tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——词袋
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理
代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-cookbook
解决问题:使用“词袋”嵌入来进行垃圾短信的预测(使用逻辑回归算法)
缺点:不考虑相关单词顺序特征,长文本的处理困难
步骤如下:
step1:导入需要的包
step2:准备数据集
step3:选择参数(每个文本保留多少单词数,最低词频是多少)
step4:构建词袋
step5:分割数据集
step6:构建图
step7:训练
step8:测试
step1:导入需要的包
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import numpy as np
import csv
import string
import requests
import io
from zipfile import ZipFile
from tensorflow.contrib import learn
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph() # Start a graph session
sess = tf.Session()
step2:准备数据集
# Check if data was downloaded, otherwise download it and save for future use
save_file_name = os.path.join('temp','temp_spam_data.csv')
if os.path.isfile(save_file_name):
text_data = []
with open(save_file_name, 'r') as temp_output_file:
reader = csv.reader(temp_output_file)
for row in reader:
text_data.append(row)
else:
zip_url = 'http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/00228/smsspamcollection.zip'
r = requests.get(zip_url)
z = ZipFile(io.BytesIO(r.content))
file = z.read('SMSSpamCollection')
# Format Data
text_data = file.decode()
text_data = text_data.encode('ascii',errors='ignore')
text_data = text_data.decode().split('\n')
text_data = [x.split('\t') for x in text_data if len(x)>=1] # And write to csv
with open(save_file_name, 'w') as temp_output_file:
writer = csv.writer(temp_output_file)
writer.writerows(text_data) texts = [x[1] for x in text_data]
target = [x[0] for x in text_data] # Relabel 'spam' as 1, 'ham' as 0
target = [1 if x=='spam' else 0 for x in target] # Normalize text,为减少无意义的词汇,对文本进行规则化处理
# Lower case
texts = [x.lower() for x in texts] # Remove punctuation
texts = [''.join(c for c in x if c not in string.punctuation) for x in texts] # Remove numbers
texts = [''.join(c for c in x if c not in '') for x in texts] # Trim extra whitespace
texts = [' '.join(x.split()) for x in texts]
step3:选择参数
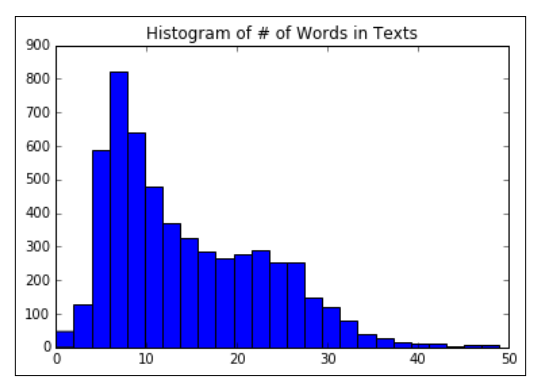
# Plot histogram of text lengths文本数据中的单词数的直方图
text_lengths = [len(x.split()) for x in texts]
text_lengths = [x for x in text_lengths if x < 50]
plt.hist(text_lengths, bins=25)
plt.title('Histogram of # of Words in Texts')
step4:构建词袋
# Choose max text word length at 25,也可以设为30或者40
sentence_size = 25
min_word_freq = 3 # Setup vocabulary processor
vocab_processor = learn.preprocessing.VocabularyProcessor(sentence_size, min_frequency=min_word_freq) # Have to fit transform to get length of unique words.
vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts)
embedding_size = len(vocab_processor.vocabulary_)
step5:分割数据集
# Split up data set into train/test
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(texts), round(len(texts)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(texts))) - set(train_indices)))
texts_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in train_indices]
texts_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(texts) if ix in test_indices]
target_train = [x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in train_indices]
target_test = [x for ix, x in enumerate(target) if ix in test_indices]
step6:构建图
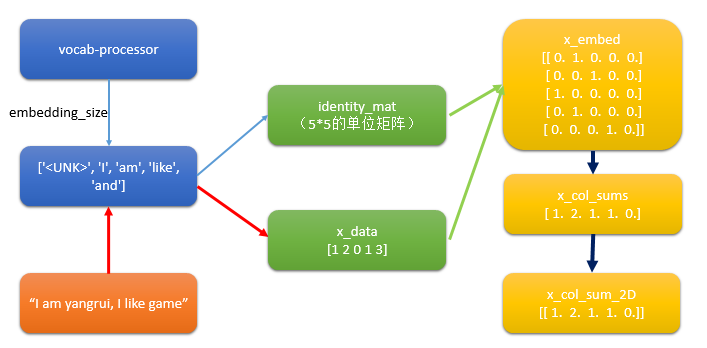
step6.1:构建出文本的向量
# Setup Index Matrix for one-hot-encoding,使用该矩阵为每个单词查找稀疏向量
identity_mat = tf.diag(tf.ones(shape=[embedding_size])) # Create variables for logistic regression
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[embedding_size,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1])) # Initialize placeholders
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[sentence_size], dtype=tf.int32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[1, 1], dtype=tf.float32) # Text-Vocab Embedding,使用tf的嵌入查找函数来映射句子中的单词为单位矩阵的one-hot向量,再进行求和
# tf.nn.embedding_lookup(y,x)x为索引,找出y中对应索引的值
x_embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(identity_mat, x_data)
x_col_sums = tf.reduce_sum(x_embed, 0) # Declare model operations
x_col_sums_2D = tf.expand_dims(x_col_sums, 0)
疑问:如何利用词袋将文本变成向量?
step6.2 构建图
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_col_sums_2D, A), b) # Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(model_output, y_target)) # Prediction operation
prediction = tf.sigmoid(model_output) # Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
step7:训练
# Intitialize Variables
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init) # Start Logistic Regression
print('Starting Training Over {} Sentences.'.format(len(texts_train)))
loss_vec = []
train_acc_all = []
train_acc_avg = []
for ix, t in enumerate(vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts_train)):
y_data = [[target_train[ix]]] sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: t, y_target: y_data})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: t, y_target: y_data})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss) if (ix+1)%10==0:
print('Training Observation #' + str(ix+1) + ': Loss = ' + str(temp_loss)) # Keep trailing average of past 50 observations accuracy
# Get prediction of single observation
[[temp_pred]] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data:t, y_target:y_data})
# Get True/False if prediction is accurate
train_acc_temp = target_train[ix]==np.round(temp_pred)
train_acc_all.append(train_acc_temp)
if len(train_acc_all) >= 50:
train_acc_avg.append(np.mean(train_acc_all[-50:]))
step8:测试
# Get test set accuracy
print('Getting Test Set Accuracy For {} Sentences.'.format(len(texts_test)))
test_acc_all = []
for ix, t in enumerate(vocab_processor.fit_transform(texts_test)):
y_data = [[target_test[ix]]] if (ix+1)%50==0:
print('Test Observation #' + str(ix+1)) # Keep trailing average of past 50 observations accuracy
# Get prediction of single observation
[[temp_pred]] = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={x_data:t, y_target:y_data})
# Get True/False if prediction is accurate
test_acc_temp = target_test[ix]==np.round(temp_pred)
test_acc_all.append(test_acc_temp) print('\nOverall Test Accuracy: {}'.format(np.mean(test_acc_all))) # Plot training accuracy over time
plt.plot(range(len(train_acc_avg)), train_acc_avg, 'k-', label='Train Accuracy')
plt.title('Avg Training Acc Over Past 50 Generations')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('Training Accuracy')
plt.show()
tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——词袋的更多相关文章
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——TF-IDF算法
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——CBOW词嵌入模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Doc2Vec情感分析
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram模型
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——Word2Vec预测
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——skip-gram & CBOW原理总结
摘自:http://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/7160330.html 先看下列三篇,再理解此篇会更容易些(个人意见) skip-gram,CBOW,Word2Vec 词向量基 ...
- tensorflow在文本处理中的使用——辅助函数
代码来源于:tensorflow机器学习实战指南(曾益强 译,2017年9月)——第七章:自然语言处理 代码地址:https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow-coo ...
- (数据科学学习手札71)在Python中制作个性化词云图
本文对应脚本及数据已上传至我的Github仓库https://github.com/CNFeffery/DataScienceStudyNotes 一.简介 词云图是文本挖掘中用来表征词频的数据可视化 ...
- TensorFlow实现文本情感分析详解
http://c.biancheng.net/view/1938.html 前面我们介绍了如何将卷积网络应用于图像.本节将把相似的想法应用于文本. 文本和图像有什么共同之处?乍一看很少.但是,如果将句 ...
随机推荐
- DTcms iis6 伪静态 iis配置方法 【图解】
1.右键点击 要设置网站的网站 2.属性 ——>主目录 ——>配置——> 3.如右侧窗口,找到 .aspx 扩展名——>编辑——>复制 可执行文件的路径——>关闭 ...
- iOS 9 学习系列:UIStack View
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150921/13492.html 在 iOS9 中,Apple 引入了 UIStackView,他让你的应用可以通过简单的方式,纵向或 ...
- CF789D Mike and distribution
题目连接 一道人类智慧题.... 这道题目可以转化为在a,b中的选出一些位置,使得这些位置处的值加起来大于没有选的位置的值 我们按照a的权值排序,选择第一个元素,其与元素两两分组,每组选择b更大的那一 ...
- Servlet Cookies
Cookie是在多个客户端请求之间持久存储的一小段信息. Cookie具有名称,单个值和可选属性,例如注释,路径和域限定符,生存周期和版本号. Cookie工作原理 默认情况下,每个请求都被视为新的请 ...
- [React Native]Promise机制
React Native中经常会看到Promise机制. Promise机制代表着在JavaScript程序中下一个伟大的范式.可以把一些复杂的代码轻松撸成一个串,和Android中的rxjava非常 ...
- QT_OPENGL-------- 2.shader
用可编程管线绘制一个三角形 1.以上一节window为基准,进行绘制. 2.下载编译glew,并在.pro添加动态链接,并在头文件中引用. LIBS +=-L/usr/lib64 -lGLEW 可能根 ...
- Libevent:0异步IO简介
一:异步IO简介 大多数的初级编程者都是从阻塞IO调用开始网络编程的.阻塞(同步)IO调用指的是:调用会一直阻塞,不会返回,直到发生下面两种情况之一.要么操作完成,要么经历相当长的时间,网络协议栈自己 ...
- SELinux 宽容模式(permissive) 强制模式(enforcing) 关闭(disabled) 几种模式之间的转换
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5aee9eaf0100y44q.html 在CentOS6.2 中安装intel 的c++和fortran 的编译器时,遇到来一个关于S ...
- python MySQLdb用法,python中cursor操作数据库(转)
数据库连接 连接数据库前,请先确认以下事项: 您已经创建了数据库 TESTDB. 在TESTDB数据库中您已经创建了表 EMPLOYEE EMPLOYEE表字段为 FIRST_NAME, LAST_N ...
- 我钟爱的HTML5和CSS3在线工具【转】
我真的喜欢上了HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript编程,但是有一些代码还是需要一些辅助工具来做才行,例如,CSS3的Gradient渐变如果手写代码的话真的不爽,还有像animation动画 ...
