B - Space Ant
The most exciting space discovery occurred at the end of the 20th century. In 1999, scientists traced down an ant-like creature in the planet Y1999 and called it M11. It has only one eye on the left side of its head and just three feet all on the right side of its body and suffers from three walking limitations:
It can not turn right due to its special body structure.
It leaves a red path while walking.
It hates to pass over a previously red colored path, and never does that.
The pictures transmitted by the Discovery space ship depicts that plants in the Y1999 grow in special points on the planet. Analysis of several thousands of the pictures have resulted in discovering a magic coordinate system governing the grow points of the plants. In this coordinate system with x and y axes, no two plants share the same x or y.
An M11 needs to eat exactly one plant in each day to stay alive. When it eats one plant, it remains there for the rest of the day with no move. Next day, it looks for another plant to go there and eat it. If it can not reach any other plant it dies by the end of the day. Notice that it can reach a plant in any distance.
The problem is to find a path for an M11 to let it live longest.
Input is a set of (x, y) coordinates of plants. Suppose A with the coordinates (xA, yA) is the plant with the least y-coordinate. M11 starts from point (0,yA) heading towards plant A. Notice that the solution path should not cross itself and all of the turns should be counter-clockwise. Also note that the solution may visit more than two plants located on a same straight line.
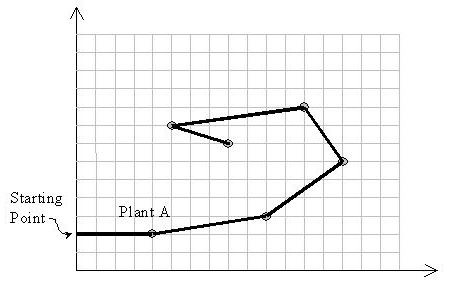
Input
The first line of the input is M, the number of test cases to be solved (1 <= M <= 10). For each test case, the first line is N, the number of plants in that test case (1 <= N <= 50), followed by N lines for each plant data. Each plant data consists of three integers: the first number is the unique plant index (1..N), followed by two positive integers x and y representing the coordinates of the plant. Plants are sorted by the increasing order on their indices in the input file. Suppose that the values of coordinates are at most 100.
Output
Output should have one separate line for the solution of each test case. A solution is the number of plants on the solution path, followed by the indices of visiting plants in the path in the order of their visits.
Sample Input
2
10
1 4 5
2 9 8
3 5 9
4 1 7
5 3 2
6 6 3
7 10 10
8 8 1
9 2 4
10 7 6
14
1 6 11
2 11 9
3 8 7
4 12 8
5 9 20
6 3 2
7 1 6
8 2 13
9 15 1
10 14 17
11 13 19
12 5 18
13 7 3
14 10 16
Sample Output
10 8 7 3 4 9 5 6 2 1 10
14 9 10 11 5 12 8 7 6 13 4 14 1 3 2
凸包,从第一个开始不停的进行排序就好了;
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<float.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define sf scanf
#define pf printf
#define mm(x,b) memset((x),(b),sizeof(x))
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i>=n;i--)
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const ll mod=1e9+100;
const db e=exp(1);
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int INF=0xfffffff;
struct Point{
int x,y,temp,num;
}p[50005],s[50005];
int top;
int direction(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) { return (p3.x-p1.x)*(p2.y-p1.y)-(p2.x-p1.x)*(p3.y-p1.y); }//点2和3,按哪个和点一的角度更小排,相同的话按哪个更近排
double dis(Point p1,Point p2) { return sqrt((p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); }
bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2)//极角排序
{
int temp=direction(p[top],p1,p2);
if(temp<0)return true ;
if(temp==0&&dis(p[top],p1)<dis(p[top],p2))return true;
return false;
}
/*vector<int>v;
void Graham(int n)
{
int pos,minx,miny;
minx=miny=INF;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//找最下面的基点
if(p[i].y<miny||(p[i].y==miny&&p[i].x<minx))
{
minx=p[i].x;
miny=p[i].y;
pos=i;
}
swap(p[0],p[pos]);
sort(p+1,p+n,cmp);
p[n]=p[0];
s[0]=p[0];s[1]=p[1];s[2]=p[2];
p[0].temp=1;p[1].temp=1;p[2].temp=1;
top=2;int i=3;
while(top<n)
{
while(p[i].temp)
{
i++;
if(i==n) i=0;
}
while(direction(s[top-1],s[top],p[i])>=0&&top>=2)
{
p[s[top].num].temp=0;
top--;
}
s[++top]=p[i];
p[i].temp=1;
}
}*/
int main()
{
int re;
sf("%d",&re);
while(re--)
{
top=0;
int n;
cin>>n;
rep(i,0,n)
{
p[i].temp=0;sf("%d%d%d",&p[i].num,&p[i].x,&p[i].y);
}
int pos,minx,miny;
minx=miny=INF;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//找最下面的基点
if(p[i].y<miny||(p[i].y==miny&&p[i].x<minx))
{
minx=p[i].x;
miny=p[i].y;
pos=i;
}
swap(p[0],p[pos]);
pf("%d",n);
rep(i,1,n)
{
sort(p+i,p+n,cmp);top++;
}
rep(i,0,n)
pf(" %d",p[i].num);
pf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
B - Space Ant的更多相关文章
- poj 1696 Space Ant (极角排序)
链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1696 Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissi ...
- POJ 1696 Space Ant(极角排序)
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 2489 Accepted: 1567 Descrip ...
- poj 1696 Space Ant(模拟+叉积)
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 3840 Accepted: 2397 Descrip ...
- POJ 1696 Space Ant 卷包裹法
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 3316 Accepted: 2118 Descrip ...
- POJ 1696 Space Ant(点积的应用)
Space Ant 大意:有一仅仅蚂蚁,每次都仅仅向当前方向的左边走,问蚂蚁走遍全部的点的顺序输出.開始的点是纵坐标最小的那个点,開始的方向是開始点的x轴正方向. 思路:从開始点開始,每次找剩下的点中 ...
- Space Ant
Space Ant The most exciting space discovery occurred at the end of the 20th century. In 1999, scient ...
- poj1696 Space Ant【计算几何】
含极角序排序模板. Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 5334 Accepted: ...
- Space Ant(极角排序)
Space Ant http://poj.org/problem?id=1696 Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions ...
- 2018.07.04 POJ 1696 Space Ant(凸包卷包裹)
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Description The most exciting space discovery occu ...
- poj 1696:Space Ant(计算几何,凸包变种,极角排序)
Space Ant Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 2876 Accepted: 1839 Descrip ...
随机推荐
- OpenGL核心技术之HDR
笔者介绍:姜雪伟.IT公司技术合伙人,IT高级讲师,CSDN社区专家.特邀编辑,畅销书作者.国家专利发明人;已出版书籍:<手把手教你架构3D游戏引擎>电子工业出版社和<Unity3D ...
- APICloud和海马玩模拟器结合调试手机页面
https://blog.csdn.net/pleasecallme_522/article/details/54577904
- 后台任务hangfire
Installation¶ There are a couple of packages for Hangfire available on NuGet. To install Hangfire in ...
- 学校公文办公处理系统_基于ASP.NET和Swfupload、FlashPaper2.2、校讯通短信发送的开发
学校新来了一个主管教学的副校长,他对他以前工作学校的公文处理系统表示高度留念,于是乎叫我们也开发一个. 我就参考了那个学校的办公管理系统,发现其实功能也蛮简单的,就是一个文件上传下载的功能,选择用户组 ...
- 简单shell指令
第一部分 简单的常用指令 1.date命令 date 2.显示日历 cal 3.显示当前目录 pwd 4.切换当前工作目录 默认情况下,超级用户的主目录是/root,而普通用户的主目录是/home下 ...
- 编程调节Win7/Win8系统音量的一种方法
不得不说, 自Win7(好像是吧), Windows的音量调节功能比以前更人性化了.... 但编程接口却变得更加复杂了............. 还要用到IAudioEndpointVolu ...
- oracle本地编译问题
oracle10.2: --将过程重新编译为本地编译方式,提示有编译错误,经查提示未设置plsql_native_library_dir 参数 SQL> alter procedure p_xx ...
- 菜鸟教程之工具使用(九)——Git如何进行分支的merge操作
今天继续我们的Git教程,Git杀手锏级的功能就是对于分支的管理,那么今天就来说说分支之间的merge操作.merge可以说是我们日常使用最多的操作之一,通常一个merge操作会包含commit.pu ...
- js中$
$符号在php中是表示变量的特征字符, 在js中它也有很多作用, 一般我们用来命名一个函数名称,获取id的1.首先可以用来表示变量, 比如变量 var s='asdsd'或var $s='asdasd ...
- emacs自动折行设置
- emacs自动折行 - 临时设置下 M-x `toggle-truncate-lines` - init.el 中添加 `(toggle-truncate-lines 1)`
