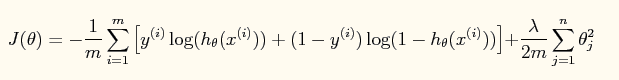Regularized logistic regression
要解决的问题是,给出了具有2个特征的一堆训练数据集,从该数据的分布可以看出它们并不是非常线性可分的,因此很有必要用更高阶的特征来模拟。例如本程序中个就用到了特征值的6次方来求解。
Data
To begin, load the files 'ex5Logx.dat' and ex5Logy.dat' into your program. This dataset represents the training set of a logistic regression problem with two features. To avoid confusion later, we will refer to the two input features contained in 'ex5Logx.dat' as
and
. So in the 'ex5Logx.dat' file, the first column of numbers represents the feature
, which you will plot on the horizontal axis, and the second feature represents
, which you will plot on the vertical axis.
After loading the data, plot the points using different markers to distinguish between the two classifications. The commands in Matlab/Octave will be:
x = load('ex5Logx.dat');
y = load('ex5Logy.dat'); figure % Find the indices for the 2 classes
pos = find(y); neg = find(y == 0); plot(x(pos, 1), x(pos, 2), '+')
hold on
plot(x(neg, 1), x(neg, 2), 'o')After plotting your image, it should look something like this:
Model
the hypothesis function is

Let's look at the
parameter in the sigmoid function
.
In this exercise, we will assign
to be all monomials (meaning polynomial terms) of
and
up to the sixth power:
To clarify this notation: we have made a 28-feature vector
where
此时加入了规则项后的系统的损失函数为:
Newton’s method
Recall that the Newton's Method update rule is
1.
is your feature vector, which is a 28x1 vector in this exercise.
2.
is a 28x1 vector.
3.
and
are 28x28 matrices.
4.
and
are scalars.
5. The matrix following
in the Hessian formula is a 28x28 diagonal matrix with a zero in the upper left and ones on every other diagonal entry.
After convergence, use your values of theta to find the decision boundary in the classification problem. The decision boundary is defined as the line where
Code
%载入数据
clc,clear,close all;
x = load('ex5Logx.dat');
y = load('ex5Logy.dat'); %画出数据的分布图
plot(x(find(y),),x(find(y),),'o','MarkerFaceColor','b')
hold on;
plot(x(find(y==),),x(find(y==),),'r+')
legend('y=1','y=0') % Add polynomial features to x by
% calling the feature mapping function
% provided in separate m-file
x = map_feature(x(:,), x(:,)); %投影到高维特征空间 [m, n] = size(x); % Initialize fitting parameters
theta = zeros(n, ); % Define the sigmoid function
g = inline('1.0 ./ (1.0 + exp(-z))'); % setup for Newton's method
MAX_ITR = ;
J = zeros(MAX_ITR, ); % Lambda is the regularization parameter
lambda = ;%lambda=,,,修改这个地方,运行3次可以得到3种结果。 % Newton's Method
for i = :MAX_ITR
% Calculate the hypothesis function
z = x * theta;
h = g(z); % Calculate J (for testing convergence) -- 损失函数
J(i) =(/m)*sum(-y.*log(h) - (-y).*log(-h))+ ...
(lambda/(*m))*norm(theta([:end]))^; % Calculate gradient and hessian.
G = (lambda/m).*theta; G() = ; % extra term for gradient
L = (lambda/m).*eye(n); L() = ;% extra term for Hessian
grad = ((/m).*x' * (h-y)) + G;
H = ((/m).*x' * diag(h) * diag(1-h) * x) + L; % Here is the actual update
theta = theta - H\grad; end % Plot the results
% We will evaluate theta*x over a
% grid of features and plot the contour
% where theta*x equals zero % Here is the grid range
u = linspace(-, 1.5, );
v = linspace(-, 1.5, ); z = zeros(length(u), length(v));
% Evaluate z = theta*x over the grid
for i = :length(u)
for j = :length(v)
z(i,j) = map_feature(u(i), v(j))*theta;%这里绘制的并不是损失函数与迭代次数之间的曲线,而是线性变换后的值
end
end
z = z'; % important to transpose z before calling contour % Plot z =
% Notice you need to specify the range [, ]
contour(u, v, z, [, ], 'LineWidth', )%在z上画出为0值时的界面,因为为0时刚好概率为0.,符合要求
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
title(sprintf('\\lambda = %g', lambda), 'FontSize', ) hold off % Uncomment to plot J
% figure
% plot(:MAX_ITR-, J, 'o--', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r', 'MarkerSize', )
% xlabel('Iteration'); ylabel('J')
Result
Regularized logistic regression的更多相关文章
- machine learning(15) --Regularization:Regularized logistic regression
Regularization:Regularized logistic regression without regularization 当features很多时会出现overfitting现象,图 ...
- matlab(7) Regularized logistic regression : mapFeature(将feature增多) and costFunctionReg
Regularized logistic regression : mapFeature(将feature增多) and costFunctionReg ex2_reg.m文件中的部分内容 %% == ...
- matlab(6) Regularized logistic regression : plot data(画样本图)
Regularized logistic regression : plot data(画样本图) ex2data2.txt 0.051267,0.69956,1-0.092742,0.68494, ...
- 编程作业2.2:Regularized Logistic regression
题目 在本部分的练习中,您将使用正则化的Logistic回归模型来预测一个制造工厂的微芯片是否通过质量保证(QA),在QA过程中,每个芯片都会经过各种测试来保证它可以正常运行.假设你是这个工厂的产品经 ...
- matlab(8) Regularized logistic regression : 不同的λ(0,1,10,100)值对regularization的影响,对应不同的decision boundary\ 预测新的值和计算模型的精度predict.m
不同的λ(0,1,10,100)值对regularization的影响\ 预测新的值和计算模型的精度 %% ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accur ...
- 吴恩达机器学习笔记22-正则化逻辑回归模型(Regularized Logistic Regression)
针对逻辑回归问题,我们在之前的课程已经学习过两种优化算法:我们首先学习了使用梯度下降法来优化代价函数
- Stanford机器学习---第三讲. 逻辑回归和过拟合问题的解决 logistic Regression & Regularization
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/7716281 本栏目(Machine learning)包括单参数的线性回归.多参数的线性回归 ...
- Machine Learning - 第3周(Logistic Regression、Regularization)
Logistic regression is a method for classifying data into discrete outcomes. For example, we might u ...
- 【机器学习】Octave 实现逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
ex2data1.txt ex2data2.txt 本次算法的背景是,假如你是一个大学的管理者,你需要根据学生之前的成绩(两门科目)来预测该学生是否能进入该大学. 根据题意,我们不难分辨出这是一种二分 ...
随机推荐
- MySql语句中select可以嵌套么,字段的重命名可以用中文么
今天文档中看到的查询语句,SELECT后面又跟了一个SELECT嵌套,而且把字段重命名为中文,请问可以这样做么 MySql语句中select可以嵌套么,字段的重命名可以用中文么 >> my ...
- 维生素C主要生理功能
维C是:维生素C又叫抗坏血酸,是一种水溶性维生素. 维生素C主要生理功能 1. 促进骨胶原的生物合成.利于组织创伤口的更快愈合: 维生素C在体内参与多种反应,如参与氧化还原过程,在生物氧化和还原作用以 ...
- Linux 运维笔试题(一)答案
答案: 1. ftp:21 远程连接telnet端口:23 smtp:25 rsync:873 SNMP:161 RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用) ...
- 去除input的前后的空格
这里用的是jquery的方法
- vue 学习笔记1 入门
可以在 JSFiddle上在线学习vue 注意:所演示的示例,都是在JS中将Vue实例绑定至HTML中的指定元素,然后再通过Vue实例中data内的属性或者methods中的方法,来对所绑定元素的子元 ...
- js001 ---- async
Node.js异步流,详细见https://caolan.github.io/async/docs.html#parallel 1, async 用的比较多的是 waterfall, 瀑布流, 就是每 ...
- [SHOI2008]堵塞的交通(线段树维护联通性)
题目 2行c列个点,开始时互不联通,支持给同一列或着同一行相邻的两个点连边,和询问两个点能否在一个联通块里. 1≤C≤100000 1<=操作数<=100000; 题解 线段树的又一个骚操 ...
- Python实现快排
Python实现快排 def quicksort(arr): if len(arr) <= 1: return arr pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2] left = [x ...
- 洛谷—— P1969 积木大赛
https://www.luogu.org/problem/show?pid=1969 题目描述 春春幼儿园举办了一年一度的“积木大赛”.今年比赛的内容是搭建一座宽度为n的大厦,大厦可以看成由n块宽度 ...
- [Python] Accessing Array Elements
NumPy Reference: Indexing Note: Indexing starts at 0 (zero). def slicing(): a = np.random.rand(5,4) ...