吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(17)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import time # 声明输入图片数据,类别
x = tf.placeholder('float', [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder('float', [None, 10])
# 输入图片数据转化
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) #第一层卷积层,初始化卷积核参数、偏置值,该卷积层5*5大小,一个通道,共有6个不同卷积核
filter1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 1, 6]))
bias1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([6]))
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(x_image, filter1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1 + bias1) maxPool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') filter2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 6, 16]))
bias2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([16]))
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(maxPool2, filter2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2 + bias2) maxPool3 = tf.nn.max_pool(h_conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') filter3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 16, 120]))
bias3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([120]))
conv3 = tf.nn.conv2d(maxPool3, filter3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(conv3 + bias3) # 全连接层
# 权值参数
W_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([7 * 7 * 120, 80]))
# 偏置值
b_fc1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([80]))
# 将卷积的产出展开
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_conv3, [-1, 7 * 7 * 120])
# 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) # 输出层,使用softmax进行多分类
W_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([80, 10]))
b_fc2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([10]))
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
# 损失函数
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
# 使用GDO优化算法来调整参数
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(cross_entropy) sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 测试正确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float")) # 所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据
mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets('F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\', one_hot=True) # 进行训练
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(20000):
# 获取训练数据
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代100个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率
if i % 2 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
# 计算间隔时间
end_time = time.time()
print('time: ', (end_time - start_time))
start_time = end_time
# 训练数据
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) # 关闭会话
sess.close()

import time
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长,
#padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围,
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 声明输入图片数据,类别
x = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 10])
# 输入图片数据转化
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 6])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([6])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 6, 16])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([16])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*16,120])
# 偏置值
b_fc1 = bias_variable([120])
# 将卷积的产出展开
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 16])
# 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([120,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 代价函数
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
# 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据
mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets('F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\', one_hot=True)
c = [] # 进行训练
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(1000):
# 获取训练数据
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率
if i % 2 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
c.append(train_accuracy)
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
# 计算间隔时间
end_time = time.time()
print('time: ', (end_time - start_time))
start_time = end_time
# 训练数据
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close()
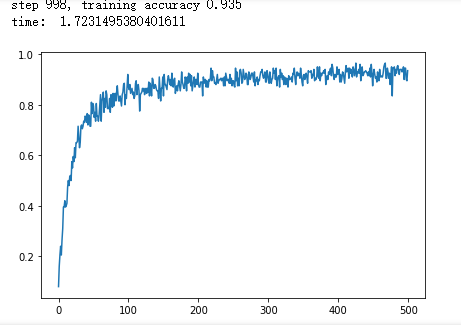
plt.plot(c)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-2.png', dpi=200)
plt.show()
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长,
#padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围,
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 声明输入图片数据,类别
x = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 10])
# 输入图片数据转化
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
# 偏置值
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
# 将卷积的产出展开
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
# 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) # 代价函数
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
# 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据
mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets('F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\', one_hot=True)
c = [] # 进行训练
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(1000):
# 获取训练数据
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率
if i % 2 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
c.append(train_accuracy)
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
# 计算间隔时间
end_time = time.time()
print('time: ', (end_time - start_time))
start_time = end_time
# 训练数据
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close()
plt.plot(c)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-1.png', dpi=200)
plt.show()
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial) #初始化单个卷积核上的偏置值
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial) #输入特征x,用卷积核W进行卷积运算,strides为卷积核移动步长,
#padding表示是否需要补齐边缘像素使输出图像大小不变
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME') #对x进行最大池化操作,ksize进行池化的范围,
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME') sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
# 声明输入图片数据,类别
x = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder('float32', [None, 10])
# 输入图片数据转化
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2) W_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
# 偏置值
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
# 将卷积的产出展开
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
# 神经网络计算,并添加relu激活函数
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1) W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,128])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([128])
h_fc2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2) W_fc3 = weight_variable([128,10])
b_fc3 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc2, W_fc3) + b_fc3)
# 代价函数
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv))
# 使用Adam优化算法来调整参数
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(1e-5).minimize(cross_entropy) # 测试正确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float32")) # 所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables()) # 获取mnist数据
mnist_data_set = input_data.read_data_sets('F:\\TensorFlow_deep_learn\\MNIST\\', one_hot=True)
c = [] # 进行训练
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(1000):
# 获取训练数据
batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist_data_set.train.next_batch(200) # 每迭代10个 batch,对当前训练数据进行测试,输出当前预测准确率
if i % 2 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
c.append(train_accuracy)
print("step %d, training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
# 计算间隔时间
end_time = time.time()
print('time: ', (end_time - start_time))
start_time = end_time
# 训练数据
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys}) sess.close()
plt.plot(c)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig('F:\\cnn-tf-cifar10-11.png', dpi=200)
plt.show()
吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(17)的更多相关文章
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(12)
import tensorflow as tf q = tf.FIFOQueue(,"float32") counter = tf.Variable(0.0) add_op = t ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(18)
# coding: utf-8 import time import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import _pickle as pickle impo ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(16)
import struct import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt dateMat = np.ones((7,7)) kernel = n ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(15)
import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist.input_data as input_data mnist = ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(14)
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt threshold = 1.0e-2 x1_dat ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(13)
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt x_data = np.random.randn(10) print(x_data) y_data ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(11)
import numpy as np from matplotlib import pyplot as plt A = np.array([[5],[4]]) C = np.array([[4],[6 ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(10)
import tensorflow as tf input1 = tf.constant(1) print(input1) input2 = tf.Variable(2,tf.int32) print ...
- 吴裕雄 python深度学习与实践(9)
import numpy as np import tensorflow as tf inputX = np.random.rand(100) inputY = np.multiply(3,input ...
随机推荐
- java-同一用户顶替操作(session过期或无效)
同一账号后者登录前者被强制退出:(可以通过监听器或过滤器进行监测session是否无效) 首先根据输入的用户名和密码做验证,通过验证查询用户信息.在用户信息不为空的前提下,比较静态变量中的sessio ...
- Spring Boot的日志配置
一.配置logback日志 Spring Boot默认使用logback打印日志 需要增加依赖 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId& ...
- Windows 10的最新版1803版本ISO下载
Windows 10推出已经有几年时间了,笔者一直在用这个新版本.据说Windows 10以后只会推出新的更新,而不会有新的操作系统推出,所以Windows 10的更新就显得重要了.这次给大家推荐一个 ...
- 剑指offer 6.查找和排序 旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转. 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素. 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋 ...
- java http 请求的工具类
/*** Eclipse Class Decompiler plugin, copyright (c) 2016 Chen Chao (cnfree2000@hotmail.com) ***/pack ...
- MAC基本操作
1:软件的安装,卸载和破解 (1)mac上的软件包的安装可以去appstore或者是去第三方网站下载,下载下来的安装包一般是dmp,pkg,iso文件.最终安装之后生成的文件是app文件就可以使用.通 ...
- python3-基础7
协程函数 面向过程编程 递归与二分法 内置函数 lambda 模块与包的使用 import from ... import ... 常用模块 ########################### ...
- 2018-2019-2 20175227张雪莹《Java程序设计》实验三 《敏捷开发与XP实践》
2018-2019-2 20175227张雪莹<Java程序设计> 实验三 <敏捷开发与XP实践> 实验报告封面 课程:Java程序设计 班级:1752班 姓名:张雪莹 学号: ...
- [php]php设计模式 (总结)
转载自[php]php设计模式 (总结) 传统的23种模式(没有区分简单工厂与抽象工厂) http://www.cnblogs.com/bluefrog/archive/2011/01/04/1925 ...
- vs2015 iis express启动不了及安装DotNetCore.1.0.0-VS2015Tools.Preview2失败的解决方法
直接用管理员账户打开cmd,进入exe所在的文件夹在运行命令DotNetCore.1.0.0-VS2015Tools.Preview2.exe SKIP_VSU_CHECK=1不要加引号. PS:如果 ...
