【转】 Understanding Component-Entity-Systems
To solve this, game programmers started to build entities
through composition instead of inheritance. An entity is simply an
aggregation (technically a composition) of components. This has some
major benefits over the object-oriented architecture described above:
- It's easy to add new, complex entities
- It's easy to define new entities in data
- It's more efficient
Here's
how a few of the entities above would be implemented. Notice that the
components are all pure data - no methods. This will be explained in
detail below.
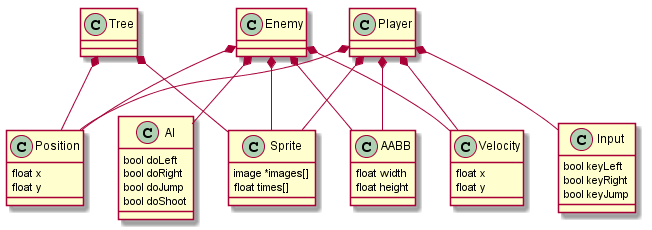
The Component
A component can be likened to a C
struct. It has no methods and is only capable of storing data, not
acting upon it. In a typical implementation, each different component
type will derive from an abstract Component class, which
provides facilities for getting a component's type and containing entity
at runtime. Each component describes a certain aspect of an entity and
its parameters. By themselves, components are practically meaningless,
but when used in conjunction with entities and systems, they become
extremely powerful. Empty components are useful for tagging entities.
Examples
- Position (x, y)
- Velocity (x, y)
- Physics (body)
- Sprite (images, animations)
- Health (value)
- Character (name, level)
- Player (empty)
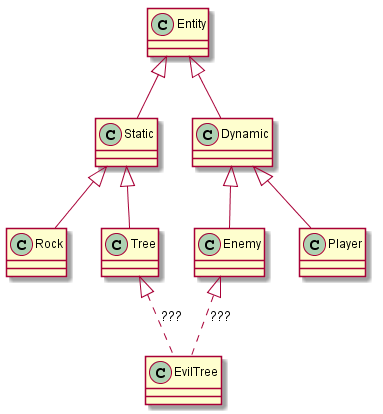
The Entity
An
entity is something that exists in your game world. Again, an entity is
little more than a list of components. Because they are so simple, most
implementations won't define an entity as a concrete piece of data.
Instead, an entity is a unique ID, and all components that make up an
entity will be tagged with that ID. The entity is an implicit
aggregation of the components tagged with its ID. If you want, you can
allow components to be dynamically added to and removed from entities.
This allows you to "mutate" entities on the fly. For example, you could
have a spell that makes its target freeze. To do this, you could simply
remove the Velocity component.
Examples
- Rock (Position, Sprite)
- Crate (Position, Sprite, Health)
- Sign (Position, Sprite, Text)
- Ball (Position, Velocity, Physics, Sprite)
- Enemy (Position, Velocity, Sprite, Character, Input, AI)
- Player (Position, Velocity, Sprite, Character, Input, Player)
The System
Notice
that I've neglected to mention any form of game logic. This is the job
of the systems. A system operates on related groups of components, i.e.
components that belong to the same entity. For example, the character
movement system might operate on a Position, a Velocity, a Collider, and an Input. Each system will be updated once per frame in a logical order. To make a character jump, first the keyJump field of the Input data is checked. If it is true, the system will look through the contacts contained in the Collider data and check if there is one with the ground. If so, it will set the Velocity's y field to make the character jump.
Because
a system only operates on components if the whole group is present,
components implicitly define the behaviour an entity will have. For
example, an entity with a Position component but not a Velocity component will be static. Since the Movement system uses a Position and a Velocity, it won't operate on the Position contained within that entity. Adding a Velocity component will make the Movement
system work on that entity, thus making the entity dynamic and affected
by gravity. This behaviour can be exploited with "tag components"
(explained above) to reuse components in different contexts. For
example, the Input component defines generic flags for jumping, moving, and shooting. Adding an empty Player component will tag the entity for the PlayerControl system so that the Input data will be populated based on controller inputs.
Examples
- Movement (Position, Velocity) - Adds velocity to position
- Gravity (Velocity) - Accelerates velocity due to gravity
- Render (Position, Sprite) - Draws sprites
- PlayerControl (Input, Player) - Sets the player-controlled entity's input according to a controller
- BotControl (Input, AI) - Sets a bot-controlled entity's input according to an AI agent
Conclusion
To
wrap up, OOP-based entity hierarchies need to be left behind in favour
of Component-Entity-Systems. Entities are your game objects, which are
implicitly defined by a collection of components. These components are
pure data and are operated on in functional groups by the systems.
I
hope I've managed to help you to understand how
Component-Entity-Systems work, and to convince you that they are better
than traditional OOP. If you have any questions about the article, I'd
appreciate a comment or message.
A follow-up article has been posted, which provides a sample C implementation and solves some design problems. Implementing Component-Entity-Systems
Article Update Log
1 April 2013 - Initial submission
2 April 2013 - Initial publication; cleaned up formatting
29 September 2013 - Added notice of follow-up article; changed some formatting)
【转】 Understanding Component-Entity-Systems的更多相关文章
- 【转】Entity Systems
“Favour composition over inheritance” If you haven’t already read my previous post on the problems o ...
- 【转】What is an entity system framework for game development?
What is an entity system framework for game development? Posted on 19 January 2012 Last week I relea ...
- Programming Entity Framework 翻译(1)-目录
1. Introducing the ADO.NET Entity Framework ado.net entity framework 介绍 1 The Entity Relationship Mo ...
- 为什么要在游戏开发中使用ECS模式
http://www.richardlord.net/blog/why-use-an-entity-framework Why use an entity system framework for g ...
- 组件-实体-系统 Entiy-Compoent-System ECS架构整理
继承体系的问题,为什么要用ECS 面向对象的问题 当一个新的类型需要多个老类型的不同功能的时候,不能很好的继承出来 游戏开发后期会有非常多的类,很难维护 游戏中子系统很多,它们对一个对象的关注点往往互 ...
- 中间件(middlebox)
Middleboxes (also known as network functions) are systems that perform sophisticated and often state ...
- writing concurrent programs
Computer Systems A Programmer's Perspective Second Edition To this point in our study of computer sy ...
- [Angular 2] Directive intro and exportAs
First, What is directive, what is the difference between component and directive. For my understandi ...
- Why your Games are Unfinished, and What To Do About It (转)
So, you've got a new game idea, and it's going to change what everyone knows about the genre! Great! ...
- uvc摄像头代码解析5
8.初始化uvc控制 8.1 重要结构体 struct uvc_control { //uvc控制 struct uvc_entity *entity; //uvc实体 struct uvc_cont ...
随机推荐
- jquery通过ajax方法获取json数据不执行success
1.jquery通过ajax方法获取json数据不执行success回调 问题描述:jquery通过ajax方法获取json数据不执行success回调方法 问题原因:json格式存在问题或不符合标准 ...
- Subgraph Search Over Large Graph Database
Subgraph Search Over Large Graph Database Problem Definition Given a graph database and a query grap ...
- 《Pro AngularJS》学习小结-02
上一篇的项目只有一个单独的模板页面,加入了相应的controller,filter,使得页面上的数据能够动态的变化.现在我们开始建立并整合多个模板,加入购物车模块和结账checkout模块. 一.在页 ...
- 318. Maximum Product of Word Lengths ——本质:英文单词中字符是否出现可以用26bit的整数表示
Given a string array words, find the maximum value of length(word[i]) * length(word[j]) where the tw ...
- 使用@Controller注解为什么要配置<mvc:annotation-driven />
自己看了官方文档,也到网上查了下,目前理解如下: <mvc:annotation-driven/>相当于注册了DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping和Annotat ...
- Eclipse导出可执行Jar文件(包含第三方Jar包)
1. 首先,右键你的Java工程,选择Export,在Java文件夹下选择Runnable JAR file,如下图所示: 2. 选择Runnable JAR file后,会弹出如下所示的对话框,选择 ...
- HDU 5768 中国剩余定理
题目链接:Lucky7 题意:求在l和r范围内,满足能被7整除,而且不满足任意一组,x mod p[i] = a[i]的数的个数. 思路:容斥定理+中国剩余定理+快速乘法. (奇+ 偶-) #incl ...
- Xmanager如何连接图形化界面
1.编辑gnome配置文件vim /etc/gdm/custom.conf # GDM configuration storage [daemon]RemoteGreeter= /usr/libexe ...
- hdu 4605 Magic Ball Game
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4605 可以离线求解 把所以可能出现的 magic ball 放在一个数组里(去重),从小到大排列 先不考虑特殊 ...
- 学习KMP算法的一点小心得
KMP算法应用于 在一篇有n个字母的文档中 查找某个想要查找的长度为m的单词:暴力枚举:从文档的前m个字母和单词对比,然后是第2到m+1个,然后是第3到m+2个:这样算法复杂度最坏就达到了O(m*n) ...
