深度增强学习--Policy Gradient
前面都是value based的方法,现在看一种直接预测动作的方法 Policy Based
Policy Gradient
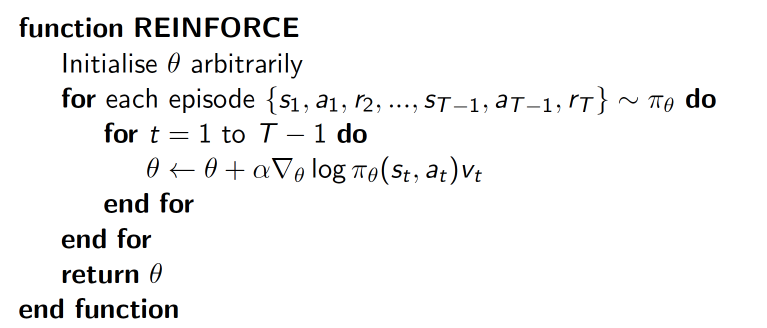
下面的例子实现的REINFORCE算法
import sys
import gym
import pylab
import numpy as np
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.optimizers import Adam EPISODES = 1000 #policy gradient的一种,REINFORCE算法
# This is Policy Gradient agent for the Cartpole
# In this example, we use REINFORCE algorithm which uses monte-carlo update rule
class REINFORCEAgent:
def __init__(self, state_size, action_size):
# if you want to see Cartpole learning, then change to True
self.render = True
self.load_model = False
# get size of state and action
self.state_size = state_size#
self.action_size = action_size# # These are hyper parameters for the Policy Gradient
self.discount_factor = 0.99
self.learning_rate = 0.001
self.hidden1, self.hidden2 = 24, 24 # create model for policy network
self.model = self.build_model() # lists for the states, actions and rewards
self.states, self.actions, self.rewards = [], [], [] if self.load_model:
self.model.load_weights("./save_model/cartpole_reinforce.h5") # approximate policy using Neural Network
# state is input and probability of each action is output of network
def build_model(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(self.hidden1, input_dim=self.state_size, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.add(Dense(self.hidden2, activation='relu', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.add(Dense(self.action_size, activation='softmax', kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform'))
model.summary()
# Using categorical crossentropy as a loss is a trick to easily
# implement the policy gradient. Categorical cross entropy is defined
# H(p, q) = sum(p_i * log(q_i)). For the action taken, a, you set
# p_a = advantage. q_a is the output of the policy network, which is
# the probability of taking the action a, i.e. policy(s, a).
# All other p_i are zero, thus we have H(p, q) = A * log(policy(s, a))
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=Adam(lr=self.learning_rate))
return model # using the output of policy network, pick action stochastically
def get_action(self, state):
policy = self.model.predict(state, batch_size=1).flatten()#
return np.random.choice(self.action_size, 1, p=policy)[0]#choose action accordding to probability # In Policy Gradient, Q function is not available.
# Instead agent uses sample returns for evaluating policy
def discount_rewards(self, rewards):
discounted_rewards = np.zeros_like(rewards)
running_add = 0
for t in reversed(range(0, len(rewards))):
running_add = running_add * self.discount_factor + rewards[t]
discounted_rewards[t] = running_add
return discounted_rewards # save <s, a ,r> of each step
def append_sample(self, state, action, reward):
self.states.append(state)
self.rewards.append(reward)
self.actions.append(action) # update policy network every episode
def train_model(self):
'''
example:
self.states:[array([[-0.00647736, -0.04499117, 0.02213829, -0.00486359]]), array([[-0.00737719, -0.24042351, 0.02204101, 0.2947212 ]]), array([[-0.01218566, -0.04562261, 0.02793544, 0.00907036]]), array([[-0.01309811, -0.24113382, 0.02811684, 0.31043471]]), array([[-0.01792078, -0.04642351, 0.03432554, 0.02674995]]), array([[-0.01884925, -0.24202048, 0.03486054, 0.33006229]]), array([[-0.02368966, -0.04741166, 0.04146178, 0.04857336]]), array([[-0.0246379 , -0.24310286, 0.04243325, 0.35404415]]), array([[-0.02949995, -0.43880168, 0.04951413, 0.65979978]]), array([[-0.03827599, -0.2444025 , 0.06271013, 0.38310959]]), array([[-0.04316404, -0.44035616, 0.07037232, 0.69488702]]), array([[-0.05197116, -0.63637999, 0.08427006, 1.00886738]]), array([[-0.06469876, -0.83251953, 0.10444741, 1.32677873]]), array([[-0.08134915, -0.63885961, 0.13098298, 1.06852366]]), array([[-0.09412634, -0.44569036, 0.15235346, 0.8196508 ]]), array([[-0.10304015, -0.25294509, 0.16874647, 0.57850069]]), array([[-0.10809905, -0.44997994, 0.18031649, 0.91923131]]), array([[-0.11709865, -0.25769299, 0.19870111, 0.68820344]])]
self.rewards:[1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, -100]
self.actions:[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1]
'''
episode_length = len(self.states)# discounted_rewards = self.discount_rewards(self.rewards)
'''
example:
disconnted_rewards:array([ -68.58863868, -70.29155422, -72.01167093, -73.74916255,-75.5042046 , -77.27697434, -79.06765085, -80.876415 , -82.7034495 , -84.54893889, -86.41306958, -88.29602988,-90.19800998, -92.119202 , -94.0598,-96.02,-98., -100. ])
'''
discounted_rewards -= np.mean(discounted_rewards)
discounted_rewards /= np.std(discounted_rewards)#将作为神经网络预测对象
'''
array([ 1.59468271, 1.41701722, 1.23755712, 1.05628429, 0.87318042,
0.68822702, 0.50140541, 0.3126967 , 0.12208185, -0.0704584 ,
-0.26494351, -0.46139311, -0.65982705, -0.86026537, -1.06272832,
-1.26723636, -1.47381013, -1.6824705 ])
'''
update_inputs = np.zeros((episode_length, self.state_size))#shape(18,4)
advantages = np.zeros((episode_length, self.action_size))#shape(18,2) for i in range(episode_length):
update_inputs[i] = self.states[i]
advantages[i][self.actions[i]] = discounted_rewards[i] self.model.fit(update_inputs, advantages, epochs=1, verbose=0)
self.states, self.actions, self.rewards = [], [], [] if __name__ == "__main__":
# In case of CartPole-v1, you can play until 500 time step
env = gym.make('CartPole-v1')
# get size of state and action from environment
state_size = env.observation_space.shape[0]
action_size = env.action_space.n # make REINFORCE agent
agent = REINFORCEAgent(state_size, action_size) scores, episodes = [], [] for e in range(EPISODES):
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
done = False
score = 0
state = env.reset()
state = np.reshape(state, [1, state_size]) while not done:
if agent.render:
env.render() # get action for the current state and go one step in environment
action = agent.get_action(state)
next_state, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
next_state = np.reshape(next_state, [1, state_size])
reward = reward if not done or score == 499 else -100 # save the sample <s, a, r> to the memory
agent.append_sample(state, action, reward) score += reward
state = next_state if done:
# every episode, agent learns from sample returns
agent.train_model() # every episode, plot the play time
score = score if score == 500 else score + 100
scores.append(score)
episodes.append(e)
pylab.plot(episodes, scores, 'b')
pylab.savefig("./save_graph/cartpole_reinforce.png")
print("episode:", e, " score:", score) # if the mean of scores of last 10 episode is bigger than 490
# stop training
if np.mean(scores[-min(10, len(scores)):]) > 490:
sys.exit() # save the model
if e % 50 == 0:
agent.model.save_weights("./save_model/cartpole_reinforce.h5")
深度增强学习--Policy Gradient的更多相关文章
- 强化学习--Policy Gradient
Policy Gradient综述: Policy Gradient,通过学习当前环境,直接给出要输出的动作的概率值. Policy Gradient 不是单步更新,只能等玩完一个epoch,再 ...
- 深度增强学习--DDPG
DDPG DDPG介绍2 ddpg输出的不是行为的概率, 而是具体的行为, 用于连续动作 (continuous action) 的预测 公式推导 推导 代码实现的gym的pendulum游戏,这个游 ...
- 深度增强学习--A3C
A3C 它会创建多个并行的环境, 让多个拥有副结构的 agent 同时在这些并行环境上更新主结构中的参数. 并行中的 agent 们互不干扰, 而主结构的参数更新受到副结构提交更新的不连续性干扰, 所 ...
- 深度增强学习--Actor Critic
Actor Critic value-based和policy-based的结合 实例代码 import sys import gym import pylab import numpy as np ...
- 深度增强学习--Deep Q Network
从这里开始换个游戏演示,cartpole游戏 Deep Q Network 实例代码 import sys import gym import pylab import random import n ...
- 深度增强学习--DPPO
PPO DPPO介绍 PPO实现 代码DPPO
- 深度增强学习--DQN的变形
DQN的变形 double DQN prioritised replay dueling DQN
- Deep Learning专栏--强化学习之从 Policy Gradient 到 A3C(3)
在之前的强化学习文章里,我们讲到了经典的MDP模型来描述强化学习,其解法包括value iteration和policy iteration,这类经典解法基于已知的转移概率矩阵P,而在实际应用中,我们 ...
- 增强学习 | AlphaGo背后的秘密
"敢于尝试,才有突破" 2017年5月27日,当今世界排名第一的中国棋手柯洁与AlphaGo 2.0的三局对战落败.该事件标志着最新的人工智能技术在围棋竞技领域超越了人类智能,借此 ...
随机推荐
- 大话Linux内核中锁机制之原子操作、自旋锁【转】
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6d7fa49b01014q7p.html 多人会问这样的问题,Linux内核中提供了各式各样的同步锁机制到底有何作用?追根到底其实 ...
- linux进程的休眠(等待队列)【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/noaming1900/archive/2011/01/14/1935526.html (转载) bojan 收录于2010-10-09 阅读数: ...
- python memcache操作-安装、连接memcache
安装memecache wget http://memcached.org/latest tar -zxvf memcached-1.x.x.tar.gz cd memcached-1.x.x ./c ...
- 输入法出现 footer被挤上去的问题
/** * 修改点击input输入框时的位置 *input框获取焦点footer隐藏,失去焦点时显示 */ $('.input-footer-none').on('focus',function(){ ...
- ttk.Treeview
TTK的目的. TreeView控件的呈现层次结构,用户可以使用鼠标动作来显示或隐藏结构的任何部分. 与术语“树”的关联是由于编程实践:树结构是一个常见的程序设计.严格地说,在一个TreeView控件 ...
- python 多进程并发与多线程并发
本文对python支持的几种并发方式进行简单的总结. Python支持的并发分为多线程并发与多进程并发(异步IO本文不涉及).概念上来说,多进程并发即运行多个独立的程序,优势在于并发处理的任务都由操作 ...
- Vuejs1.0学习
1.数据双向绑定 双向绑定以后,表单中数据的改变会同步改变H2中的输出 2.v-show 内容输入前: 内容输入后:隐藏提示,展示按钮 代码实现: 此处的v-show可以换成v-if,v-show是隐 ...
- 记录一次WebService使用的经历
于业务需要,需要和第三方对接一些接口,但是问题是,他们的接口提供是webservice的,本人只精通restful接口(也就是说我比较年轻^-^).好在对面人特别奈斯,一顿指导我,感谢. 废话不多说了 ...
- JS中对数组的操作方法
不断加入中.... 一.数组的增删 1.push():从后面追加 pop():从后面删除一个. 二.数组与字符串的转换 split():用分隔符生成数组 join():将数组用分隔符连为字符串. 三. ...
- HDU 2050 折线分割平面(转)
折线分割平面 http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2050 Problem Description 我们看到过很多直线分割平面的题目,今天的这个题目稍微 ...
