吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split def load_data_regression():
'''
加载用于回归问题的数据集
'''
#使用 scikit-learn 自带的一个糖尿病病人的数据集
diabetes = datasets.load_diabetes()
# 拆分成训练集和测试集,测试集大小为原始数据集大小的 1/4
return train_test_split(diabetes.data,diabetes.target,test_size=0.25,random_state=0) #集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型
def test_RandomForestRegressor(*data):
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor()
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
print("Traing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_train,y_train))
print("Testing Score:%f"%regr.score(X_test,y_test)) # 获取分类数据
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=load_data_regression()
# 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor
test_RandomForestRegressor(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
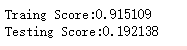
def test_RandomForestRegressor_num(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 n_estimators 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
nums=np.arange(1,100,step=2)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for num in nums:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=num)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(nums,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(nums,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("estimator num")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(-1,1)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_num
test_RandomForestRegressor_num(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
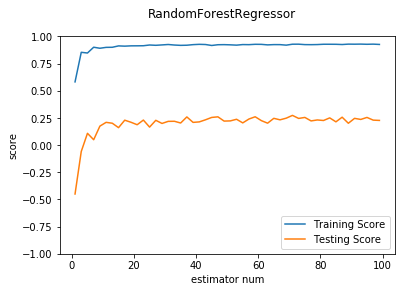
def test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 max_depth 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
maxdepths=range(1,20)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for max_depth in maxdepths:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=max_depth)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(maxdepths,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(maxdepths,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_depth")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth
test_RandomForestRegressor_max_depth(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
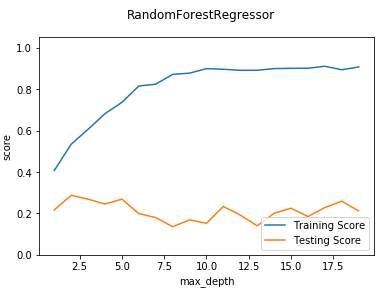
def test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features(*data):
'''
测试 RandomForestRegressor 的预测性能随 max_features 参数的影响
'''
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=data
max_features=np.linspace(0.01,1.0)
fig=plt.figure()
ax=fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
testing_scores=[]
training_scores=[]
for max_feature in max_features:
regr=ensemble.RandomForestRegressor(max_features=max_feature)
regr.fit(X_train,y_train)
training_scores.append(regr.score(X_train,y_train))
testing_scores.append(regr.score(X_test,y_test))
ax.plot(max_features,training_scores,label="Training Score")
ax.plot(max_features,testing_scores,label="Testing Score")
ax.set_xlabel("max_feature")
ax.set_ylabel("score")
ax.legend(loc="lower right")
ax.set_ylim(0,1.05)
plt.suptitle("RandomForestRegressor")
plt.show() # 调用 test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features
test_RandomForestRegressor_max_features(X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test)
吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestRegressor回归模型的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习随机森林RandomForestClassifier分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习梯度提升决策树GradientBoostingRegressor回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法回归模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——集成学习AdaBoost算法分类模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,ensemble from sklear ...
- 机器学习:集成学习:随机森林.GBDT
集成学习(Ensemble Learning) 集成学习的思想是将若干个学习器(分类器&回归器)组合之后产生一个新学习器.弱分类器(weak learner)指那些分类准确率只稍微好于随机猜测 ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——伯努利贝叶斯BernoulliNB模型
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn import datasets,naive_bayes from skl ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理过滤式特征选取SelectPercentile模型
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectPercentile,f_classif #数据预处理过滤式特征选取SelectPercentile模型 def ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理过滤式特征选取VarianceThreshold模型
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold #数据预处理过滤式特征选取VarianceThreshold模型 def test_Va ...
- 吴裕雄 python 机器学习——数据预处理字典学习模型
from sklearn.decomposition import DictionaryLearning #数据预处理字典学习DictionaryLearning模型 def test_Diction ...
随机推荐
- SDOI2010 粟粟的书架 lg2468(可持久化,前缀和)
题面见https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P2468 然后这道题属于合二为一题,看一眼数据范围就能发现 首先我们先考虑50分,二维前缀和维护一下(反正我不记得公 ...
- 在Unity5中使用C#脚本实现UI的下滑、变色、渐隐渐现效果
一.首先,我们先创建一个Text 依次选择Component→UI→Text创建一个Text,创建完成后如下: 二.创建完成后,在Project面板点击Create→C# Script,本例命名 ...
- Eclipse的使用配置
Eclipse 是一个开放源代码的.基于Java的可扩展开发平台.目前许多开发者开发时仍会选择使用Eclipse,很多初学者刚开始接触Java也是从使用Eclipse开始的.本篇博客主要介绍Eclip ...
- C++ 获取当前正在执行的函数的相关信息(转)
该功能用在日志打印中 原文地址:C++ 获取当前正在执行的函数的相关信息
- 模块一:shell 脚本基础
一.shell脚本介绍 (一)脚本案例及介绍: #!/bin/bash LOG_DIR=/var/log ROOT_UID=0 if ["$UID -ne "$ROOT_UID&q ...
- 3ds Max File Format (Part 4: The first useful data; Scene, AppData, Animatable)
The most interesting part of this file is, evidently, the Scene. Opening it up in the chunk parser, ...
- Data Manipulation with dplyr in R
目录 select The filter and arrange verbs arrange filter Filtering and arranging Mutate The count verb ...
- 2020算法设计竞赛 H 坐火车
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/3005/H来源:牛客网 大致题意:让我们针对每一个数,求这个数左区间和右区间颜色相同(也就是数字相同)得对数: 比如:左 ...
- 16day 逻辑符号系列
&& 与逻辑符号 前一个命令执行成功, 再执行后面的命令 || 或逻辑符号 前一个命令执行失败, 再执行后面的命令 &&符号实践操作: [root@oldboyedu ...
- 【Python】输出12个星座
原理:利用Unicode编码 for i in range(12): print(chr(9800+i),end="")
