HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][区间反转+删除根节点]
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
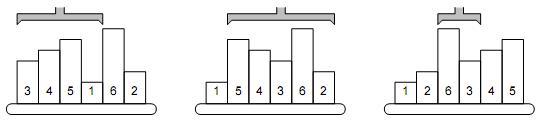
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too.
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero.
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed.
题意:
给出一个n,给出n个样品的高度,
给出一种根据高度排序的算法,其第 i 次操作:找到第 i 小的那个数的位置为Pi,将整个区间[i,Pi]反转,这样一来第 i 小的数就在位置 i 上;从 i 等于 1 到 n 循环这样的操作。
现在要求你给出每次操作的Pi。
题解:
伸展树1~n建树,把每个节点key值等于节点的编号(即key[x] = x),同时使得中序遍历伸展树得到的序列为1~n,
以题目中两个样例为例,建成的树应为如下图:
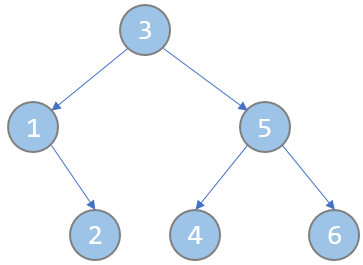
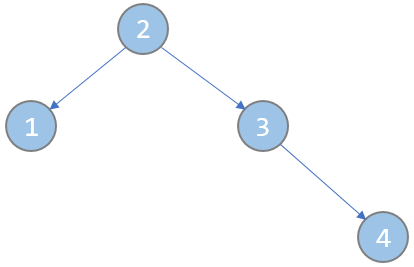 (注意,图中节点内的数字,既是节点编号,也是key值,即key[3] = 3,key[1] = 1,key[5] = 5……)
(注意,图中节点内的数字,既是节点编号,也是key值,即key[3] = 3,key[1] = 1,key[5] = 5……)
我们此时的伸展树维护的是n个样品的编号(编号为1~n);
将n个样品按输入顺序编号,再按照first高度second编号进行升序排序,那么新的顺序,就是题目中所描述的排序算法中的每次操作的顺序,
这样,按新的顺序依次枚举n个样品,对于第 i 个样品,其编号为sample[i].id,
我们此时就要去伸展树中寻找某个节点x,其key[x] = sample[i].id;而我们要求的Pi,就是比这个节点小的节点个数加1;
根据上面反复提到的,key[x] = x,所以我们其实就是把节点x = sample[i].id伸展到根,然后求其左子树内节点个数,再加1,
同时,因为需要区间翻转,所以我们可以翻转左子树,并且删除根节点,相当于翻转了[i,Pi],
由于我们不断的删除节点,因此实际答案就应该是左子树内节点个数 + 1 + (i - 1)。
AC代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define Key_value ch[ch[root][1]][0]
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+; int n;
struct Sample
{
int h;
int id;
}sample[maxn];
bool cmp(Sample a,Sample b)
{
if(a.h==b.h) return a.id<b.id;
else return a.h<b.h;
} /******************************** splay - st ********************************/
int root,nodecnt;
int par[maxn],ch[maxn][];
int key[maxn],size[maxn];
bool rev[maxn];
void NewNode(int &x,int p,int k)
{
x=k;
par[x]=p;
ch[x][]=ch[x][]=;
key[x]=k;
size[x]=;
rev[x]=;
}
void Update_Rev(int x)
{
if(x==) return;
rev[x]^=1;
}
void Pushup(int x)
{
size[x]=size[ch[x][]]+size[ch[x][]]+;
}
void Pushdown(int x)
{
if(rev[x])
{
swap(ch[x][],ch[x][]);
Update_Rev(ch[x][0]);
Update_Rev(ch[x][1]);
rev[x]=;
}
}
void Rotate(int x,int type) //旋转,0为左旋zag,1为右旋zig
{
int y=par[x];
Pushdown(y); Pushdown(x); //先把y的标记向下传递,再把x的标记往下传递
ch[y][!type]=ch[x][type]; par[ch[x][type]]=y;
if(par[y]) ch[par[y]][(ch[par[y]][]==y)]=x;
par[x]=par[y];
ch[x][type]=y; par[y]=x;
Pushup(y); Pushup(x);
}
void Splay(int x,int goal)
{
Pushdown(x);
while(par[x]!=goal)
{
if(par[par[x]]==goal)
{
Pushdown(par[x]); Pushdown(x);
Rotate(x,ch[par[x]][]==x); //左孩子zig,有孩子zag
}
else
{
Pushdown(par[par[x]]); Pushdown(par[x]); Pushdown(x);
int y=par[x];
int type=(ch[par[y]][]==y); //type=0,y是右孩子;type=1,y是左孩子
if(ch[y][type]==x)
{
Rotate(x,!type);
Rotate(x,type);
}
else
{
Rotate(y,type);
Rotate(x,type);
}
}
}
if(goal==) root=x;
}
int Get_Kth(int x,int k) //得到第k个节点
{
Pushdown(x);
int t=size[ch[x][]]+;
if(t==k) return x;
if(t>k) return Get_Kth(ch[x][],k);
else return Get_Kth(ch[x][],k-t);
}
int Get_Min(int x)
{
Pushdown(x);
while(ch[x][])
{
x=ch[x][];
Pushdown(x);
}
return x;
}
int Get_Max(int x)
{
Pushdown(x);
while(ch[x][])
{
x=ch[x][];
Pushdown(x);
}
return x;
}
void Build(int &x,int l,int r,int par)
{
if(l>r) return;
int mid=(l+r)/;
NewNode(x,par,mid);
Build(ch[x][],l,mid-,x);
Build(ch[x][],mid+,r,x);
Pushup(x);
}
void Init()
{
root=nodecnt=;
ch[root][]=ch[root][]=size[root]=key[root]=par[root]=rev[root]=;
Build(root,,n,);
}
void Del()
{
if(ch[root][]== && ch[root][]==) root=;
else if(ch[root][]==)
{
par[ch[root][]]=;
root=ch[root][];
}
else if(ch[root][]==)
{
par[ch[root][]]=;
root=ch[root][];
}
else
{
int pre=Get_Max(ch[root][]);
int nxt=Get_Min(ch[root][]);
Splay(pre,); Splay(nxt,root);
par[Key_value]=;
Key_value=;
Pushup(ch[root][]);
Pushup(root);
}
}
/******************************** splay - ed ********************************/ int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n) && n!=)
{
Init();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&sample[i].h);
sample[i].id=i;
}
sort(sample+,sample+n+,cmp); for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
Splay(sample[i].id,);
printf("%d ",i+size[ch[root][]]);
Update_Rev(ch[root][]);
Del();
}
printf("%d\n",n);
}
}
HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][区间反转+删除根节点]的更多相关文章
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort(splay 区间反转+删点)
题目链接:hdu 1890 Robotic Sort 题意: 给你n个数,每次找到第i小的数的位置,然后输出这个位置,然后将这个位置前面的数翻转一下,然后删除这个数,这样执行n次. 题解: 典型的sp ...
- HDU1890 Robotic Sort Splay tree反转,删除
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 题目中涉及数的反转和删除操作,需要用Splay tree来实现.首先对数列排序,得到每个数在数列 ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort | Splay
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) [Pr ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort (splay tree)
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- 数据结构(Splay平衡树):HDU 1890 Robotic Sort
Robotic Sort Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Tota ...
- hdu1890 Robotic Sort (splay+区间翻转单点更新)
Problem Description Somewhere deep in the Czech Technical University buildings, there are laboratori ...
- HDU 1890 Robotic Sort(splay)
[题目链接] http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 [题意] 给定一个序列,每次将i..P[i]反转,然后输出P[i],P[i]定义为当前数字i ...
- hdu 1890 Robotic Sort
原题链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890 如下: #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib&g ...
- 算法模板——splay区间反转 2
实现功能:同splay区间反转 1(基于BZOJ3223 文艺平衡树) 这次改用了一个全新的模板(HansBug:琢磨了我大半天啊有木有),大大简化了程序,同时对于splay的功能也有所完善 这里面没 ...
随机推荐
- [Model] LeNet-5 by Keras
典型的卷积神经网络. 数据的预处理 Keras傻瓜式读取数据:自动下载,自动解压,自动加载. # X_train: array([[[[ 0., 0., 0., ..., 0., 0., 0.], [ ...
- Linux+Redis实战教程_day03_Redis-set【重点】_有序set(了解)
2.redis-set[重点] Java HashSet 无序,不重复. Redis操作中,涉及到两个大数据集合的并集,交集,差集运算. 赋值: l sadd key values[value1.v ...
- js数组获取相同元素个数,归档排序
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- 编译Android 必须安装的库
要安装的库: 正在卸载 build-essential ...正在卸载 g++-multilib ...正在卸载 g++ ...正在卸载 gcc-multilib ...正在卸载 gcc ...正在卸 ...
- inux跟踪线程的方法:LWP和strace命令
摘要:在使用多线程程序时,有时会遇到程序功能异常的情况,而这种异常情况并不是每次都发生,很难模拟出来.这时就需要运用在程序运行时跟踪线程的手段,而linux系统的LWP和strace命令正是这种技术手 ...
- curses.h: No such file or directory
嵌入式linux移植时,编译busybox或者内核时使用make menuconfig有时会遇到这个错误 Linux Error: ncurses.h: No such file or directo ...
- linux文件和目錄管理的基本命令命令
ls命令 作用:顯示目標列表或目錄的內容 語法:ls[選項][目錄或文件] -a:顯示指定目錄下所有子目錄與文件,包括隱藏文件 -l:顯示文件的詳細信息 -d: 顯示目錄 例:ls -dl cd命令 ...
- 偶值得纪念的一天-初学习C#
今天好悲催啊,竟然生病啦,不过一切还好! 今天我们在云和数据学习的第二天,上午没有听课,似乎学习了变量的定义以及命名方法,还有变量类型的显隐式转换:我感觉这些还是在之前看书知道啦把,因此看啦看老师做的 ...
- 【Java并发编程一】线程安全和共享对象
一.什么是线程安全 当多个线程访问一个类时,如果不用考虑这些线程在运行时环境下的调度和交替执行,并且不需要额外的同步及在调用代码代码不必作其他的协调,这个类的行为仍然是正确的,那么称这个类是线程安全的 ...
- HipHop的原理
HipHop的原理 HipHop将PHP代码转换为高度优化的C++代码,然后再用g++编译器编译.它可以保持语义等效地执行源代码,但为了提高性能,牺牲了一些很少用到的特性,比如eval(). HipH ...