《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.25


用match-z方法,将模拟低通转换为数字低通
代码:
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------
%% Output Info about this m-file
fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 8.25 \n\n'); banner();
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ % -------------------------------
% ω = ΩT = 2πF/fs
% Digital Filter Specifications:
% -------------------------------
wp = 0.4*pi; % digital passband freq in rad/sec
ws = 0.6*pi; % digital stopband freq in rad/sec
Rp = 0.5; % passband ripple in dB
As = 50; % stopband attenuation in dB Ripple = 10 ^ (-Rp/20) % passband ripple in absolute
Attn = 10 ^ (-As/20) % stopband attenuation in absolute % Analog prototype specifications: Inverse Mapping for frequencies
T = 2; % set T = 1
Fs = 1/T;
OmegaP = wp/T; % prototype passband freq
OmegaS = ws/T; % prototype stopband freq % Analog Butterworth Prototype Filter Calculation:
[cs, ds] = afd_butt(OmegaP, OmegaS, Rp, As); % Calculation of second-order sections:
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: START *****\n');
[CS, BS, AS] = sdir2cas(cs, ds)
fprintf('\n***** Cascade-form in s-plane: END *****\n'); % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db_s, mag_s, pha_s, ww_s] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 0.5*pi); % Calculation of Impulse Response:
%[ha, x, t] = impulse(cs, ds);
% Impulse Invariance Transformation:
%[b, a] = imp_invr(cs, ds, T); % Calculation of Step Response:
[ha, x, t] = step(cs, ds); % Step Invariance Transformation:
[b, a] = stp_invr(cs, ds, T); [C, B, A] = dir2par(b, a) % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[db, mag, pha, grd, ww] = freqz_m(b, a); %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% -----------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.25 Analog Butterworth lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 1; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww_s, mag_s); grid on; axis([-M, M, 0, 1.2]);
xlabel(' Analog frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude in Absolute');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-0.3, -0.2, 0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.6]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0032, 0.5, 0.9441, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww_s, db_s); grid on; %axis([0, M, -50, 10]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-0.3, -0.2, 0, 0.4, 0.6]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-65, -50, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['65';'50';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww_s, pha_s/pi); grid on; axis([-M, M, -1.2, 1.2]);
xlabel('Analog frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [-0.3, -0.2, 0, 0.4, 0.6]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:0.5:1]); subplot(2,2,4); plot(t, ha); grid on; %axis([0, 30, -0.05, 0.25]);
xlabel('time in seconds'); ylabel('ha(t)'); title('Step Response'); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.25 Digital Butterworth lowpass')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
M = 2; % Omega max subplot(2,2,1); plot(ww/pi, mag); axis([0, M, 0, 1.2]); grid on;
xlabel(' frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('|H|'); title('Magnitude Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0, 0.0032, 0.5, 0.9441, 1]); subplot(2,2,2); plot(ww/pi, pha/pi); axis([0, M, -1.1, 1.1]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi nuits'); ylabel('radians in \pi units'); title('Phase Response');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-1:1:1]); subplot(2,2,3); plot(ww/pi, db); axis([0, M, -100, 10]); grid on;
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Decibels'); title('Magnitude in dB ');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, M]);
set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [-70, -50, -1, 0]);
set(gca,'YTickLabelMode','manual','YTickLabel',['70';'50';' 1';' 0']); subplot(2,2,4); plot(ww/pi, grd); grid on; %axis([0, M, 0, 35]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Samples'); title('Group Delay');
set(gca, 'XTickMode', 'manual', 'XTick', [0, 0.4, 0.6, 1.0, M]);
%set(gca, 'YTickMode', 'manual', 'YTick', [0:5:35]); figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.25 Pole-Zero Plot')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
zplane(b,a);
title(sprintf('Pole-Zero Plot'));
%pzplotz(b,a); % ----------------------------------------------
% Calculation of Impulse Response
% ----------------------------------------------
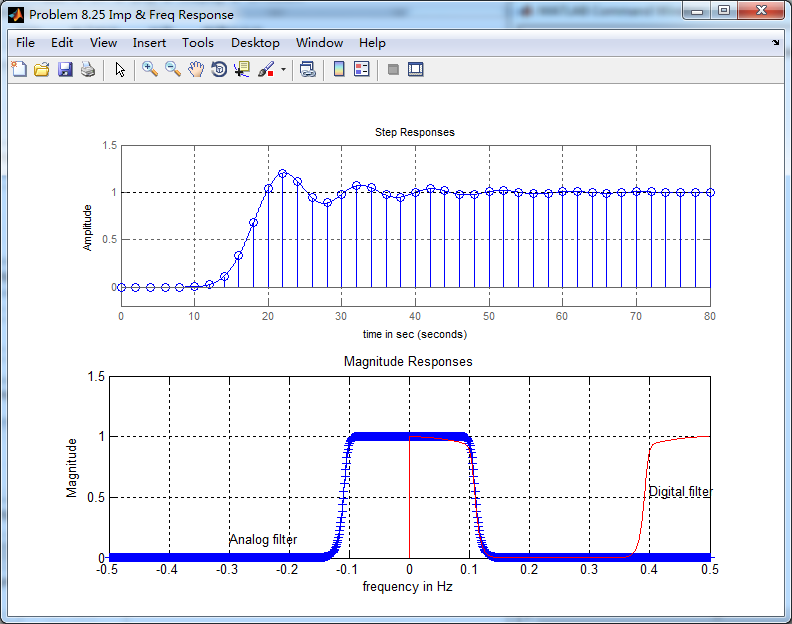
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Problem 8.25 Imp & Freq Response')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
t = [0:0.01:80]; subplot(2,1,1); step(cs,ds,t); grid on; % Step response of the analog filter
axis([0,80,-0.2,1.5]);hold on n = [0:1:80/T]; hn = filter(b,a,stepseq(0,0,80/T)); % Step response of the digital filter
stem(n*T,hn); xlabel('time in sec'); title ('Step Responses');
hold off % Calculation of Frequency Response:
[dbs, mags, phas, wws] = freqs_m(cs, ds, 2*pi/T); % Analog frequency s-domain [dbz, magz, phaz, grdz, wwz] = freqz_m(b, a); % Digital z-domain %% -----------------------------------------------------------------
%% Plot
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------- subplot(2,1,2); plot(wws/(2*pi),mags,'b+', wwz/(2*pi)*Fs,magz,'r'); grid on; xlabel('frequency in Hz'); title('Magnitude Responses'); ylabel('Magnitude'); text(-0.3,0.15,'Analog filter'); text(0.4,0.55,'Digital filter');
运行结果:
通带、阻带绝对指标

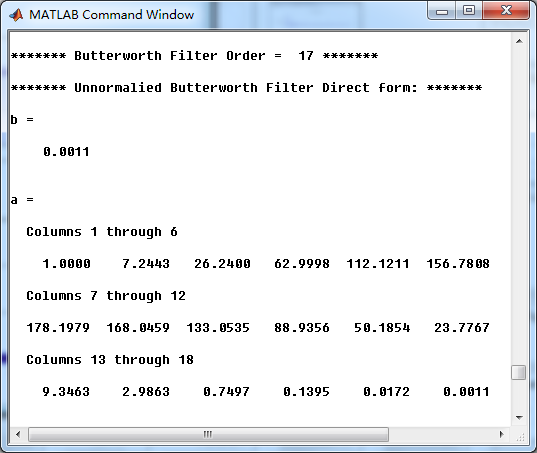
模拟原型Butterworth低通滤波器,直接形式系数
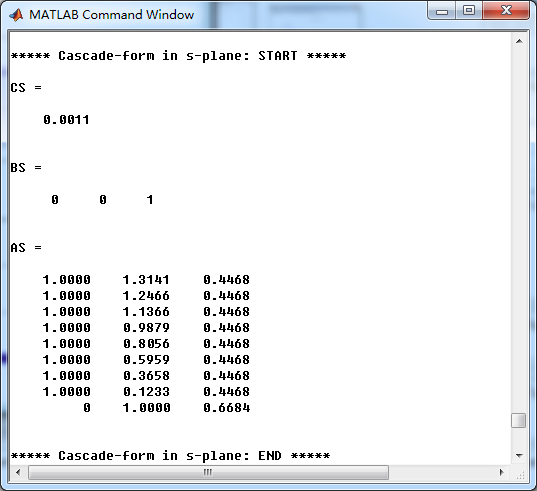
模拟原型Butterworth低通滤波器,串联形式系数
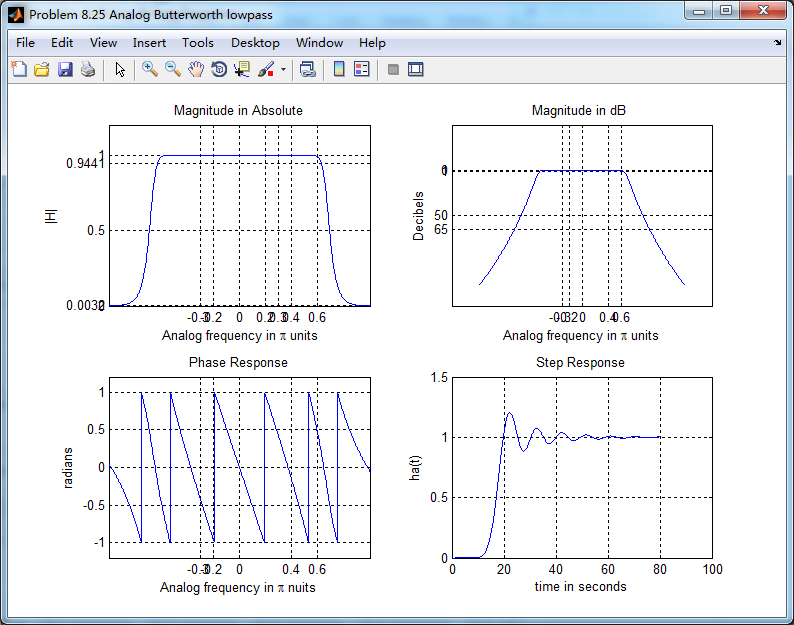
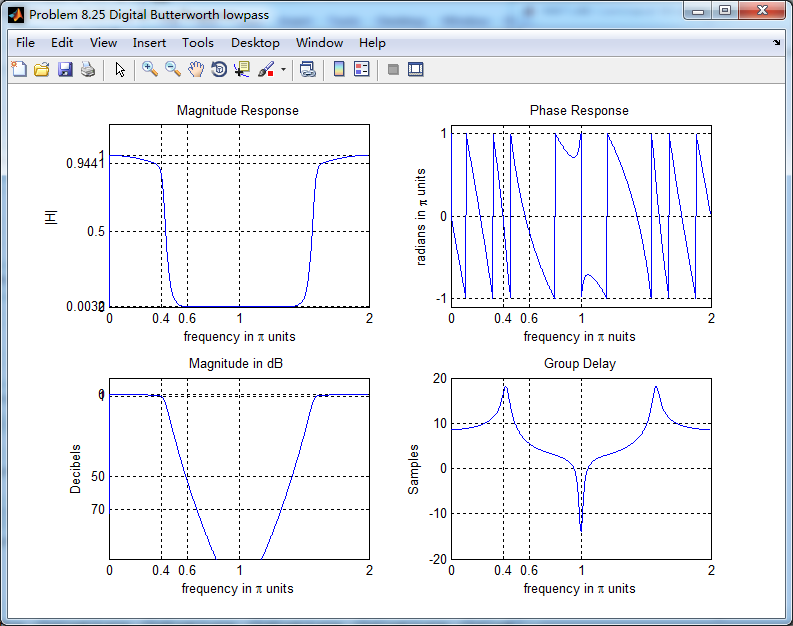
转换成数字低通后,并联形式系数

《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.25的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.25
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》示例Example7.25
今天清明放假的第二天,早晨出去吃饭时天气有些阴,十点多开始“清明时节雨纷纷”了. 母亲远在他乡看孙子,挺劳累的.父亲照顾生病的爷爷…… 我打算今天把<DSP using MATLAB>第7 ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.27
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.14
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.13
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 6.23
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.24-5.25-5.26
代码: function y = circonvt(x1,x2,N) %% N-point Circular convolution between x1 and x2: (time domain) ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 4.21
快到龙抬头,居然下雪了,天空飘起了雪花,温度下降了近20°. 代码: %% -------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 4.15
只会做前两个, 代码: %% ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- %% Outpu ...
随机推荐
- 21个CSS技巧
级联样式表(CSS)在当代Web设计中已经成为重要的环节,如果没有CSS现在的网站将像10年前一样不堪入目.随着CSS技术的普及,越来越多的高质量CSS教程涌入互联网,让我们的学习更加方便. 1.CS ...
- Apache Spark 2.2.0 中文文档 - Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets
Spark SQL, DataFrames and Datasets Guide Overview SQL Datasets and DataFrames 开始入门 起始点: SparkSession ...
- MD5/SHA1/Hmac_SHA1
1.MD5 #import <CommonCrypto/CommonDigest.h> + (NSString *) md5:(NSString *) input { const char ...
- vue解决sass-loader的版本过高导致的编译错误
Module build failed: TypeError: this.getResolve is not a function at Object.loader (E:\appEx\PreRese ...
- 【学术篇】SDOI2008 仪仗队
Part1:传送门&吐槽 水题... 然而由于线筛里面的\(j\)打成了\(i\)然后就不能1A了OvO Part2:题目分析 这个正方形是对称的... 而且很显然对角线上只有一个点会被看到. ...
- 什么是 Hexo?
Hexo 文档 欢迎使用 Hexo,本文档将帮助您快速上手.如果您在使用过程中遇到问题,请查看 问题解答 中的解答,或者在 GitHub.Google Group 上提问. 什么是 Hexo? H ...
- Android开发 如何最优的在Activity里释放资源
前言 当前你已经入门Android开发,开始关注深入的问题,你就会碰到一个Android开发阶段经常碰到的问题,那就是内存泄漏. 其实大多数Android的内存泄漏都是因为activity里的资源释放 ...
- adb命令 logcat日志抓取
一.logcat抓log方法:adb logcat命令,可以加条件过滤 1.安装SDK(参考android sdk环境安装) 2.使用数据线链接手机,在手机助手的sdcard中建立一个1.log的文件 ...
- 一道Oracle子查询小练习
一道Oracle子查询小练习 昨天晚上躺在床上看Oracle(最近在学习这个),室友说出个题目让我试试.题目如下: 有如下表结构,请选择出成绩为前三名的人的信息(如果成绩相同,则算并列),表名为t ...
- JS函数进阶
函数的定义方式 函数声明 函数表达式 new Function 函数声明 function foo () { } 函数表达式 var foo = function () { } 函数声明与函数 ...
