Entity Framework Code-First(5):Code First Conventions
Code First Conventions:
We have seen how EF Code-First creates DB tables from domain classes in the previous section. Here, we will learn about default Code-First conventions.
What is Convention?
Convention is a set of default rules to automatically configure a conceptual model based on domain class definitions when working with Code-First. Code-First conventions are defined inSystem.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.Conventions namespace.
Let's see an overview of the various Code-First conventions.
Type Discovery:
In the previous section, we created a context class with DbSet properties for the classes that we want to be part of the model. Code-First will create tables for classes included as DbSet properties, as we have seen the previous section. Code-First also includes any referenced types included in these classes, even if the referenced types are defined in a different assembly.
For example, the following Student entity class includes reference of Teacher class. However, context class does not include Teacher as DbSet property.
public class Student
{
public Student()
{ }
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public byte[] Photo { get; set; }
public decimal Height { get; set; }
public float Weight { get; set; } public Teacher Teacher { get; set; } public Standard Standard { get; set; }
} public class Teacher
{
public Teacher()
{ }
public int TeacherId { get; set; }
public string TeacherName { get; set; }
}
The following is a context class which does not include Teacher as a DbSet property (entity set)
namespace EF_Code_First_Tutorials
{ public class SchoolContext: DbContext
{
public SchoolContext(): base()
{ } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Standard> Standards { get; set; } }
}
So, even if Teacher is not included as an entity set in the context class, Code-First will include it in conceptual model and create a DB table for it, as shown below.
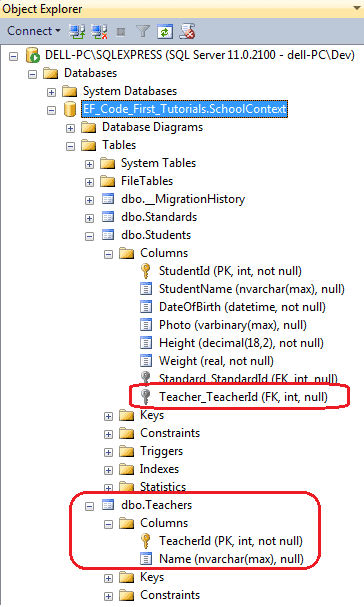
Code-First also includes derived classes even if the context class only includes base class as a DbSet property.
The conventions for the type discovery are:
- Code-First includes types defined as a DbSet property in context class.
- Code-First includes reference types included in entity types even if they are defined in different assembly.
- Code-First includes derived classes even if only the base class is defined as DbSet property.
Primary Key Convention:
In the previous section, we have seen that Code-First automatically creates a Primary Key in each table. The default convention for primary key is that Code-First would create a primary key for a property if the property name is Id or <class name>Id (NOT case sensitive). The data type of a primary key property can be anything, but if the type of the primary key property is numeric or GUID, it will be configured as an identity column.
If you have defined key property other than Id or <ClassName>Id then ModelValidationException will be thrown. For example, consider the following Standard class:
public class Standard
{
public Standard()
{ }
public int StdId { get; set; }
public string StandardName { get; set; } public IList<Student> Students { get; set; } }
As you can see in the above code, Standard class is defined with StdId key property. Entity Framework will throw the following exception for this.
'System.Data.Entity.ModelConfiguration.ModelValidationException' occurred in EntityFramework.dll
EntityType 'Standard' has no key defined. Define the key for this EntityType.
If you want to define StdId as primary key then you have to use DataAnnotations or Fluent API to configure it as primary key. We will see how to do it later in these tutorials.
Relationship Convention:
Code First infer the relationship between the two entities using navigation property. This navigation property can be simple reference type or collection type. For example, we defined Standard navigation property in Student class and ICollection<Student> navigation property in Standard class. So, Code First automatically created one-to-many relationship between Standards and Students DB table by inserting Standard_StandardId foreign key column in the Students table.
public class Student
{
public Student()
{ }
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public byte[] Photo { get; set; }
public decimal Height { get; set; }
public float Weight { get; set; } //Navigation property
public Standard Standard { get; set; }
} public class Standard
{
public Standard()
{ }
public int StandardId { get; set; }
public string StandardName { get; set; } //Collection navigation property
public IList<Student> Students { get; set; } }
The above entities created the following relationship using Standard_StandardId foreign key.
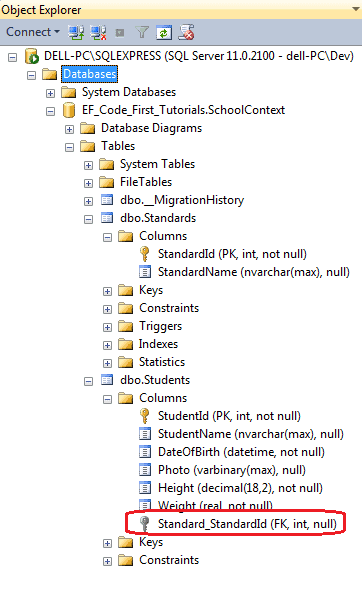
Thus, the default code first convention for relationship automatically inserted a foreign key with<navigation property Name>_<primary key property name of navigation property type> e.g. Standard_StandardId.
Foreign key Convention:
We have seen above that Code First automatically inserts a foreign key when it encounters a navigation property. It is recommended to include a foreign key property on the dependent end of a relationship. Consider the following example:
public class Student
{
public Student()
{ }
public int StudentID { get; set; }
public string StudentName { get; set; }
public DateTime DateOfBirth { get; set; }
public byte[] Photo { get; set; }
public decimal Height { get; set; }
public float Weight { get; set; } //Foreign key for Standard
public int StandardId { get; set; } public Standard Standard { get; set; }
} public class Standard
{
public Standard()
{ }
public int StandardId { get; set; }
public string StandardName { get; set; } public IList<Student> Students { get; set; } }
As you can see in the above code, Student class includes foreign key StandardId, which is the key property in Standard class. Now, Code First will create StandardId column in Students class instead of Standard_StandardId column, as shown below.
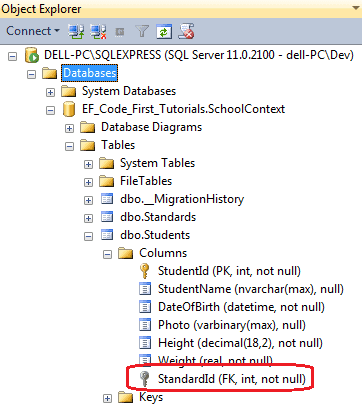
Notice that StandardId foreign key is not null in the above figure. This is because int data type is not nullable.
Code First infers the multiplicity of the relationship based on the nullability of the foreign key. If the property is nullable then the relationship is registered as null. Otherwise, the relationship is registered as NOT NULL. Modify data type of StandardId property from int to Nullable<int> in the Student class above to create a nullable foreign key column in the Students table.
Complex type Convention:
Code First creates complex type for the class which does not include key property and also primary key is not registered using DataAnnotation or Fluent API.
Default Code-First Conventions:
The following table lists default code first conventions:
| Default Convention For | Description |
|---|---|
| Table Name | <Entity Class Name> + 's' EF will create DB table with entity class name suffixed by 's' |
| Primary key Name | 1) Id 2) <Entity Class Name> + "Id" (case insensitive) EF will create primary key column for the property named Id or <Entity Class Name> + "Id" (case insensitive) |
| Foreign key property Name | By default EF will look for foreign key property with the same name as principal entity primary key name. If foreign key property does not exists then EF will create FK column in Db table with <Dependent Navigation Property Name> + "_" + <Principal Entity Primary Key Property Name> e.g. EF will create Standard_StandardId foreign key column into Students table if Student entity does not contain foreignkey property for Standard where Standard contains StandardId |
| Null column | EF creates null column for all reference type properties and nullable primitive properties. |
| Not Null Column | EF creates NotNull columns for PrimaryKey properties and non-nullable value type properties. |
| DB Columns order | EF will create DB columns same as order of properties in an entity class. However, primary key columns would be moved first. |
| Properties mapping to DB | By default all properties will map to database. Use [NotMapped] attribute to exclude property or class from DB mapping. |
| Cascade delete | Enabled By default for all types of relationships. |
The following table list C# datatype mapped with SQL datatype and primary key column datatype and lengt
| C# DataType | Related DB Column DataType | PK Column DataType & Length |
|---|---|---|
| int | int | int, Identity column increment by 1 |
| string | nvarchar(Max) | nvarchar(128) |
| decimal | decimal(18,2) | decimal(18,2) |
| float | real | real |
| byte[] | varbinary(Max) | varbinary(128) |
| datetime | datetime | datetime |
| bool | bit | bit |
| byte | tinyint | tinyint |
| short | smallint | smallint |
| long | bigint | bigint |
| double | float | float |
| char | No mapping | No mapping |
| sbyte | No mapping (throws exception) |
No mapping |
| object | No mapping | No mapping |
This was an overview of code first conventions. These conventions can be overriden using DataAnnotation or Fluent API. Also, you can define custom conventions for your application using Entity Framework 6.0, onwards.
Entity Framework Code-First(5):Code First Conventions的更多相关文章
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(11):Code First
Code First development with Entity Framework: Entity Framework supports three different development ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(37):Lazy Loading
Lazy Loading: One of the important functions of Entity Framework is lazy loading. Lazy loading means ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(36):Eager Loading
Eager Loading: Eager loading is the process whereby a query for one type of entity also loads relate ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(32):Enum Support
Enum in Entity Framework: You can now have an Enum in Entity Framework 5.0 onwards. EF 5 should targ ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(29):Stored Procedure in Entity Framework
Stored Procedure in Entity Framework: Entity Framework has the ability to automatically build native ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(28):Concurrency
Concurrency in Entity Framework: Entity Framework supports Optimistic Concurrency by default. In the ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(27):Update Entity Graph
Update Entity Graph using DbContext: Updating an entity graph in disconnected scenario is a complex ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(22):Disconnected Entities
Disconnected Entities: Before we see how to perform CRUD operation on disconnected entity graph, let ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(19):Change Tracking
Change Tracking in Entity Framework: Here, you will learn how entity framework tracks changes on ent ...
- Entity Framework Tutorial Basics(15):Querying with EDM
Querying with EDM: We have created EDM, DbContext, and entity classes in the previous sections. Here ...
随机推荐
- nginx日志配置,以及日志轮询
一.为nginx配置错误日志 Nginx错误日志是调试nginx的重要手段,属于核心功能模块的参数(ngx_core_module)该参数名字为err_log,是放在Main区块中全局配置 err_l ...
- Delphi 的进制转换
1.10进制转16进制 intTohex(10,4); //第一个参数为要转换的数据,第二个参数为要转换后的16进制位数:得到:000A; 2. 16进制转10进制 strToInt('$'+'64 ...
- hdu 1701 (Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树前序中序推后序)
Binary Tree Traversals T ...
- codeforces 54A
题意:收到礼物的规则为每个假日必收到一份礼物,每K天里至少收到一份礼物,求出N天中收到的礼物的最小数量. 思路:将N天根据假日所在天数分为一段段,当假日与假日之间间隔天数hol[i]>-hol[ ...
- mysql备份,知识点
1.mysql错误日志 show variables like '%log_error%'; my.cnf中log-error=/tmp/SZDB.err 开启 tail -f 错误日志 观察mys ...
- ajax删除当前行
$(function(){ $("tr #del").click(function(){ var id = $(this).attr("data-id"); v ...
- java打包命令
(1)首先,必须保证java的所有路径都设置好,在dos提示符下输入jar -help 出现C:\Documents and Settings\dly>jar -help 非法选项:h 用法:j ...
- ThinkPad.E440_安装固态硬盘
1.ThinkPad(E440) 加装SSD固态硬盘,并改装双硬盘_百度经验.html(https://jingyan.baidu.com/article/9f63fb91856ec7c8400f0e ...
- python第四篇:linux命令行总结 + 自动备份Python程序
由于最近需要学习Python爬虫相关的知识,所以就先从Python基础.Linux基础开始进行了学习,下面主要是总结了常见的Linux的命令行.最后为了巩固学到的东西,尝试写了个自动备份的Python ...
- Android数据存储的五种方法汇总
本文介绍Android中的5种数据存储方式. 数据存储在开发中是使用最频繁的,在这里主要介绍Android平台中实现数据存储的5种方式,分别是: 1 使用SharedPreferences存储数据 2 ...
