训练的嵌套,并使用这些单词嵌套进行情感分析,通过训练线性逻辑回归模型来预测电影的好坏
步骤如下:
- 必要包
- 声明模型参数
- 读取并转换文本数据集,划分训练集和测试集
- 构建图
- 训练
step1:必要包
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import os
import pickle
import string
import requests
import collections
import io
import tarfile
import urllib.request
import text_helpers
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph() os.chdir(os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))) # Start a graph session
sess = tf.Session()
step2:声明模型参数
# Declare model parameters
embedding_size = 200
vocabulary_size = 2000
batch_size = 100
max_words = 100 # Declare stop words
stops = stopwords.words('english')
step3:读取并转换本文数据集,划分训练集和测试集
# Load Data
print('Loading Data')
data_folder_name = 'temp'
texts, target = text_helpers.load_movie_data(data_folder_name) # Normalize text
print('Normalizing Text Data')
texts = text_helpers.normalize_text(texts, stops) # Texts must contain at least 3 words
target = [target[ix] for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if len(x.split()) > 2]
texts = [x for x in texts if len(x.split()) > 2] # Split up data set into train/test
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(target), round(0.8*len(target)), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(target))) - set(train_indices)))
texts_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in train_indices]
texts_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in test_indices]
target_train = np.array([x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in train_indices])
target_test = np.array([x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in test_indices]) # Load dictionary and embedding matrix加载CBOW嵌套中保存的单词字典
dict_file = os.path.join(data_folder_name, 'movie_vocab.pkl')
word_dictionary = pickle.load(open(dict_file, 'rb')) # Convert texts to lists of indices根据单词字典将加载的句子转化为数值型numpy数组
text_data_train = np.array(text_helpers.text_to_numbers(texts_train, word_dictionary))
text_data_test = np.array(text_helpers.text_to_numbers(texts_test, word_dictionary)) # Pad/crop movie reviews to specific length电影影评长度不一,不满100维的用0凑满,超过100维的取前100维
text_data_train = np.array([x[0:max_words] for x in [y+[0]*max_words for y in text_data_train]])
text_data_test = np.array([x[0:max_words] for x in [y+[0]*max_words for y in text_data_test]])
step4:构建图
print('Creating Model')
# Define Embeddings:创建嵌套变量,用于之后加载CBOW训练好的嵌套向量
embeddings = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocabulary_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0))
# Define model:
# Create variables for logistic regression变量
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[embedding_size,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
# Initialize placeholders数据占位符
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, max_words], dtype=tf.int32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# Lookup embeddings vectors
embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embeddings, x_data)
# Take average of all word embeddings in documents计算句子中所有单词的平均嵌套
embed_avg = tf.reduce_mean(embed, 1)
# Declare logistic model (sigmoid in loss function)
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(embed_avg, A), b)
# Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(model_output, y_target))
# Actual Prediction
prediction = tf.round(tf.sigmoid(model_output))
predictions_correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(predictions_correct)
# Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.AdagradOptimizer(0.005)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
step5:训练
# Intitialize Variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init) # Load model embeddings加载CBOW训练好的嵌套矩阵
model_checkpoint_path = os.path.join(data_folder_name,'cbow_movie_embeddings.ckpt')
saver = tf.train.Saver({"embeddings": embeddings})
saver.restore(sess, model_checkpoint_path) # Start Logistic Regression
print('Starting Model Training')
train_loss = []
test_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_acc = []
i_data = []
for i in range(10000):
rand_index = np.random.choice(text_data_train.shape[0], size=batch_size)
rand_x = text_data_train[rand_index]
rand_y = np.transpose([target_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) # Only record loss and accuracy every 100 generations
if (i+1)%100==0:
i_data.append(i+1)
train_loss_temp = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
train_loss.append(train_loss_temp) test_loss_temp = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: text_data_test, y_target: np.transpose([target_test])})
test_loss.append(test_loss_temp) train_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
train_acc.append(train_acc_temp) test_acc_temp = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: text_data_test, y_target: np.transpose([target_test])})
test_acc.append(test_acc_temp)
if (i+1)%500==0:
acc_and_loss = [i+1, train_loss_temp, test_loss_temp, train_acc_temp, test_acc_temp]
acc_and_loss = [np.round(x,2) for x in acc_and_loss]
print('Generation # {}. Train Loss (Test Loss): {:.2f} ({:.2f}). Train Acc (Test Acc): {:.2f} ({:.2f})'.format(*acc_and_loss))

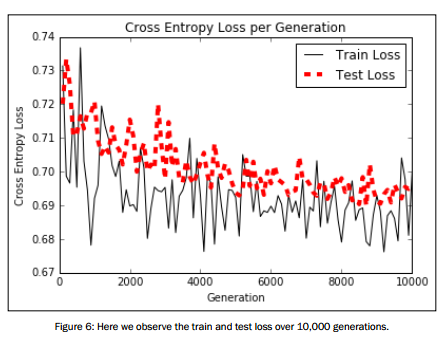
可视化结果展示:
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(i_data, train_loss, 'k-', label='Train Loss')
plt.plot(i_data, test_loss, 'r--', label='Test Loss', linewidth=4)
plt.title('Cross Entropy Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Cross Entropy Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
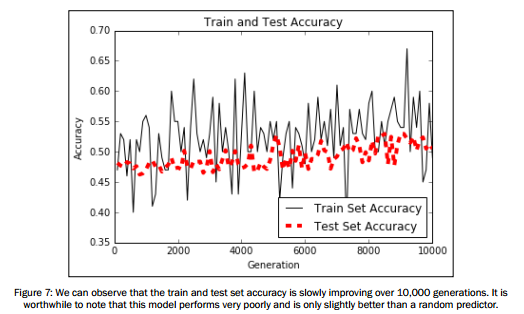
plt.show() # Plot train and test accuracy
plt.plot(i_data, train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy')
plt.plot(i_data, test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy', linewidth=4)
plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Word2Vec预测的更多相关文章
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Doc2Vec情感分析
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——CBOW词嵌入模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——TF-IDF算法
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——词袋
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——辅助函数
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram & CBOW原理总结
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7160330.html 先看下列三篇,再理解此篇会更容易些(个人意见) skip-gram,CBOW,Word2Vec 词向量基 ...
- TensorFlow实现文本情感分析详解
http://c.biancheng.net/view/1938.html 前面我们介绍了如何将卷积网络应用于图像.本节将把相似的想法应用于文本. 文本和图像有什么共同之处?乍一看很少.但是,如果将句 ...
- jQuery文本框中的事件应用
jQuery文本框中的事件应用 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "ht ...
随机推荐
- js 全角与半角互转
///全角空格为12288,半角空格为32 ///其他字符半角(33-126)与全角(65281-65374)的对应关系是:均相差65248 //半角转换为全角函数 function ...
- Directx教程(22) 简单的光照模型(1)
原文:Directx教程(22) 简单的光照模型(1) 在前面的教程中,我们在顶点属性中直接给顶点赋颜色,这样生成的三维物体缺乏真实感,如下图中两个立方体,左边的是通过光照生成物体表面颜色的 ...
- Spark in action on Kubernetes - Spark Operator的原理解析
前言 在上篇文章中,向大家介绍了如何使用Spark Operator在kubernetes集群上面提交一个计算作业.今天我们会继续使用上篇文章中搭建的Playground进行调试与解析,帮助大家更深入 ...
- JavaScript--for in循环访问属性用"."和[ ]的区别
// for in 循环遍历对象的时候// 内部要访问属性的时候不能点语法访问,因为for in 的key是字符串格式// 可通过方括号实现访问 for(var key in manObj) { co ...
- pytorch利用多个GPU并行计算多gpu
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明.本文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Answer3664/article/de ...
- iOS 万能跳转界面方法 (runtime实用篇一)
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150824/13104.html 作者:汉斯哈哈哈 授权本站转载. 在开发项目中,会有这样变态的需求: 推送:根据服务端推送过来的数据 ...
- Person Re-identification 系列论文笔记(五):SVD-net
SVDNet for Pedestrian Retrieval Sun Y, Zheng L, Deng W, et al. SVDNet for Pedestrian Retrieval[J]. 2 ...
- bzoj1614 架设电话线
Description Farmer John打算将电话线引到自己的农场,但电信公司并不打算为他提供免费服务.于是,FJ必须为此向电信公司支付一定的费用. FJ的农场周围分布着N(1 <= N ...
- CNN如何识别一幅图像中的物体
让我们对卷积神经网络如何工作形成更好直观感受.我们先看下人怎样识别图片,然后再看 CNNs 如何用一个近似的方法来识别图片. 比如说,我们想把下面这张图片识别为金毛巡回犬. 一个需要被识别为金毛巡 ...
- BZOJ 1935 Tree 园丁的烦恼 CDQ分治/主席树
CDQ分治版本 我们把询问拆成四个前缀和,也就是二维前缀和的表达式, 我们把所有操作放入一个序列中 操作1代表在x,y出现一个树 操作2代表加上在x,y内部树的个数 操作3代表减去在x,y内部树的个数 ...
