[leetcode]380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)常数时间插入删除取随机值
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time.
insert(val): Inserts an item val to the set if not already present.remove(val): Removes an item val from the set if present.getRandom: Returns a random element from current set of elements. Each element must have the same probability of being returned.
Example:
// Init an empty set.
RandomizedSet randomSet = new RandomizedSet(); // Inserts 1 to the set. Returns true as 1 was inserted successfully.
randomSet.insert(1); // Returns false as 2 does not exist in the set.
randomSet.remove(2); // Inserts 2 to the set, returns true. Set now contains [1,2].
randomSet.insert(2); // getRandom should return either 1 or 2 randomly.
randomSet.getRandom(); // Removes 1 from the set, returns true. Set now contains [2].
randomSet.remove(1); // 2 was already in the set, so return false.
randomSet.insert(2); // Since 2 is the only number in the set, getRandom always return 2.
randomSet.getRandom();
Solution1: HashMap + ArrayList
1. use an ArrayList together with HashMap, making hashmap save key(item)->value(idx)
2. To reverse item in O(1), avoiding traversal the whole arrayList in O(n) time, we swap the toDelete item with last item in the list
3. Go through an example like this:

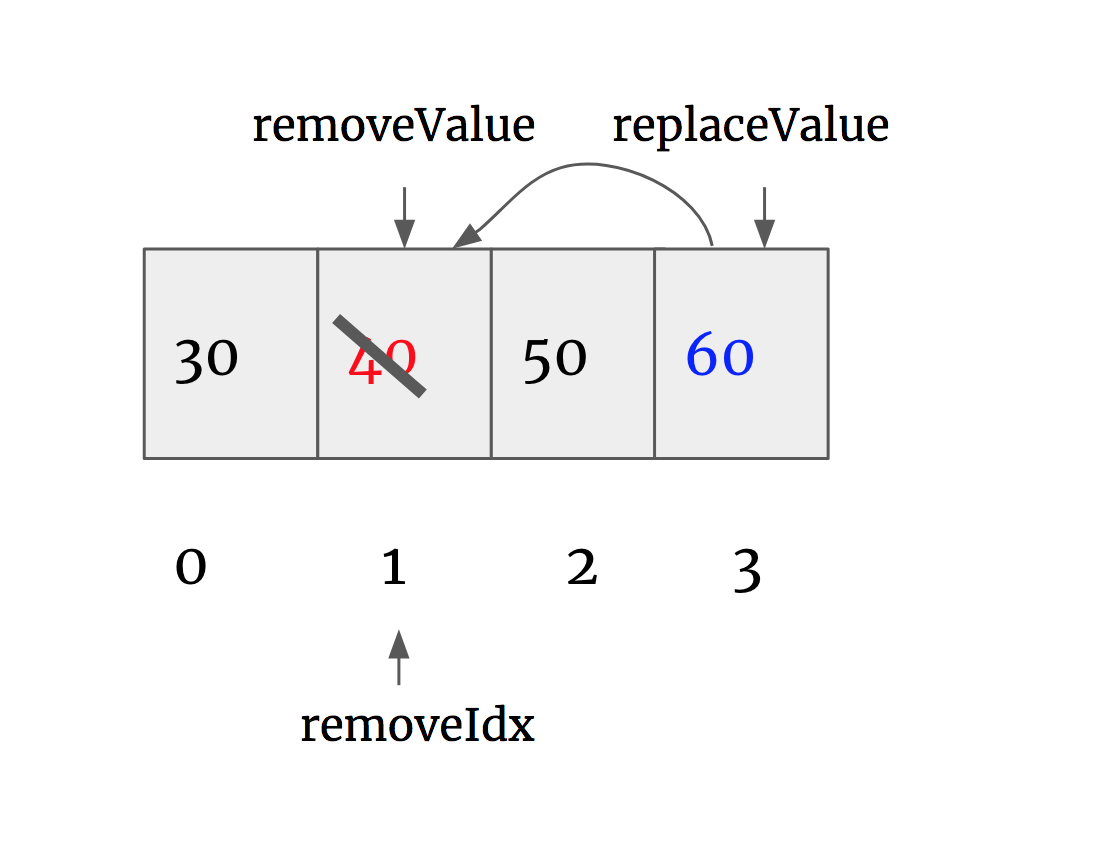
use HashMap to get removeIdx:

Set the last item in the list as replaceValue, why the last item? In order to maintain other indices.

Deal with HashMap: (1) put (2)delete

Deal with List: (1) set (2)delete
code:
class RandomizedSet {
Map<Integer, Integer> map;
List<Integer> list;
Random r; // java 自带类
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public RandomizedSet() {
list = new ArrayList<>();
map = new HashMap<>();
r = new Random();
}
/** Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element. */
public boolean insert(int val) {
if (map.containsKey(val)) {
return false;
}
map.put(val, list.size());
list.add(val);
return true;
}
/** Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. */
public boolean remove(int val) {
/**
hashmap
30 - 0
40 - 1
50 - 2
60 - 3
list: 30 40 50 60
0 1 2 3
**/
if (!map.containsKey(val)) return false;
int removeIdx = map.get(val); // Idx: 1
int replaceValue = list.get(list.size()-1); // replaceValue : 60
// deal with map
map.put(replaceValue, removeIdx);
map.remove(val);
// deal with list
list.set(removeIdx, replaceValue);
list.remove(list.size() -1);
return true;
}
/** Get a random element from the set. */
public int getRandom() {
return list.get(r.nextInt(list.size()));
}
}
[leetcode]380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)常数时间插入删除取随机值的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 常数时间内插入删除和获得随机数
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. insert(val): In ...
- LeetCode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 常数时间插入、删除和获取随机元素(C++/Java)
题目: Design a data structure that supports all following operations in averageO(1) time. insert(val): ...
- [leetcode]381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed常数时间插入删除取随机值
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- [LeetCode] 381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed 插入删除和获得随机数O(1)时间 - 允许重复
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. Note: Duplicate ...
- [LeetCode] Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 常数时间内插入删除和获得随机数
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. insert(val): In ...
- [LeetCode] 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 插入删除获得随机数O(1)时间
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. insert(val): In ...
- LeetCode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1)
380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) Add to List Description Submission Solutions Total Accepted: 21771 ...
- leetcode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 、381. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) - Duplicates allowed
380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) 实现插入.删除.获得随机数功能,且时间复杂度都在O(1).实际上在插入.删除两个功能中都包含了查找功能,当然查找也必须是O(1). ...
- LeetCode 380. Insert Delete GetRandom O(1) (插入删除和获得随机数 常数时间)
Design a data structure that supports all following operations in average O(1) time. insert(val): In ...
随机推荐
- 给大厨写的R数据分析代码
###************************************** 新老客户统计 ***************************************### dachu &l ...
- 单源最短路径Dijkstra算法,多源最短路径Floyd算法
1.单源最短路径 (1)无权图的单源最短路径 /*无权单源最短路径*/ void UnWeighted(LGraph Graph, Vertex S) { std::queue<Vertex&g ...
- 配置jboss为windows服务
先确保jdk和jboss的环境变量是正常可用的 1.(下载binaries 2.x.x-windows x86)找到service.bat和jbosssvc.exe两个文件 1.1 binaries ...
- python2的reload模块
在刚开始写python程序的时候,都会遇到一个很头疼的问题——编码错误,在之前的文章中也做了介绍: 由__future__中unicode_literals引起的错误来研究python中的编码问题 . ...
- 服务器tcp连接timewait过多优化及详细分析
[背景说明] 在7层负载均衡上,查询网络状态发现timewait太多,于是开始准备优化事宜 整体的拓扑结构,前面是lvs做dr模式的4层负载均衡,后端使用(nginx.or haproxy)做7层负载 ...
- 廖雪峰Java6 IO编程-2input和output-7序列化
1.序列化 序列化是指把一个Java对象变成二进制内容byte[] 序列化后可以把byte[]保存到文件中 序列化后可以把byte[]通过网络传输 一个Java对象要能序列化,必须实现Serializ ...
- linux添加zabbix service并开机自动启动
最近有个数据库相关操作后需要重启操作系统,重启后发现zabbix监控一直没有数据,迷了半天原来zabbix压根就没有启动.想了半天决定把zabbix添加到系统服务,并设置开机启动. 1.按一定的规则编 ...
- 实验三:xen环境下的第一个虚拟机的安装
实验名称: xen环境下的第一个虚拟机的安装 实验环境: 我们这里继续上面实验二来完成这个实验: 环境则是xen的安装环境,如下图: 开启虚拟机的的硬件辅助虚拟化功能: 实验要求: 这里我们通过安装b ...
- 剑指offer题目解答合集(C++版)
数组中重复的数字 二维数组中查找 字符串 替换空格 二叉树的编码和解码 从尾到头打印链表 重建二叉树 二叉树的下一个节点 2个栈实现队列 斐波那契数列 旋转数字 矩阵中的路径 机器人的运动范围 剪绳子 ...
- wepy打开页面首次不显示,但是数据已经有了
page页面首次打开异步数据无法通过props传递到子组件 解决:在开发者工具关闭上传代码时自动压缩就解决了,在wepy文档里也有强调
