Learning OSG programing---osgwindows
/* OpenSceneGraph example, osgwindows.
*
* Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
* of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
* in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
* to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
* copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
* furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*
* THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
* IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
* FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
* LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
* OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
* THE SOFTWARE.
*/ #include <osgDB/ReadFile>
#include <osgUtil/Optimizer>
#include <osgViewer/Viewer> #include <iostream> int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
// use an ArgumentParser object to manage the program arguments.
osg::ArgumentParser arguments(&argc,argv); // read the scene from the list of file specified commandline args.
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Node> loadedModel = osgDB::readRefNodeFiles(arguments); // if not loaded assume no arguments passed in, try use default mode instead.
if (!loadedModel) loadedModel = osgDB::readRefNodeFile("/home/ding/Downloads/OpenSceneGraph-Data/cow.osgt");
//this path was modified because the OSG_FILE_PATH is not configed correctly in my computer!
//so it is an alternative method // if no model has been successfully loaded report failure.
if (!loadedModel)
{
std::cout << arguments.getApplicationName() <<": No data loaded" << std::endl;
return ;
} // construct the viewer.
osgViewer::Viewer viewer; int xoffset = ;
int yoffset = ; // left window + left slave camera
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext::Traits> traits = new osg::GraphicsContext::Traits; traits->x = xoffset + ;
traits->y = yoffset + ;
traits->width = ;
traits->height = ;
traits->windowDecoration = true;
traits->doubleBuffer = true;
traits->sharedContext = ;
traits->readDISPLAY();
traits->setUndefinedScreenDetailsToDefaultScreen(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext> gc = osg::GraphicsContext::createGraphicsContext(traits.get()); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Camera> camera = new osg::Camera;
camera->setGraphicsContext(gc.get());
camera->setViewport(new osg::Viewport(,, traits->width, traits->height));
GLenum buffer = traits->doubleBuffer ? GL_BACK : GL_FRONT;
camera->setDrawBuffer(buffer);
camera->setReadBuffer(buffer); // add this slave camera to the viewer, with a shift left of the projection matrix
viewer.addSlave(camera.get(), osg::Matrixd::translate(1.0,-1.0,0.0), osg::Matrixd());
} // right window + right slave camera
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext::Traits> traits = new osg::GraphicsContext::Traits;
traits->x = xoffset + ;
traits->y = yoffset + ;
traits->width = ;
traits->height = ;
traits->windowDecoration = true;
traits->doubleBuffer = true;
traits->sharedContext = ;
traits->readDISPLAY();
traits->setUndefinedScreenDetailsToDefaultScreen(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext> gc = osg::GraphicsContext::createGraphicsContext(traits.get()); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Camera> camera = new osg::Camera;
camera->setGraphicsContext(gc.get());
camera->setViewport(new osg::Viewport(,, traits->width, traits->height));
GLenum buffer = traits->doubleBuffer ? GL_BACK : GL_FRONT;
camera->setDrawBuffer(buffer);
camera->setReadBuffer(buffer); // add this slave camera to the viewer, with a shift right of the projection matrix
viewer.addSlave(camera.get(), osg::Matrixd::translate(-1.0,-1.0,0.0), osg::Matrixd());
} // left_down window + right slave camera
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext::Traits> traits = new osg::GraphicsContext::Traits;
traits->x = xoffset + ;
traits->y = yoffset + ;
traits->width = ;
traits->height = ;
traits->windowDecoration = true;
traits->doubleBuffer = true;
traits->sharedContext = ;
traits->readDISPLAY();
traits->setUndefinedScreenDetailsToDefaultScreen(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext> gc = osg::GraphicsContext::createGraphicsContext(traits.get()); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Camera> camera = new osg::Camera;
camera->setGraphicsContext(gc.get());
camera->setViewport(new osg::Viewport(,, traits->width, traits->height));
GLenum buffer = traits->doubleBuffer ? GL_BACK : GL_FRONT;
camera->setDrawBuffer(buffer);
camera->setReadBuffer(buffer); // add this slave camera to the viewer, with a shift right of the projection matrix
viewer.addSlave(camera.get(), osg::Matrixd::translate(1.0,1.0,0.0), osg::Matrixd());
} // right_down window + right slave camera
{
osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext::Traits> traits = new osg::GraphicsContext::Traits;
traits->x = xoffset + ;
traits->y = yoffset + ;
traits->width = ;
traits->height = ;
traits->windowDecoration = true;
traits->doubleBuffer = true;
traits->sharedContext = ;
traits->readDISPLAY();
traits->setUndefinedScreenDetailsToDefaultScreen(); osg::ref_ptr<osg::GraphicsContext> gc = osg::GraphicsContext::createGraphicsContext(traits.get()); osg::ref_ptr<osg::Camera> camera = new osg::Camera;
camera->setGraphicsContext(gc.get());
camera->setViewport(new osg::Viewport(,, traits->width, traits->height));
GLenum buffer = traits->doubleBuffer ? GL_BACK : GL_FRONT;
camera->setDrawBuffer(buffer);
camera->setReadBuffer(buffer); // add this slave camera to the viewer, with a shift right of the projection matrix
viewer.addSlave(camera.get(), osg::Matrixd::translate(-1.0,1.0,0.0), osg::Matrixd());
}
// optimize the scene graph, remove redundant nodes and state etc.
osgUtil::Optimizer optimizer;
optimizer.optimize(loadedModel); // set the scene to render
viewer.setSceneData(loadedModel); return viewer.run();
}
The routine of each slave camera is alike. While the key point is this sentence:
viewer.addSlave(camera.get(), osg::Matrixd::translate(-1.0,1.0,0.0), osg::Matrixd());
This sentence set the viewpoint of slave camera,which translate the position of view point. Four slave camera view the common model in different direction, combine together.
the command to complie this program is following:
g++ -o osgwindows_1 osgwindows_1.cpp -losg -losgDB -losgViewer -lOpenThreads -losgUtil
After compling, just run it with:
sudo ./osgwindows_1
The outcome of above program is shown:
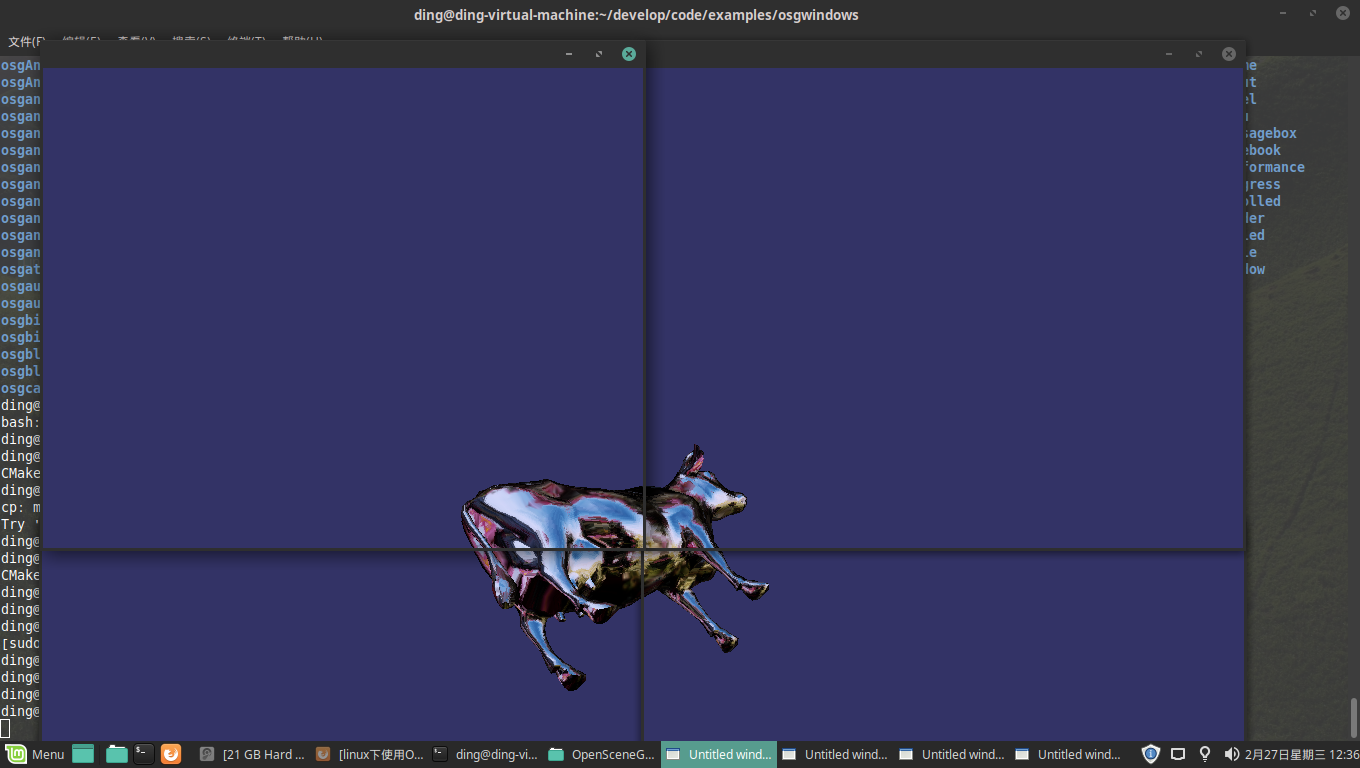
Like moniter constructed with four screen. Drag mouse in one window, the model will rotate in other three screen meanwhile. Great!
Learning OSG programing---osgwindows的更多相关文章
- Learning OSG programing---osgScribe
Learning OSG programing---osgScribe Scribe可以翻译为素描,抄写等.本例通过在模型表面添加一层素描,来显示模型的骨架. 关键代码: osg::ref_ptr&l ...
- Learning OSG programing---Multi Camera in Multi window 在多窗口中创建多相机
这个例子演示了在多个窗口中创建多个相机,函数的代码如下: void multiWindowMultipleCameras(osgViewer::Viewer& viewer,bool mult ...
- Learning OSG programing---Multi Camera in one window 在单窗口中创建多相机
在学习OSG提供的例子osgCamera中,由于例子很长,涉及很多细节,考虑将其分解为几个小例子.本文介绍实现在一个窗口中添加多个相机的功能. 此函数接受一个Viewer引用类型参数,设置图形上下文的 ...
- Learning OSG programing---osgAnimation(3)
接下来是用createModel函数创建模型: osg::ref_ptr<osg::Group> createModel(bool overlay, osgSim::OverlayNode ...
- Learning OSG programing---osgAnimation(2)
osg::Node* createBase(const osg::Vec3& center,float radius) { ; ; *radius; *radius; osg::Vec3 v0 ...
- Learning OSG programing---osgAnimation(1)
osg::AnimationPath* createAnimationPath(const osg::Vec3& center,float radius,double looptime) { ...
- Learning OSG programing---osgShape
本例示范了osg中Shape ---- 基本几何元素的绘制过程.参照osg官方文档,Shape 类包含以下子类: 在示例程序中,函数createShapes函数用于生成需要绘制的几何形状. osg:: ...
- Learning OSG programing---osgClip
OSG Clip例程剖析 首先是创建剪切节点的函数代码: osg::ref_ptr<osg::Node> decorate_with_clip_node(const osg::ref_pt ...
- Coursera Deep Learning 2 Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter tuning, Regularization and Optimization - week3, Hyperparameter tuning, Batch Normalization and Programming Frameworks
Tuning process 下图中的需要tune的parameter的先后顺序, 红色>黄色>紫色,其他基本不会tune. 先讲到怎么选hyperparameter, 需要随机选取(sa ...
随机推荐
- IIS 应用池资源定时回收
方法1: 方法2:
- vue简单的v-for - - 路由跳转
前几天写了一个特特特简单的小图片页面,主要用到的就是v-for遍历以及路由跳转到详情页.路由跳转需要在router文件夹下index.js引入. 导航栏(element ui导航栏为模板): < ...
- linux系统部署war包,查看tomcat日志
1.部署war包app/tomcat/bin在tomcat/bin 目录下启动 .startup.sh,在启动过程中tomcat会对war包进行解压,形成相应的项目目录 执行命令:./startup. ...
- Codeforces 633F 树的直径/树形DP
题意:有两个小孩玩游戏,每个小孩可以选择一个起始点,并且下一个选择的点必须和自己选择的上一个点相邻,问两个选的点权和的最大值是多少? 思路:首先这个问题可以转化为求树上两不相交路径的点权和的最大值,对 ...
- Sass-数字运算
在 Sass 运算中数字运算是较为常见的,数字运算包括前面介绍的:加法.减法.乘法和除法等运算.而且还可以通过括号来修改他们的运算先后顺序.和我们数学运算是一样的,一起来看个示例. .box { wi ...
- vue之路由传参三种基本方式
现有如下场景,点击父组件的li元素跳转到子组件中,并携带参数,便于子组件获取数据. 父组件中: <li v-for="article in articles" @click= ...
- 用pycharm运行pytest
安装pytest 1. 在pycharm中建项目,建文件,文件名字要以test_开头 2.在文件中插入pytest模块 import pytest #引用pytest模块 3.定义test函数,以及断 ...
- nyoj 471:好多的树(容斥原理)
题目链接: http://acm.nyist.net/JudgeOnline/problem.php?pid=471 还是直接上代码.. #include<bits/stdc++.h> u ...
- Vue学习笔记-插槽基本使用
为了让我们的组件更加具有扩展性,可以使用插槽 <div id="app"> <cpn> <span>返回</span> <in ...
- pycharm之black配置for python file(代码格式化工具)
一.介绍下black 源码;https://github.com/ambv/blackpei 二.具体步骤 第一步 安装black: 从命令行安装:例如Windows的cmd窗口,运行命令pip3 i ...
