python Scrapy 从零开始学习笔记(一)
在之前我做了一个系列的关于 python 爬虫的文章,传送门:https://www.cnblogs.com/weijiutao/p/10735455.html,并写了几个爬取相关网站并提取有效信息的案例:https://www.cnblogs.com/weijiutao/p/10614694.html 等,从本章开始本人将继续深入学习 python 爬虫,主要是基于 Scrapy 库展开,特此记录,与君共勉!
Scrapy 官方网址:https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/
Scrapy 中文网址:https://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/index.html
Scrapy 框架
Scrapy是用纯Python实现一个为了爬取网站数据、提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,用途非常广泛。
框架的力量,用户只需要定制开发几个模块就可以轻松的实现一个爬虫,用来抓取网页内容以及各种图片,非常之方便。
Scrapy 使用了 Twisted
['twɪstɪd](其主要对手是Tornado)异步网络框架来处理网络通讯,可以加快我们的下载速度,不用自己去实现异步框架,并且包含了各种中间件接口,可以灵活的完成各种需求。
Scrapy架构图(绿线是数据流向):

Scrapy Engine(引擎): 负责Spider、ItemPipeline、Downloader、Scheduler中间的通讯,信号、数据传递等。Scheduler(调度器): 它负责接受引擎发送过来的Request请求,并按照一定的方式进行整理排列,入队,当引擎需要时,交还给引擎。Downloader(下载器):负责下载Scrapy Engine(引擎)发送的所有Requests请求,并将其获取到的Responses交还给Scrapy Engine(引擎),由引擎交给Spider来处理,Spider(爬虫):它负责处理所有Responses,从中分析提取数据,获取Item字段需要的数据,并将需要跟进的URL提交给引擎,再次进入Scheduler(调度器),Item Pipeline(管道):它负责处理Spider中获取到的Item,并进行进行后期处理(详细分析、过滤、存储等)的地方.Downloader Middlewares(下载中间件):你可以当作是一个可以自定义扩展下载功能的组件。Spider Middlewares(Spider中间件):你可以理解为是一个可以自定扩展和操作引擎和Spider中间通信的功能组件(比如进入Spider的Responses;和从Spider出去的Requests)
以上是 Scrapy 的架构图,从流程上看还是很清晰的,我就只简单的说一下,首先从红色方框的 Spider 开始,通过引擎发送给调度器任务,再将请求任务交给下载器并处理完后返回结果给 Spider,最后将结果交给关到来处理我们的结果就可以了。
上面的话可能还是会有些拗口,在接下来我们会一点点进行剖析,最后会发现利用 Scrapy 框架来做爬虫是如此简单。
Scrapy的安装
windows 安装 pip install scrapy
Mac 安装 sudo pip install scrapy
pip 升级 pip install --upgrade pip
本人目前使用的是Mac电脑,目前使用的是 python3 版本,内容上其实都大同小异,如遇系统或版本问题可及时联系,互相学习!
安装完成后我们在终端输出 Scrapy 即可安装是否成功:
新建项目
在 Scrapy 安装成功之后,我们就需要用它来开发我们的爬虫项目了,进入自定义的项目目录中,运行下列命令:
scrapy startproject spiderDemo
运行上面的命令行就会在我们项目目录下生成一下目录结构:
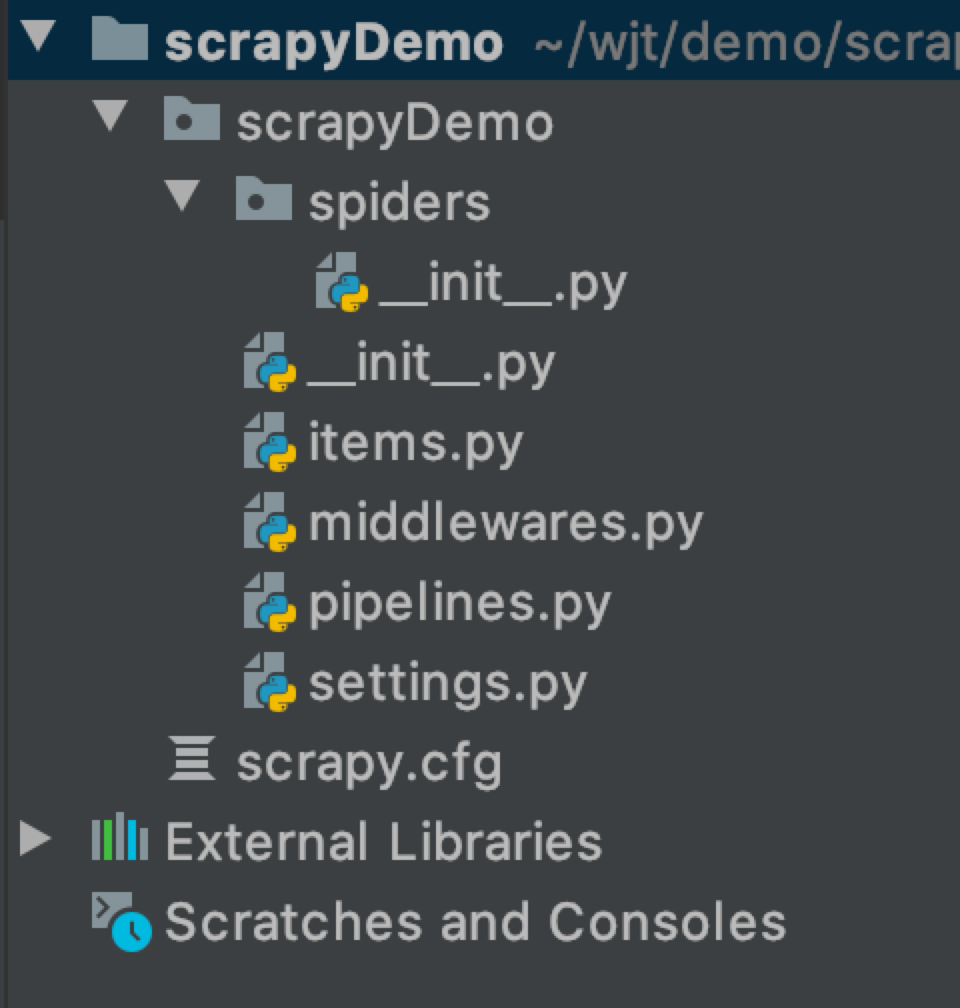
下面来简单介绍一下各个主要文件的作用:
scrapy.cfg :项目的配置文件
scrapyDemo/ :项目的Python模块,将会从这里引用代码
scrapyDemo/items.py :项目的目标文件
scrapyDemo/middlewares.py :项目的中间件文件
scrapyDemo/pipelines.py :项目的管道文件
scrapyDemo/settings.py :项目的设置文件
scrapyDemo/spiders/ :存储爬虫代码目录
接下来我们对各文件里的内容简单说一下,里面的代码目前都是最简单的基本代码,在接下来做案例的时候我们会再有针对地对文件做一下解释。
其中的 __init_.py 文件内容都是空的,但是却不能删除掉,否则项目将无法启动。
spiderDemo/items.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class ScrapydemoItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
pass
该文件是用来定义我们通过爬虫所获取到的有用的信息,即 scrapy.Item
scrapyDemo/middlewares.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your spider middleware
#
# See documentation in:
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html from scrapy import signals class ScrapydemoSpiderMiddleware(object):
# Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined,
# scrapy acts as if the spider middleware does not modify the
# passed objects. @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
s = cls()
crawler.signals.connect(s.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
return s def process_spider_input(self, response, spider):
# Called for each response that goes through the spider
# middleware and into the spider. # Should return None or raise an exception.
return None def process_spider_output(self, response, result, spider):
# Called with the results returned from the Spider, after
# it has processed the response. # Must return an iterable of Request, dict or Item objects.
for i in result:
yield i def process_spider_exception(self, response, exception, spider):
# Called when a spider or process_spider_input() method
# (from other spider middleware) raises an exception. # Should return either None or an iterable of Request, dict
# or Item objects.
pass def process_start_requests(self, start_requests, spider):
# Called with the start requests of the spider, and works
# similarly to the process_spider_output() method, except
# that it doesn’t have a response associated. # Must return only requests (not items).
for r in start_requests:
yield r def spider_opened(self, spider):
spider.logger.info('Spider opened: %s' % spider.name) class ScrapydemoDownloaderMiddleware(object):
# Not all methods need to be defined. If a method is not defined,
# scrapy acts as if the downloader middleware does not modify the
# passed objects. @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
# This method is used by Scrapy to create your spiders.
s = cls()
crawler.signals.connect(s.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
return s def process_request(self, request, spider):
# Called for each request that goes through the downloader
# middleware. # Must either:
# - return None: continue processing this request
# - or return a Response object
# - or return a Request object
# - or raise IgnoreRequest: process_exception() methods of
# installed downloader middleware will be called
return None def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
# Called with the response returned from the downloader. # Must either;
# - return a Response object
# - return a Request object
# - or raise IgnoreRequest
return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
# Called when a download handler or a process_request()
# (from other downloader middleware) raises an exception. # Must either:
# - return None: continue processing this exception
# - return a Response object: stops process_exception() chain
# - return a Request object: stops process_exception() chain
pass def spider_opened(self, spider):
spider.logger.info('Spider opened: %s' % spider.name)
该文件为中间件文件,名字后面的s表示复数,说明这个文件里面可以放很多个中间件,我们用到的中间件可以在此定义
spiderDemo/pipelines.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html class ScrapydemoPipeline(object):
def process_item(self, item, spider):
return item
该文件俗称管道文件,是用来获取到我们的Item数据,并对数据做针对性的处理。
scrapyDemo/settings.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for scrapyDemo project
#
# For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or
# commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation:
#
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html BOT_NAME = 'scrapyDemo' SPIDER_MODULES = ['scrapyDemo.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'scrapyDemo.spiders' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
#USER_AGENT = 'scrapyDemo (+http://www.yourdomain.com)' # Obey robots.txt rules
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16)
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay
# See also autothrottle settings and docs
#DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 3
# The download delay setting will honor only one of:
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16
#CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16 # Disable cookies (enabled by default)
#COOKIES_ENABLED = False # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default)
#TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False # Override the default request headers:
#DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
# 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
# 'Accept-Language': 'en',
#} # Enable or disable spider middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
#SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'scrapyDemo.middlewares.ScrapydemoSpiderMiddleware': 543,
#} # Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
#DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'scrapyDemo.middlewares.ScrapydemoDownloaderMiddleware': 543,
#} # Enable or disable extensions
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html
#EXTENSIONS = {
# 'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole': None,
#} # Configure item pipelines
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
#ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# 'scrapyDemo.pipelines.ScrapydemoPipeline': 300,
#} # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html
#AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True
# The initial download delay
#AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5
# The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies
#AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60
# The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to
# each remote server
#AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0
# Enable showing throttling stats for every response received:
#AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default)
# See https://docs.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings
#HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True
#HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0
#HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache'
#HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = []
#HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
该文件为我们的设置文件,一些基本的设置需要我们在此文件中进行配置,如我们的中间件文件当中的两个类 ScrapydemoSpiderMiddleware,ScrapydemoDownloaderMiddleware 在 settings.py 中就能找到。
在 settings 文件中,我们常会配置到如上面的字段 如:ITEM_PIPELINES(管道文件),DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS(请求报头),DOWNLOAD_DELAY(下载延迟)
,ROBOTSTXT_OBEY(是否遵循爬虫协议)等。
本章我们就先简单的介绍一下 scrapy 的基本目录,下一章我们来根据 scrapy 框架实现一个爬虫案例。
python Scrapy 从零开始学习笔记(一)的更多相关文章
- python Scrapy 从零开始学习笔记(二)
在之前的文章中我们简单了解了一下Scrapy 框架和安装及目录的介绍,本章我们将根据 scrapy 框架实现博客园首页博客的爬取及数据处理. 我们先在自定义的目录中通过命令行来构建一个 scrapy ...
- Python scrapy爬虫学习笔记01
1.scrapy 新建项目 scrapy startproject 项目名称 2.spiders编写(以爬取163北京新闻为例) 此例中用到了scrapy的Itemloader机制,itemloade ...
- Requests:Python HTTP Module学习笔记(一)(转)
Requests:Python HTTP Module学习笔记(一) 在学习用python写爬虫的时候用到了Requests这个Http网络库,这个库简单好用并且功能强大,完全可以代替python的标 ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记
python网络爬虫学习笔记 By 钟桓 9月 4 2014 更新日期:9月 4 2014 文章文件夹 1. 介绍: 2. 从简单语句中開始: 3. 传送数据给server 4. HTTP头-描写叙述 ...
- Python Built-in Function 学习笔记
Python Built-in Function 学习笔记 1. 匿名函数 1.1 什么是匿名函数 python允许使用lambda来创建一个匿名函数,匿名是因为他不需要以标准的方式来声明,比如def ...
- 2019-03-22 Python Scrapy 入门教程 笔记
Python Scrapy 入门教程 入门教程笔记: # 创建mySpider scrapy startproject mySpider # 创建itcast.py cd C:\Users\theDa ...
- Python快速入门学习笔记(二)
注:本学习笔记参考了廖雪峰老师的Python学习教程,教程地址为:http://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/001374738125095c955c1e6d8bb49318210 ...
- python数据分析入门学习笔记
学习利用python进行数据分析的笔记&下星期二内部交流会要讲的内容,一并分享给大家.博主粗心大意,有什么不对的地方欢迎指正~还有许多尚待完善的地方,待我一边学习一边完善~ 前言:各种和数据分 ...
- python网络爬虫学习笔记(二)BeautifulSoup库
Beautiful Soup库也称为beautiful4库.bs4库,它可用于解析HTML/XML,并将所有文件.字符串转换为'utf-8'编码.HTML/XML文档是与“标签树一一对应的.具体地说, ...
随机推荐
- linux网络编程-posix信号量与互斥锁(39)
-posix信号量信号量 是打开一个有名的信号量 sem_init是打开一个无名的信号量,无名信号量的销毁用sem_destroy sem_wait和sem_post是对信号量进行pv操作,既可以使用 ...
- springboot_自动配置原理
目录 1.1 @SpringBootApplication 2.1 @EnableAutoConfiguration 2.1.1 @AutoConfigurationPackage 2.1.2 @Im ...
- NodeMCU手把手入门:配置NodeMCU ESP8266开发板环境及点亮LED灯
之前一直在玩树莓派,最近实验室买了些NodeMCU就想着玩一玩,没想到挺有意思的.其实树莓派能实现的功能,它大部分也可以,价格比派也便宜不少,舍不得买派的同学可以先买这个开发板玩一玩. 本文主要介绍了 ...
- 如何在Vim中更改颜色和主题
大家好,我是良许. Vim是我们在Linux中非常常用的一款文本编辑器.Vim 是一款免费.开源的文本编辑器,它的功能和许多其他的文本编辑器大致相同,比如 Sublime 和 Notepad++ .V ...
- Security 10:权限管理
SQL Server 用于管理权限的TSQL命令有:GRANT用于授予权限,REVOKE 用于移除授予的权限,而DENY用于防止安全主体通过GRANT获得权限.但是,SQL Server的权限管理不是 ...
- 在linux上安装jdk(转载)
软件环境: 虚拟机:VMware Workstation 10 操作系统:Ubuntu-12.04-desktop-amd64 JAVA版本:jdk-7u55-linux-x64 软件下载地址: JD ...
- 如何实现html页面自动刷新
使用场景: 1. 页面需要定时刷新,实时加载数据,需要实时查看监控数据(H5中的WebSocket和SSE可以实现局部刷新) 2. 一定时间之后跳转到指定页面(登录注册之类) 3. 前端开发使用伪数据 ...
- 线程基础知识01-Thread类,Runnable接口
常见面试题:创建一个线程的常用方法有哪些?Thread创建线程和Runnable创建线程有什么区别? 答案通常集中在,继承类和实现接口的差别上面: 如果深入问一些问题:1.要执行的任务写在run()方 ...
- 洛谷P2602 [ZJOI2010]数字计数 题解
题目描述 输入格式 输出格式 输入输出样例 输入样例 1 99 输出样例 9 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 说明/提示 数据规模与约定 分析 很裸的一道数位DP的板子 定义f[ ...
- js返回上一页并刷新思路
在网上找了很多办法,比如window.history.go(-1):window.history.go(0): 试了下根本没用(不知道是不是我哪里写错了),想着在上一个页面写一个关闭页面并刷新的方法, ...
